The tri-culture model is a unique approach to assessing the functional and morphological effects on cardiac cells.
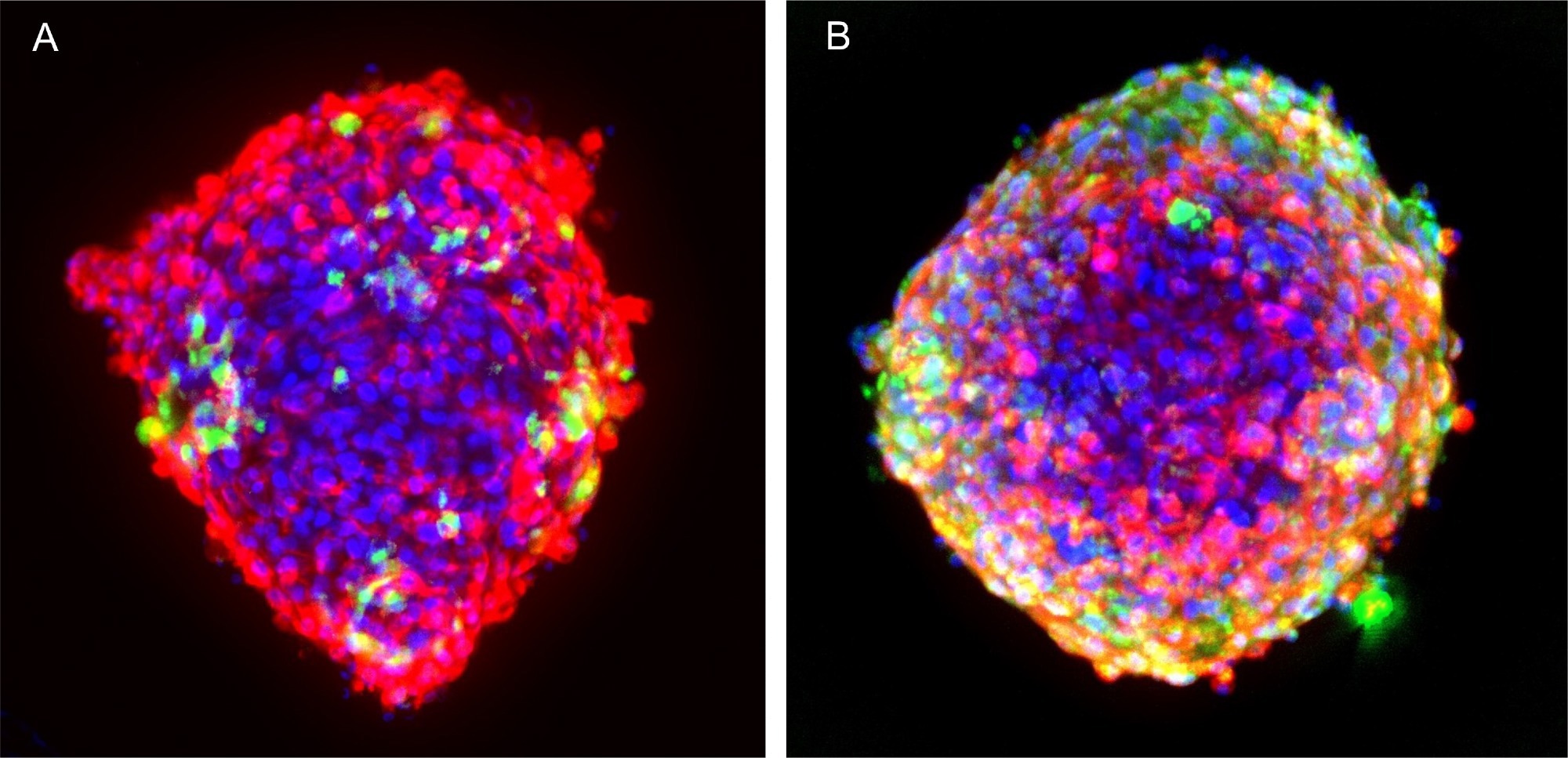
Image Credit: Molecular Devices
Recent studies have shown that tri-cellular co-culture microtissues of cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and cardiac fibroblasts derived from human iPSCs improve cell maturation and functional activity compared to 2D cardiomyocytes, more closely mimicking actual heart physiology.
This app note discusses the usability and biological significance of employing iPSC-derived cell types in 3D micro-tissues as a potential model for assessing chemical effects on human cardiac tissues in a high-throughput format.
Download the App Note
About Molecular Devices UK Ltd 
Molecular Devices is one of the world’s leading providers of high-performance life science technology. We make advanced scientific discovery possible for academia, pharma, and biotech customers with platforms for high-throughput screening, genomic and cellular analysis, colony selection and microplate detection. From cancer to COVID-19, we've contributed to scientific breakthroughs described in over 230,000 peer-reviewed publications.
Over 160,000 of our innovative solutions are incorporated into laboratories worldwide, enabling scientists to improve productivity and effectiveness – ultimately accelerating research and the development of new therapeutics. Molecular Devices is headquartered in Silicon Valley, Calif., with best-in-class teams around the globe. Over 1,000 associates are guided by our diverse leadership team and female president that prioritize a culture of collaboration, engagement, diversity, and inclusion.
To learn more about how Molecular Devices helps fast-track scientific discovery, visit www.moleculardevices.com.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.