Stem cells are multipotent cells that can self-renew, reproduce, and develop into various cell types, including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), neural stem cells (NSCs), embryonic stem cells (ESCs), and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
There has been remarkable development in isolating and culturing different stem cells for disease therapy. Studies have shown that stem cells can potentially treat various diseases, like cancer and heart disease.
Cytokines are essential for the differentiation and renewal of stem cells. Sino Biological provides a broad selection of high-grade, GMP-grade recombinant cytokines with high bioactivity, lot-to-lot consistency, and purity to support stem cell research. Sino Biological also sells biological reagents, such as ELISA kits, genes, and antibodies.
Products highlights
- High purity: Purity >95% by SDS-PAGE & HPLC
- Vast selection: Includes both research and GMP-grade cytokines
- High bioactivity: Validated by ELISA, cell-based assays
- Quality control: ISO 9001/ISO 13485/GMP quality systems
- Low endotoxin: 5-10 EU/mg
- High lot-to-lot consistency
Exploring stem cell culture cytokines by cell type
Mesenchymal stem cells
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are adult stem cells in several organs, including the umbilical cord, bone marrow, and adipose tissue. They have an amazing capacity to self-renew and distinguish. MSCs are renowned for their immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties, achieved via regulating lymphocytes in both the innate and adaptive immune systems.
This makes them an attractive target for treating a variety of diseases, such as autoimmune, cardiovascular, inflammatory, and neurodegenerative conditions. MSCs' therapeutic promise is further bolstered by their ease of access, genetic stability, minimal immunogenicity, ability to repair tissue, and immunomodulation.
Sino Biological offers cytokines, marker antibodies, and identification kits for MSC culture to assist in research and development.
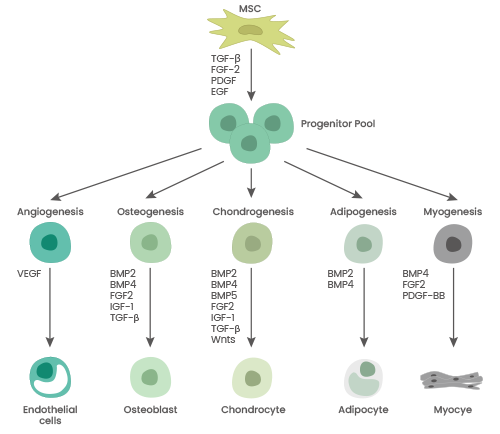
Schematic overview of cytokines involved in NSC differentiation. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Cytokine applications in MSC culture
MSCs differentiate into hepatoid cells
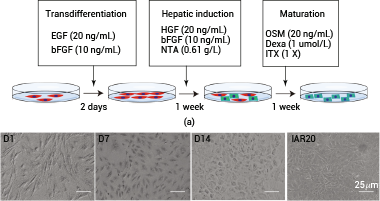
(a) Flowchart illustrating the induction process of MSCs differentiating into hepatoid cells in vitro. (b) Morphological representation of MSCs during their differentiation into hepatoid cells. Source: https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6890299.
Expansion of bone marrow MSCs
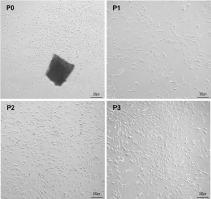
P0 denotes the primary cell, while P1, P2, and P3 correspond to the first, second, and third-generation cells, respectively. Source: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-022-02393-2.
