The small intestine is a tubular structure within the abdominal cavity that carries the food in continuation with the stomach up to the colon from where the large intestine carries it to the rectum and out of the body via the anus. The main function of this organ is to aid in digestion.
How big is the small intestine?
As a person grows the small intestine increases 20 times in length from about 200 cm in a newborn to almost 6 m in an adult. The length of the small intestine is approximated by three times the length of the infant, or height of the child or adult.
The duodenum is about 25 cm (10 inches) long; the jejunum is about 2.5 m (8 feet) long and the ileum is about 3.6 m (12 feet) long.
Anatomy of the small intestine
The small intestine begins with the duodenum. The duodenum begins at the duodenal bulb and goes around the head of the pancreas and ends as it returns to the peritoneal cavity at the ligament of Treitz. The peritoneal cavity is a thin membrane cavity that covers the organs within the abdomen with some exceptions.
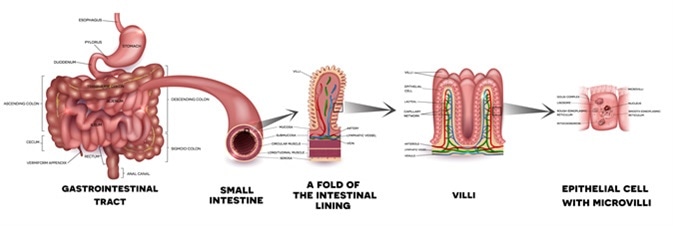
The remainder of the small intestine is suspended within the peritoneal cavity by a thin, broad-based mesentery that is attached to the posterior abdominal wall. This allows free movement of the small intestine within the abdominal cavity.
After the duodenum comes the next 40% of the mobile small intestine called the jejunum. The remaining 60% is the ileum.
The jejunum occupies the left upper portion of the abdomen while the ileum is positioned in the right side and upper part of the pelvis.
The inner walls of the small intestine show mucosal folds. These are called the plicae circulares. The plicae are more numerous in the early jejunum and reduce in numbers in the later part and are completely absent in the ileum.
Absorption takes place via primary cell type of the epithelial layer. Goblet cells, located throughout the epithelial layer, secrete mucus that helps protect the epithelial layer from digestion.
Enteroendocrine cells secrete hormones into blood vessels that penetrate each villus. Paneth cells, located in the epithelial layer facing the intestinal crypts, secrete lysozyme, an enzyme that destroys bacteria. An inner core of lamina propria (connective tissues) contains blood capillaries and small lymphatic capillaries called lacteals.
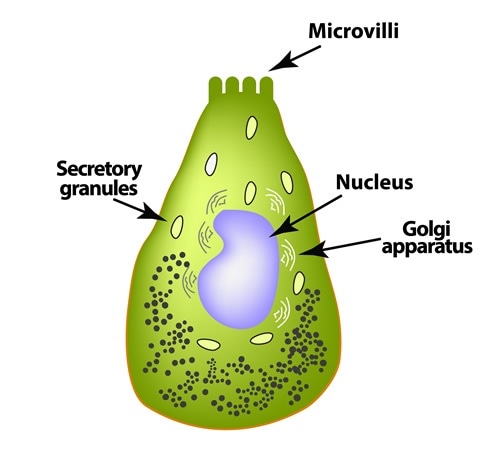
Enteroendocrine cell
The submucosa under the mucosa contains Brunner's (duodenal) glands, found only in the submucosa of the duodenum. It secretes an alkaline mucus that neutralizes the gastric acid in the incoming chyme.
Aggregates of lymphoid follicles are scattered throughout the small intestine but are found in highest concentration within the ileum, where they are designated Peyer's patches. These are more prominent among children and infants. The small intestine ends at the ileocecal valve that leads it to the colon. The ileocecal valve provides a barrier to the back flow of the colonic contents into the small intestine.
The wall of the small intestine and colon is composed of four layers: mucosa (or mucous membrane), submucosa, muscularis (or muscularis propria), and adventitia (or serosa).
