Core Needle Biopsies (CNBs) and Fine Needle Aspirates (FNAs) are the primary biopsy techniques utilized for pre-operative diagnosis, in many cases dictating the therapeutic approach for patient care.
A CNB is created in a clinical setting utilizing a hollow needle to extract a small piece of tissue from the area of interest. CNBs are often a favored form of biopsy as it removes a greater amount of tissue compared with fine needle aspiration.
An FNA is performed in a clinical setting whereby a needle is inserted into the area of interest, and a tiny amount of fluid and cells are aspirated into the needle for cytological and pathological assessment.
These techniques are less invasive than surgical biopsies and deliver an accurate diagnosis. As a result, CNBs and FNAs are extremely valuable and essential for the development of diagnostic assays. However, CNBs and FNAs are challenging to acquire for research and development as they are perceived as diagnostic materials. Additionally, samples are frequently exhausted during diagnosis workup.
BioIVT has successfully developed a procedure to replicate CNB and FNA from fresh surgical collections. This enables the creation of matched CNB, FNA, and preserved tissue blocks (FFPE, OCT embedded, or Fresh Frozen), furthering the development of companion diagnostic assays for clinical use.
Methods
Tissue procurement
Fresh tissue was obtained via the ASTERAND® Human Tissue network of surgical sites following specific collection protocol and project proposal requirements, in line with regulations supporting subject/donor protection. Fresh tissue samples and clinical data were transported to a CAP-certified laboratory for processing.
Laboratory-synthesized CNBs, FNAs, and resection FFPE blocks were processed and assessed using a standard histology review and a pathology review. This two-level assessment was conducted by a board-certified pathologist for tissue-type confirmation, diagnosis, cellular component estimation/determination and to guarantee tissue origin and diagnosis were consistent with clinical data.
Tri-format tumor processing
Tissue processing was conducted according to aseptic technique immediately following the arrival of tissue at the facility. The tumor was divided into two mirrored sections, with one being processed into an FFPE block.
CNB and FNA generation was performed using the second tumor section. Laboratory technicians extracted up to 4-6 cores from the tumor using a standard core needle biopsy gun, from which an FFPE block was processed.
The FNA was created from the remaining tumor, which was first hydrated and disrupted by injecting ethanol using a 14-gauge needle. After this step, the aspirate was collected, pelleted, washed, and then processed into an FFPE block.
The resection, CNB, and FNA FFPEs were reviewed using standard histology and pathology reviews, and by comparison of pathology data for all three formats for consistency.
Regulatory
BioIVT collaborates with centralized and local US-based IRBs, EU-based IECs, and Health Ministries in different countries as necessitated. BioIVT is also in compliance with its UK HTA license for the storage, application, and disposal of human biomaterials.
Tri-format process
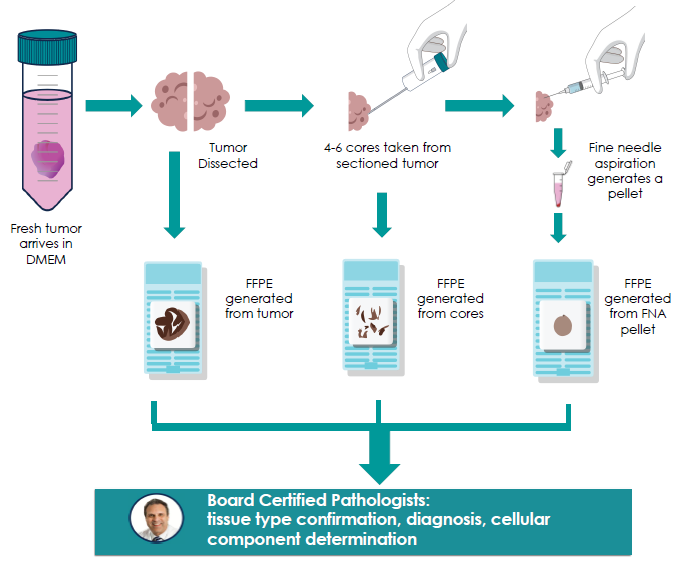
Image Credit: BioIVT
Applications
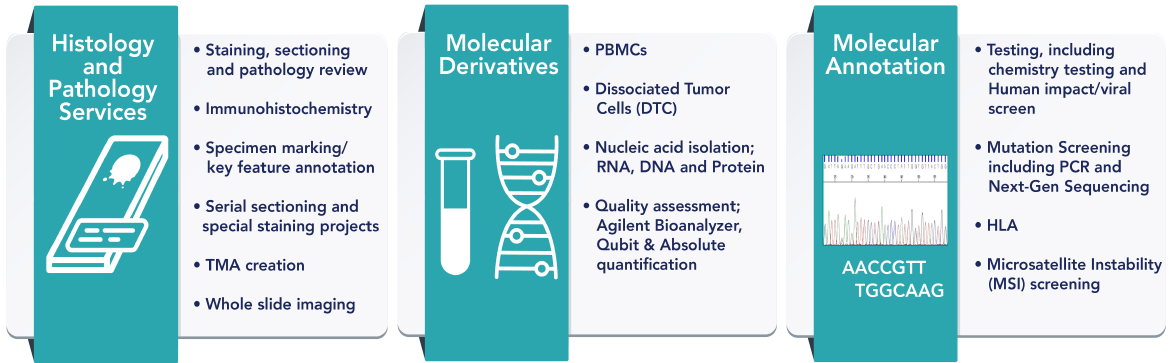
Image Credit: BioIVT
Conclusions
To reproduce the clinical situation for diagnostic development, BioIVT has created a procedure to replicate CNBs and FNAs from fresh surgical collections. BioIVT’s Tri-Format solutions can be utilized in several downstream applications to aid diagnostic assay development without the use of valuable clinical material.
About BioIVT
BioIVT, formerly BioreclamationIVT, is a leading global provider of high-quality biological specimens and value-added services. We specialize in control and disease state samples including human and animal tissues, cell products, blood, and other biofluids. Our unmatched portfolio of clinical specimens directly supports precision medicine research and the effort to improve patient outcomes by coupling comprehensive clinical data with donor samples.
Our Research Services team works collaboratively with clients to provide in vitro hepatic modeling solutions. And as the world’s premier supplier of ADME-Tox model systems, including hepatocytes and subcellular fractions, BioIVT enables scientists to better understand the pharmacokinetics and drug metabolism of newly discovered compounds and the effects on disease processes. By combining our technical expertise, exceptional customer service, and unparalleled access to biological specimens, BioIVT serves the research community as a trusted partner in ELEVATING SCIENCE®.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.