Role of different cytokines on MSC
Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| . |
. |
| Basic FGF/FGF2 |
- Enhance MSC proliferation
- Support chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation
|
| PDGF-BB |
- Promote MSC proliferation and survival
- Promote myoblast proliferation
|
| IGF1 |
- Enhance MSC proliferation
- Promote MSC differentiation into chondrocytes
|
| VEGF-A |
- Promote MSC proliferation and survival
- Involved in the formation, proliferation and survival of vascular endothelial cells
|
| EGF |
- Stimulate MSC proliferation without altering MSC differentiation potential
- Enhance paracrine and autocrine functions of MSCs
|
| TGF beta 1 |
- Enhance MSC proliferation
- Promote MSC differentiation into chondrocytes
|
| SCF |
- Promote MSC proliferation
|
Featured cytokines for MSC culture
GMP-grade human FGF2 (Cat#: GMP-10014-HNAE) 
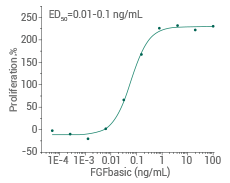
Cell proliferation assay using Balb/c 3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Human PDGF-BB protein (Cat#: 10572-HNAE)
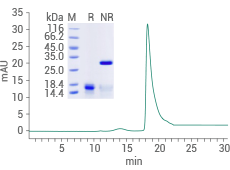
Purity: ≥ 95% by SDS-PAGE and SEC-HPLC. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
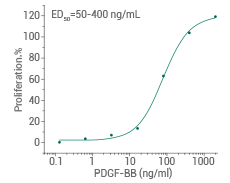
Cell proliferation assay using Balb/c 3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
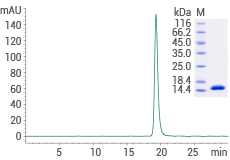
Human EGF protein (Cat#: 10605-HNAE)
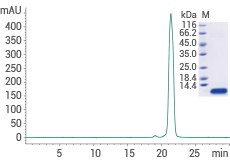
≥ 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE and SEC-HPLC. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
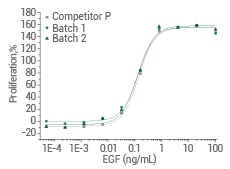
Cell proliferation assay using Balb/C 3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
- High batch-to-batch consistency
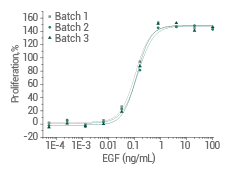
Cell proliferation assay using Balb/C 3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
 GMP-grade cytokines in stock
GMP-grade cytokines in stock
Antibodies for MSC surface profiling
Three primary methods are available for identifying MSC: identifying specific MSC surface markers, assessing the ability for multidirectional differentiation, and analyzing morphological features to assess cell adhesion. Cell surface markers are used to identify human MSCs according to a criteria developed in 2006 by the International Society for Cell Therapy.
To be categorized as MSCs, cells must be negative for CD34, CD45, CD11b or CD14, CD19 or CD79α, and HLA-DR and positive for CD73, CD90, and CD105.
Sino Biological offers a selection of premium antibodies for MSC surface markers, which could assist with MSC differentiation characterization and cell quality and function assessment. These resources offer thorough assistance with MSC identification and research.
Flow cytometry antibody panel for MSC identification
Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Target |
Type |
Cat# |
| CD73 |
PE |
10904-MM07-P |
| CD90 |
PerCP |
16897-MM10-C |
| CD105 |
APC |
10149-MM13-A |
| CD44 |
FITC |
12211-MM02-F |
| CD166 |
APC |
10045-MM03-A |
Embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells
Pluripotent stem cells, such as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and embryonic stem cells (ESCs), can develop into any type of cell and have an infinite capacity for self-renewal. Of all the pluripotent stem cell types, ESCs are the most well-known. However, the fact that they are derived from human embryos raises possible ethical concerns, which restricts their broad application.
Many characteristics of ESCs and iPSCs produced via reprogramming adult somatic cells are similar. Due to their broad capacity for self-renewal and differentiation, they hold great promise for novel cell/gene treatments, disease modeling, regenerative medicine, and drug testing.
To differentiate human iPSCs into diverse cell lines, cytokines, and growth factors, such as GM-CSF, Activin A, DLL4, NOG, TNF-α, IL-2, VEGF, FGF, IL1β, and EGF, are crucial.
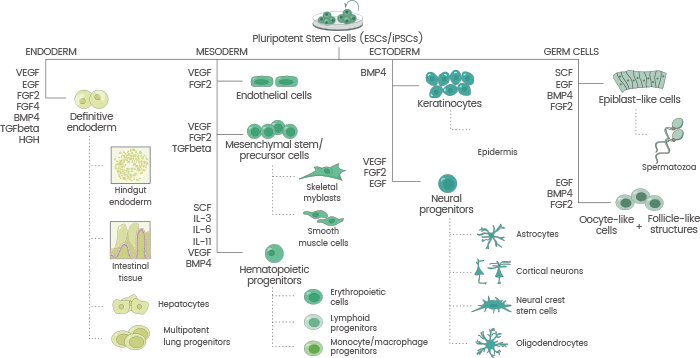
Schematic overview of cytokines involved in ESC/iPSC differentiation. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Featured cytokines for ESC/iPSC culture
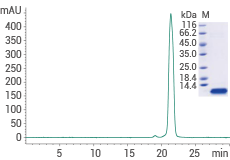
High-purity: ≥ 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE & SEC-HPLC. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
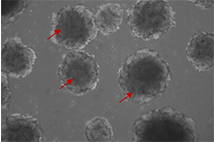
Human vascular organoids derived from iPSCs were cultured using FGF2, VEGFA, and EGF. The vascular organoids are indicated by red arrows. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
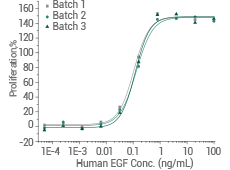
High batch-to-batch consistency: Cell proliferation assay using Balb/C 3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
High-purity: ≥ 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE & SEC-HPLC. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
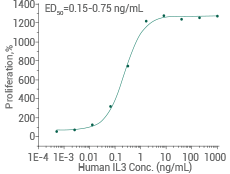
Activity-validated: Cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
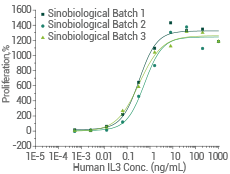
High batch-to-batch consistency: Cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Hematopoietic stem cells
HSCs are multipotent stem cells capable of self-renewing and differentiating into various blood cell types, including myeloid and lymphoid. This distinction is critical to maintaining the hematopoietic system’s dynamic equilibrium. HSCs are present in various organs, including peripheral blood, bone marrow, and umbilical cord blood.