Functions of the small intestine
The small intestine is the part of the intestines where 90% of the digestion and absorption of food occurs, the other 10% taking place in the stomach and large intestine. The main function of the small intestine is absorption of nutrients and minerals from food.
Digestion involves two distinct parts. The first is mechanical digestion by chewing, grinding, churning and mixing that takes place in the mouth and the stomach. The second part of digestion is the chemical digestion that uses enzymes, bile acids etc. in order to break down food material into a form that can then be absorbed, then assimilated into the tissues of the body. Chemical digestion occurs in the small intestine (and, to a lesser extent, also in some other part of the gastrointestinal tract.
Digestion of proteins
Proteins, peptides and amino acids are acted upon by enzymes such as trypsin and chymotrypsin, secreted by the pancreas. This breaks them down to smaller peptides. Chemical breakdown begins in the stomach and continues until the large intestine.
Digestion of lipids
Enzymes, like lipases secreted from the pancreas, act on fats and lipids in diet. This breaks the triglycerides into free fatty acids and monoglycerides. It is helped by bile salts secreted by the liver and the gall bladder. The lipase is soluble in water but the fatty triglycerides are not. The bile salts hold the triglycerides in the watery environment until the lipase can break them into the smaller parts that can enter the intestinal villi for absorption.
Digestion of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are broken down to simple sugars and monosaccharides like glucose. Pancreatic amylase breaks down some carbohydrates to oligosaccharides as well. Some carbohydrates and fibers pass undigested to the large intestine where they may, depending on their type, be broken-down by intestinal bacteria.
Absorption in the small intestines
Once broken down the nutrients are absorbed by the inner walls of the small intestine into the blood stream. The nutrients are rendered small enough so that they may pass, or "be transported", across the epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract. The nutrients are absorbed by processes of simple/passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, primary active transport, or secondary active transport.
The small intestine is good for absorption since it has a large inner surface area. This is formed due to the plicae circulares which project many tiny finger-like structures of tissue called villi. The individual epithelial cells also have finger-like projections, which are called known as microvilli.
For transport, nutrients commonly rely upon:
- Lipids – undergo passive or simple diffusion
- Short-chain fatty acids – diffusion
- Amino acids – primary active transport
- Glucose – secondary active transport
- Fructose – facilitated diffusion
Other absorbed substances in the small intestines include:
Water
Most of the water in ingested food and beverages is absorbed by osmosis.
Approximately 80% is absorbed by the small intestine, 10% by the large intestine and the remaining 10% excreted in the faeces.
Electrolytes
Of these sodium is absorbed by diffusion and active transport. Chloride (Cl-) is absorbed passively along with sodium or actively transported. Iodine (I-) and Nitrate (NO3-) can passively follow Na+ ions or are absorbed actively. Calcium ions (Ca2+) are absorbed actively in a process stimulated by calcitriol (active form of Vitamin D). Iron ions (Fe2+ and Fe3+), Potassium ions (K+), Magnesium ions (Mg2+) and Phospate ions (PO43-) are absorbed by active transport mechanisms.
Vitamins and minerals
Vitamins including fat soluble ones (Vitamins A, D, E and K) are absorbed together with dietary fats. Water soluble vitamins like vitamins B and C are absorbed by diffusion. Vitamin B12 combined with intrinsic factor (from the stomach) is absorbed by active transport.
Of these iron is absorbed in the duodenum, most are absorbed in the jejunum and Vitamin B12 and bile salts are absorbed in the later part of the ileum.
Disorders of the small intestine
Some of the disorders of the small intestine include:
- Obstruction of the small intestine. This may occur due to external pressure, masses in the lumen (foreign bodies, bezoar, gallstones), paralytic ileus, Crohn's disease, Celiac disease, Carcinoid, Meckel's Diverticulum, Gastric dumping syndrome, inguinal hernia, intussuseption, mesenteric ischemia etc.
- Infections including Giardiasis, Ascariasis, Tropical sprue, Tape worm infestation etc.
- Small intestine cancer
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jul 7, 2023