Cyto-Cellect®PLUS is intended to function in tandem with the Cyto-Mine® Platform. It captures whole-molecule human IgG with κ and λ light chains produced by cells enclosed in picodroplets (Figure 1).

Image Credit: Fluidic Sciences and Sphere Bio
After encapsulated cells secrete human IgG, the fluorescent probes attach to the protein. The combination of Cyto-Cellect®PLUS and Cyto-Mine® provides a test for measuring single-cell productivity by immediately identifying secreted IgG, allowing cells with the highest productivity to be identified and selected.
Cyto-Cellect®PLUS is certified animal origin free (AOF) and tested utilizing Cyto-Mine® to isolate IgG-secreting CHO cells (IgG4κ and IgG1λ light chains). The donor and acceptor probes are confirmed to bind to human IgG1-4λ and IgG1-4κ.
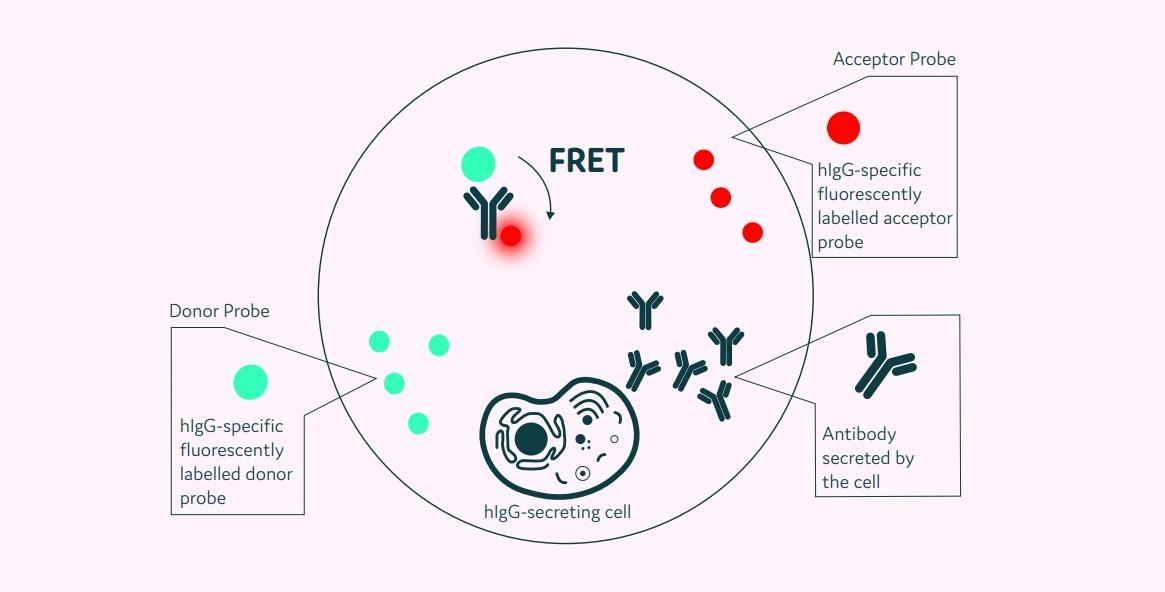
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the Cyto-Cellect®PLUS detection kit for IgG secreting cells. A customized pair of IgG-specific AOF fluorescent probes are trapped within each picodroplet. IgG secreted from the encapsulated cell is recognized by the detection probe pair forming a ternary FRET complex that induces a change in fluorescent signal. Image Credit: Fluidic Sciences and Sphere Bio
Aims and objectives
This article exhibits Cyto-Cellect®PLUS's capacity to detect human IgG (κ and λ light chains).
The article also demonstrates how it may be utilized in a plate reader to consistently detect human IgG. Cyto-Mine® effectively isolates IgGκ and λ secreting cells. Cross-reactivity with human IgM, IgA, and mouse IgG was determined to be low.
Methods and results
Binding of Cyto-Cellect®PLUS probes to human IgG molecules
Using ELISA, cyto-Cellect®PLUS donor and acceptor probes were tested for binding to human IgGκ and IgGλ.
The binding of human IgG to the donor probe was measured by covering ELISA plates with a predetermined dose of the donor (unconjugated). Wells were blocked and titrated with human IgG antibodies (IgG1-4λ, 1κ, or 4κ).
The plates were then cleaned and treated with a detection antibody. The binding was created using a TMB solution.
