Jan 16 2007
Coating characterisation of polymer-coated cardiovascular stents has been undertaken utilising ToFSIMS, DSIMS and 3DP.
Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (ToFSIMS) provides detailed molecular information from the very outer surface of a stent to investigate the molecular make-up of the contact point between stent and host.
Contamination on the surface of stents can also be investigated by ToFSIMS providing spectra and images of the surface i.e. what is the chemistry and where is it lying?
Dynamic Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (DSIMS) depth profiles monitor the active pharmaceutical ingredient as a function of depth and are repeated at set intervals through the elution studies to determine the rate of elution. Valuable information about the elution rate and state of the active pharmaceutical ingredient can be gained.
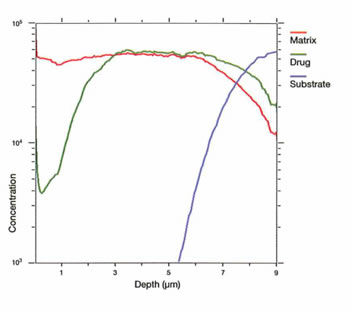 |
| Figure 2-Representative DSIMS depth profile |
3D Non-Contact Profiling (3DP), a white light interferometry technique, has been utilised to determine the uniformity and roughness of the polymer coating. The interference patterns are interpreted to produce linescans, 2D and 3D images of the surface form which roughness, peak height and valley depth can be determined.
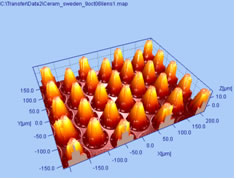 |
| Figure 3-3DP example image showing a microlens array. |
CSMA's surface analysis expertise is world renowned and has been built up over twenty years of solving problems for a wide range of industries and materials.
Click here for more information from CSMA.