HSCs can replace defective hematopoietic and immunological tissues, making them a promising treatment for diseases such as hematological malignancies and certain liver problems. Sino Biological provides cytokines for HSC culture, including GMP-grade choices, to support HSC research fully.
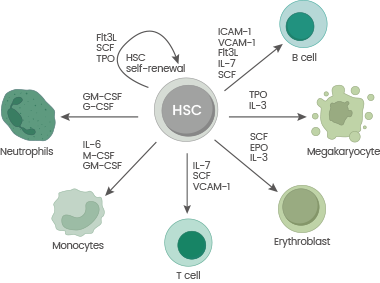
Schematic overview of cytokines involved in HSC differentiation. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Featured cytokines for HSC culture
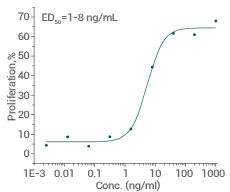
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
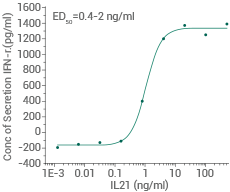
Measured by its ability to induce Interferon gamma secretion by human natural killer lymphoma NK-92 cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
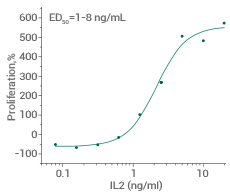
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using CTLL2. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
 GMP grade cytokines in stock!
GMP grade cytokines in stock!  Animal-Free
Animal-Free
Neural stem cells
The nervous system contains neural stem cells (NSCs) that can self-renew and differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. Under some settings, NSCs develop into functional cells that replenish lost cells and restore function. This ability is required for neural development and the healing of damaged neural tissues.
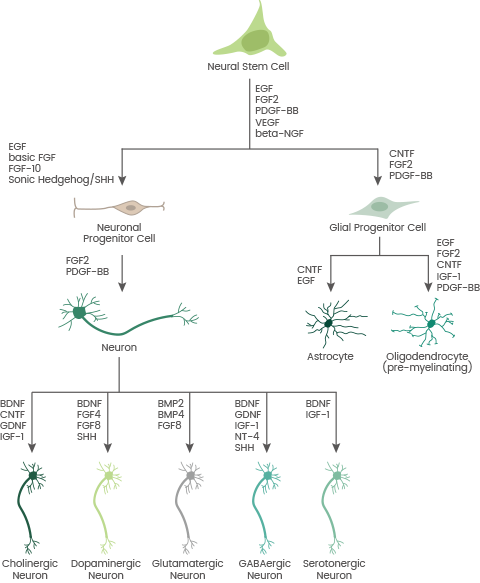
Schematic overview of cytokines involved in NSC differentiation. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Featured cytokines for NSC culture
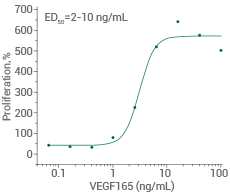
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
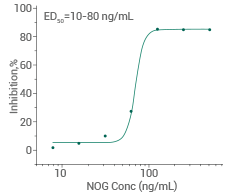
Measured by its ability to inhibit BMP4-induced alkaline phosphatase production by MC3T3E1 mouse preosteoblast cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
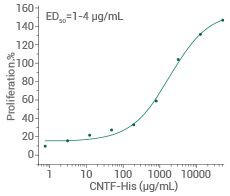
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Learn More About Reagents