To test the binding of human IgG to the acceptor probe, plates were coated with IgG (1-4 λ, 1κ, or 4κ; titrated) and detected with acceptor-HRP. The binding was created using a TMB solution.
Detection of human IgG using Cyto-Cellect®PLUS in a plate reader
Cyto-Cellect®PLUS FRET probes were used to titrate commercially available or secreted human IgG in cell culture supernatant (20 µg/mL - 0.625 µg/mL (or 0.310 µg/mL, 2-fold dilution).
The FRET response was measured in a plate reader at 488 nm excitation and emission at 520 nm (Green Channel) and 620 nm (Red Channel). It was estimated by dividing the red channel intensity by the green channel intensity. The FRET response was standardized to 0 µg/mL IgG (medium control).
Using Cyto-Cellect®PLUS for detection and dispensing of IgG-secreting CHO cells in Cyto-Mine®
CHO cells secreting IgG 1λ or IgG 4κ were resuspended in Encapsulation Medium (83% growth medium, 16% Opti-prep, 1% PF-68) with Cyto-Cellect®PLUS FRET probes. Cells were then placed into the Cyto-Cartridge®, and antibody secretion was measured using Cyto-Mine®.
Figure 2 summarizes the integrated steps of the Cyto-Mine® process. In brief, cells and Cyto-Cellect®PLUS FRET probes are packed in picodroplets. These are incubated in the incubation chamber at 37 °C to provide optimal conditions for antibody production.
Cyto-Cellect®PLUS FRET probes collect and detect the secreted antibody as it accumulates inside the picodroplet. Cells that secrete antibodies are discovered in Cyto-Mine® during sorting and distributed into tissue culture plates.
Cross-reactivity of Cyto-Cellect®PLUS with human IgM, IgA, and mouse IgG
Cyto-Cellect®PLUS's capacity to identify human IgM, IgA, and mouse IgG was tested using a plate reader. The publicly accessible antibodies were titrated and treated with Cyto-Cellect®PLUS probes.
The FRET response was measured in a plate reader at 488 nm excitation and 520 nm and 620 nm emission (Green and Red channels, respectively). The FRET response was estimated by dividing the red and green channel intensity. The FRET response was standardized to 0 µg/mL IgG (medium control).
