On June 14, 2024, the U.S. FDA approved AstraZeneca's Durvalumab (IMFINZI®) for primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer with mismatch repair deficiency. Endometrial cancer is the most prevalent gynecologic cancer, with an estimated 66,200 new U.S. cases in 2023. This approval demonstrates the effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors, particularly targeting PD-L1 (CD274, B7-H1), a crucial factor in tumor immune evasion. Studying PD-L1 is essential for developing therapies that enhance immune responses to various cancers, potentially improving treatment success and patient outcomes.
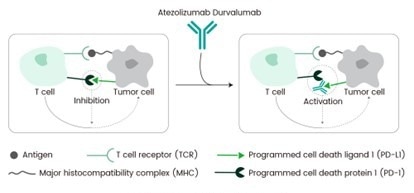 Mechanism of action of Durvalumab. Image Credit: Sino Biological
Mechanism of action of Durvalumab. Image Credit: Sino Biological
Mechanism of action
Durvalumab targets PD-L1, a key immune checkpoint. Normally, antigen-presenting cells (APCs) recognize cancer cell antigens and activate cytotoxic T cells, which travel to the tumor site for eradication. However, tumors enhance their survival by suppressing these T-cell responses via PD-L1.
PD-L1, a type 1 transmembrane protein, is induced by inflammatory signals such as IFN-gamma and is found on both tumor and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. It inhibits T cell activation and function by binding to PD-1 and CD80 receptors on T cells, reducing the immune response.
By binding to PD-L1, Durvalumab blocks its interactions with PD-1 and CD80, reactivating the cytotoxic T cells and enabling them to effectively target and destroy tumor cells. Durvalumab’s specificity for PD-L1, without affecting PD-L2, enhances its ability to potentiate the immune response against tumors, highlighting its role in countering cancer's immune evasion tactics.
PD-L1 as drug target
PD-L1 is a crucial immune checkpoint protein that modulates immune responses by binding to PD-1 on T cells, suppressing their activity and allowing tumors to evade immune detection. PD-L2, a related protein, also interacts with PD-1, contributing to immune regulation but with a different expression pattern and role. Both PD-L1 and PD-L2 are involved in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmunity, making them significant targets in cancer immunotherapy. Understanding the distinct and overlapping functions of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in immune regulation is essential for developing comprehensive and effective cancer treatments.
Source: Sino Biological
| TARGET |
ACTIONS |
ORGANISM |
| Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) |
Inhibits T cell activation |
Humans |
| Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) |
Inhibits T cell activation |
Humans |
| Programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (PD-L2) |
Modulates immune responses and expression patterns |
Humans |
Sino Biological's tools for PD-L1 immunotherapy research
Sino Biological is a leading international reagent supplier and contract research service provider, specializing in recombinant protein production and antibody development. The company provides a comprehensive range of reagents to support PD-L1 immunotherapy research. Our offerings include vigorously tested PD-L1 recombinant proteins, antibodies, ELISA kits, lysates, and cDNA clones, all designed to advance your cancer research in immunotherapy.