Presbyopia is a medical condition whereby a person loses the ability to see objects clearly at near distance, while maintaining clear vision for long distance vision. Practically everyone will experience presbyopia after a point in their lives. In fact, it is a fairly predictable sign that one has entered mid-life, because it is most prevalent in those who are 50 years or older.
Presbyopia, as one may guess, is a process that does not happen overnight. It is a consequence of the progressive and gradual decline in the accommodative properties of the eyes that occurs as we age.
Eye condition Presbyopia. Image Credit: Alila Medical Media / Shutterstock
Accommodation
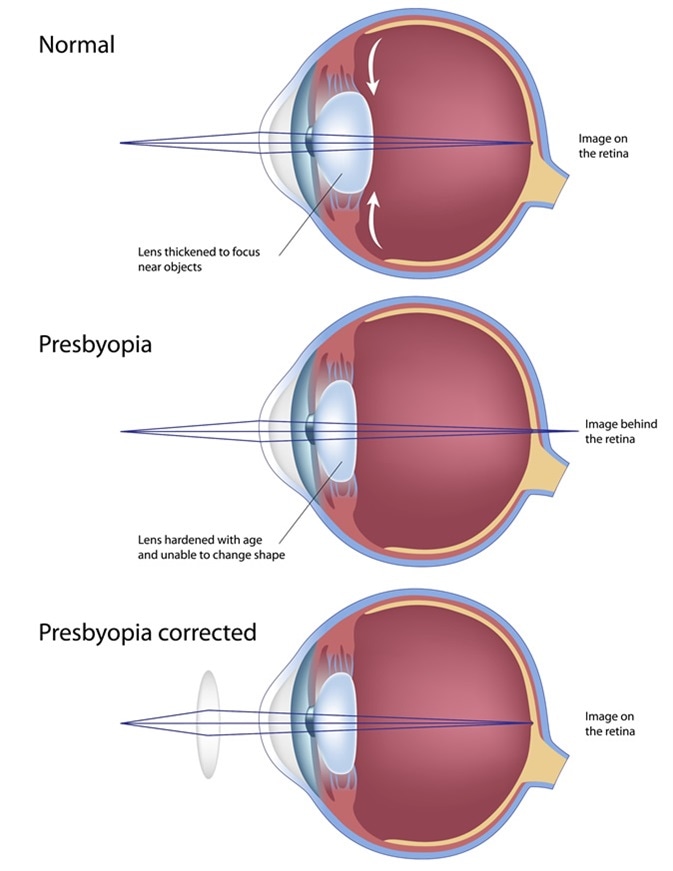
Accommodation is a process that occurs in the eyes, by which the eyes change their optical power in order to maintain clear foci or create clear images of objects even at varying distances. These distances must be between the near and far points, which corresponds to the minimum or maximum distance, respectively, that is necessary for a clear image of an object to be seen. Accommodation is basically a reflex that occurs in the eyes to adjust foci from far distances to those as close as 65 mm from the eye. It is mediated by the ciliary muscles and the tension in the zonular fibers.
The exact mechanism as to how the ciliary muscles and zonular fibers work in unison to achieve accommodation is, to date, not completely understood. As a result of this gap in our ophthalmological understanding, several theories have been postulated to help shed light on the process. German physician, Hermann von Helmholtz put forth the most widely accepted Helmholtz or capsular theory with regards to accommodation. He hypothesized that the ciliary muscle is relaxed during distance vision and simultaneously there is a resting tension within the zonular fibers, which cross between the lens equator and the ciliary body.
According to the Helmholtz theory, the ciliary muscle contracts with accommodation and there is a resulting release in zonular tension. This allows for the contraction of the elastic lens capsule to occur, thereby decreasing the diameter of the lens equator, and increasing the anterior and posterior curvatures of the lens surfaces. All together, these changes cause the lens to become rounded and increases its dioptric power, which is vital for near distance vision.
Once the effort of accommodation ceases, the ciliary muscles relax, the tension in the zonular fibers reverts back to the resting states and this in turn pulls on the equator of the lens, thereby flattening the lens. This reversion of the process towards an unaccommodated state decreases the dioptric power of the eye, which is necessary for distance vision.
Another theory of accommodation is the Schachar theory. This theory opposes the Helmholtz theory diametrically. It proposes that there is selective, rather than uniform decrease and direct zonular fiber effect rather than passive (as suggested by Helmholtz) in the zonular tension at the lens equator.
What is Presbyopia?
Accommodation and Aging
The strength of accommodation declines with age to the point where the minimum distance at which one can obtain a clear image of an object is further than the normal reading distance. This can have several results depending on whether or not a patient is emmetropic (normal vision), myopic (nearsighted) or hyperopic (farsighted) already. People who are emmetropic will require reading glasses once presbyopia occurs, while those who suffer with myopia will actually notice better near vision without needing correction for distance vision. In contrast, hyperopic individuals will require correction for both near and distance vision once presbyopia occurs.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Mar 13, 2023