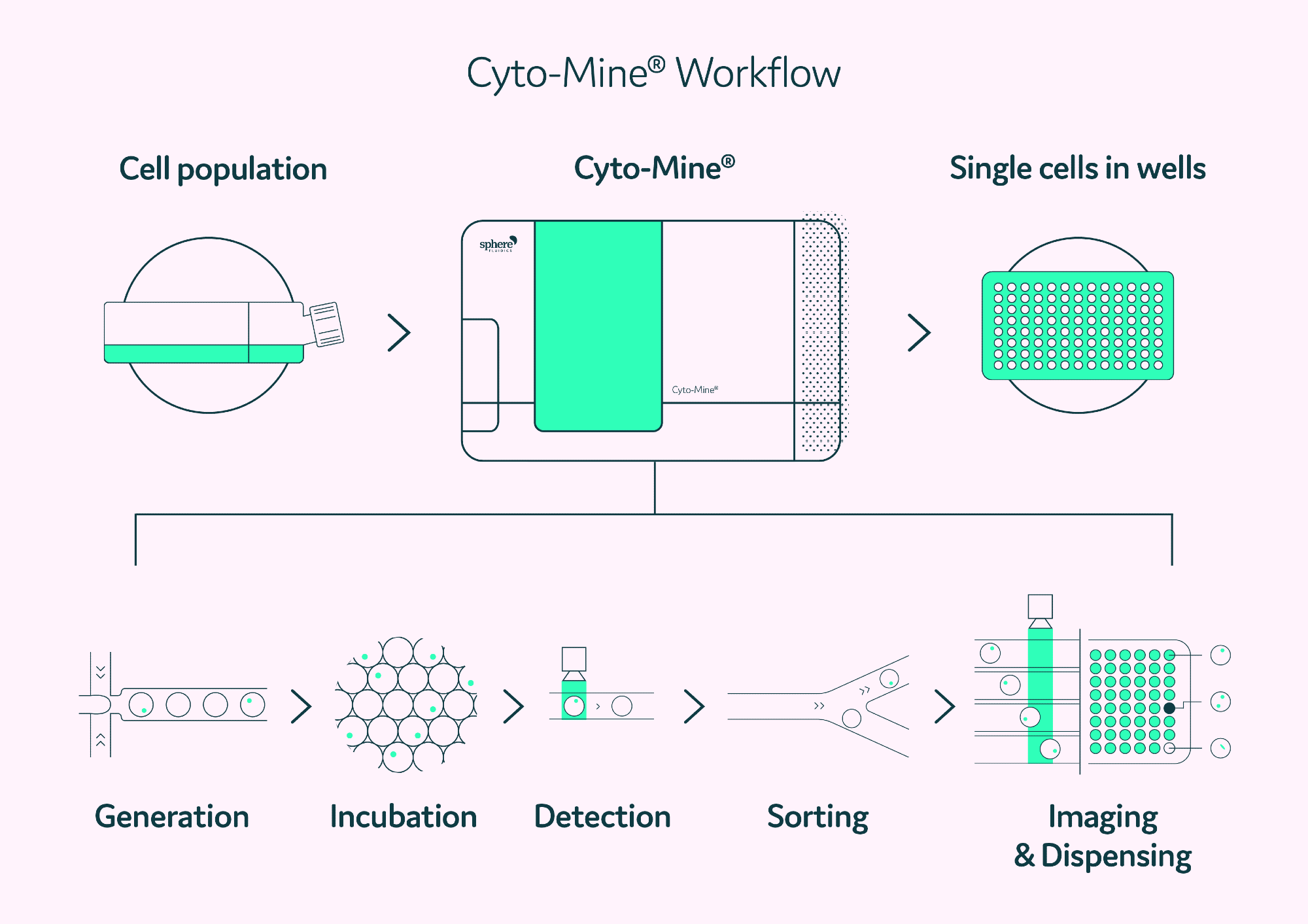 Figure 2. The Cyto-Mine® workflow integrates the screening, sorting, isolation and verification of high-secreting clones into a fully automated process. Image Credit: Fluidic Sciences and Sphere Bio
Figure 2. The Cyto-Mine® workflow integrates the screening, sorting, isolation and verification of high-secreting clones into a fully automated process. Image Credit: Fluidic Sciences and Sphere Bio
Results
Cyto-Cellect®PLUS probes bind to both κ and λ light chains of the human IgG molecule
The Cyto-Cellect®PLUS probes' capacity to bind to human IgGκ and λ molecules was assessed using ELISA. Figure 3 demonstrates that the Cyto-Cellect®PLUS kit's donor (Figure 3A) and acceptor (Figure 3B) probes bind IgGκ and λ molecules with great affinity.
IgG3λ and IgG4λ exhibited much higher binding to the donor and acceptor than IgG1λ and IgG2λ (EC50 value).
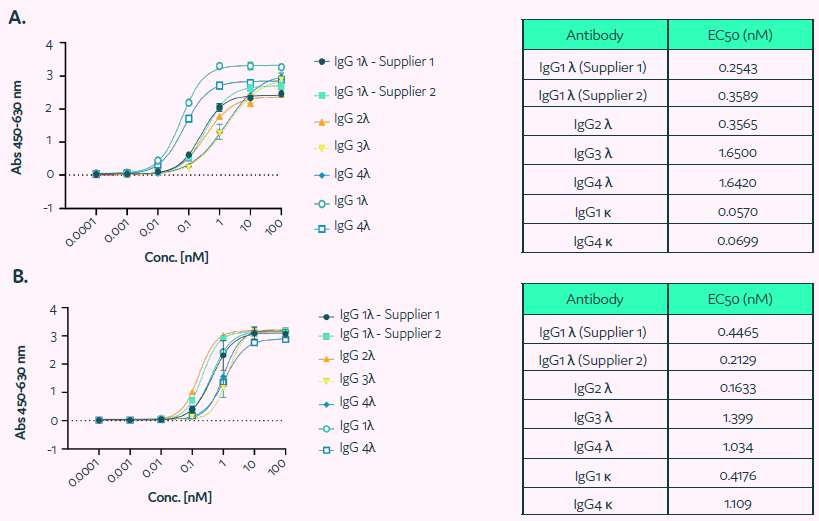
Figure 3. Binding of Cyto-Cellect®PLUS probes to human IgG molecules was determined using ELISA. (A) ELISA plates were coated with fixed concentration of the donor (unconjugated). Wells were blocked and incubated with titration of human IgG antibodies (IgG 1-4 λ, 1κ or 4κ). Subsequently plates were washed and incubated with a detection antibody. The binding was visualized using TMB solution. (B) The binding of the human IgG to acceptor was determined by coating plates with commercially supplied human IgG (IgG 1-4λ, 1κ or 4κ; titrated), followed by detection using acceptor-HRP. The binding was developed using TMB solution. Image Credit: Fluidic Sciences and Sphere Bio
Detection of human IgG using Cyto-Cellect®PLUS in a plate reader
The capacity of Cyto-Cellect®PLUS to identify human IgG molecules was tested with commercially available IgG or secreted IgG in cell culture supernatant. CytoCellect®PLUS demonstrated a dose-dependent response to commercial IgG1-4κ (Figure 4A).
FRET responses to IgG1λ and 3λ were evaluated using Cyto-Cellect®PLUS (Figure 4B & C). IgG1λ from several commercial sources demonstrated acceptable detection. However, IgG3λ could not be identified at lower amounts tested. The Cyto-Cellect® kit detected IgG4κ but not IgG1λ light chains (Figure 4C).
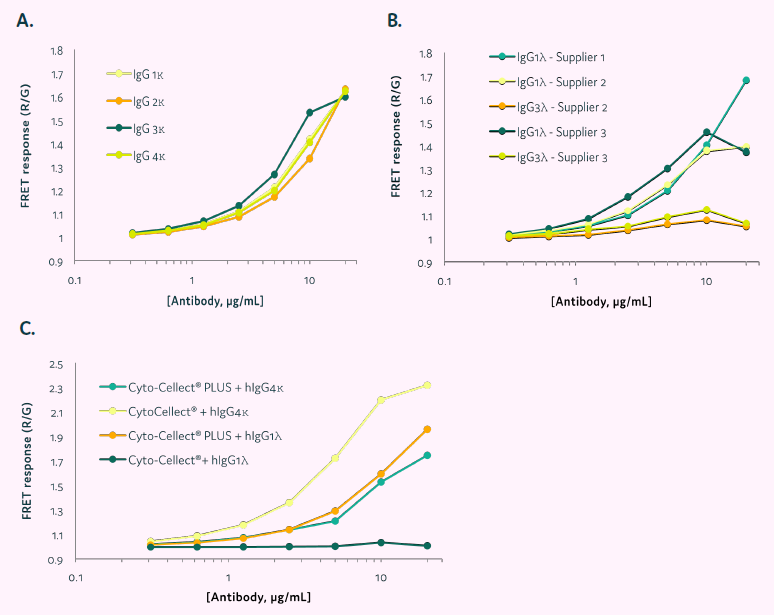
Figure 4. FRET response of Cyto-Cellect®PLUS in the presence of commercial and secreted IgG in cell culture supernatant. (A&B) Commercially sourced antibodies were titrated in the presence of Cyto-Cellect®PLUS probes. Data show normalized FRET response, calculated by dividing Red intensity/Green intensity. (C) Supernatant containing IgG 1λ was titrated in the presence of either Cyto-Cellect® or Cyto-Cellect®PLUS probes. As a control, commercially available IgG4κ was titrated and detection by the two assay kits determined. Data show normalized FRET response, calculated by dividing Red intensity/Green intensity. Image Credit: Fluidic Sciences and Sphere Bio
Using Cyto-Cellect®PLUS for detection and dispensing of IgG-secreting CHO cells in Cyto-Mine®
Cyto-Cellect®PLUS was utilized to identify CHO cells that secrete IgG in Cyto-Mine®. Figure 5A shows the FRET response of CHO cells secreting IgG4 after a two-hour incubation with the Cyto-Cellect®PLUS probes.
Cyto-Cellect®PLUS was utilized to identify, sort, and dispense CHO cells that secrete IgG1λ (Figure 5B-C). Cells were enriched (Figure 5B), followed by single-cell dispensing (Figure 5C), utilizing Cyto-Cellect®PLUS in Cyto-Mine®.
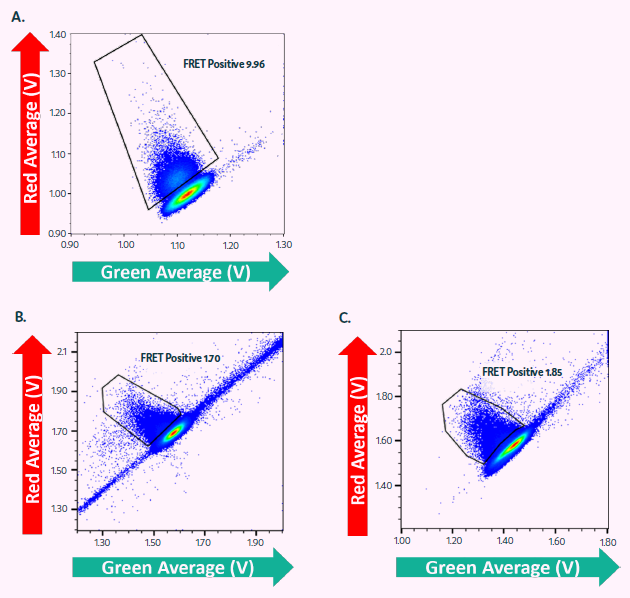
Figure 5. Cyto-Cellect®PLUS used for enrichment and single cell dispensing of IgG secreting CHO cells in Cyto-Mine®. (A) CHO cells, secreting IgG4κ were resuspended in Encapsulation Medium containing Cyto-Cellect®PLUS FRET probes and loaded onto Cyto-Mine®. Cells were incubated for 2 hours and dispensed as single cells into microtiter plates. (B-C) CHO cells, secreting IgG1λ were resuspended in Encapsulation Medium containing Cyto-Cellect®PLUS FRET probes and loaded onto Cyto-Mine®. Cells were incubated for 2.5 hours and dispensed as either (B) pool of cells or (C) single cells, into microtiter plates. Image Credit: Fluidic Sciences and Sphere Bio
Cyto-Cellect®PLUS shows no cross-reactivity with human IgA or mouse IgG
To test the Cyto-Cellect®PLUS probes' cross-reactivity with immunoglobulin isotypes other than human IgG, commercially supplied human IgM, IgA, and mouse IgG were titrated in the presence of the probes.
FRET response was measured using a plate reader and compared to human IgG1λ. Figure 6 reveals that the kit does not cross-react with human IgA or mouse IgG at the quantities tested; however, human IgM is negligibly detected at high concentrations.
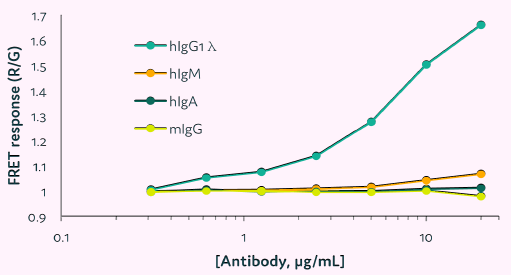
Figure 6. Cross-reactivity of Cyto-Cellect®PLUS with human and mouse immunoglobulins. The human IgM, IgA and mouse IgG were titrated in the presence of Cyto-Cellect®PLUS probes, and the FRET response was detected using plate reader. IgG1λ was used as a control. Image Credit: Fluidic Sciences and Sphere Bio
Conclusions
The given data reveals that Cyto-Cellect®PLUS delivers a sensitive FRET response to secreted human IgG (both κ and λ light chains) and is compatible with a plate reader and Cyto-Mine®. The test kit allows for the enrichment and distribution of single CHO cells based on productivity.
Compatibility with Cyto-Mine®: Cyto-Cellect®PLUS is compatible with Cyto-Mine®, allowing for the sorting and distributing of individual cells based on productivity.
Enhanced detection capability for human IgG: Detects both κ and λ light chains in human IgG molecules.
Low cross-reactivity: The kit has no/minimal cross-reactivity with human IgM, IgA, and mouse IgG.
Animal Origin Free (AOF): Cyto-Cellect®PLUS is AOF and may be employed in a therapeutic Cell Line Development (CLD) process alongside Cyto-Mine®.

Image Credit: Fluidic Sciences and Sphere Bio
About Fluidic Sciences and Sphere Bio
Fluidic Sciences develops transformative in‑solution technologies for protein interaction analysis. Its flagship Fluidity One‑M instrument leverages Microfluidic Diffusional Sizing (MDS) to measure binding affinity, stoichiometry, size, and concentration without immobilization - directly in complex backgrounds such as serum, plasma, and lysate.
Sphere Bio is a brand of Fluidic Sciences. Its technology develops and manufactures single‑cell analysis and monoclonality assurance systems that enable researchers to find, analyze, and isolate the most valuable cells with speed and precision. Its proprietary picodroplet microfluidics and Cyto‑Mine® Chroma multiplexing platform power applications across antibody discovery, cell line development, cell engineering, and cell therapy.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.