Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) have shown that microbes can be molded into an array of unusual, elaborate shapes that are not seen in nature.
..jpg) Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy images reveal the molded shapes of bacterial Z-rings (montage, pseudo-colored). (Credit: OIST)
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy images reveal the molded shapes of bacterial Z-rings (montage, pseudo-colored). (Credit: OIST)
The study shows how robust these microbes can be – a finding that could have important ramifications in an age of antibiotic resistance.
The study focused on the molecule FtsZ; a protein that serves as a scaffold for the assembly of other proteins during cell division.
Thousands of FtsZ proteins gather together in the center of the cell and form a circle-like structure called the Z-Ring.
In the bacterium Escherichia coli, these rings form at the site of cell division but Bill Söderström and colleagues wanted to know whether this would always be the case.
This ring forms along the circumference at the midcell, but I wanted to know how important cell shape itself is in creating that. If the cell wasn't rod-shaped, would the Z-ring still be round?"
Bill Söderström, Lead Author
The technology that would enable them to find out had already been used in previous studies conducted at OIST.
A microscale frame had been used to position bacterial cells upright rather than at the surface of an agarose pad.
Söderström asked whether the design could be altered to use a square shape and with one simple modification, the team were able to introduce the bacterial cells to a cubic-shaped environment.
The team then used chemicals that would reduce the cells’ structural integrity to ease them into the new shape.
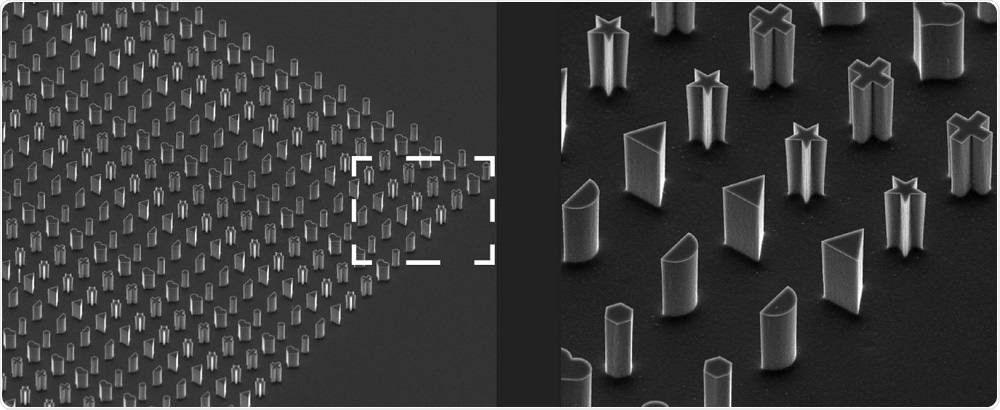 Magnified view of the microfabricated bacteria molds in various shapes. (Credit: OIST)
Magnified view of the microfabricated bacteria molds in various shapes. (Credit: OIST)
As recently reported in the journal Nature Communications, the bacteria grew into cubic shapes and the Z-rings became Z-squares.
The researchers then wondered what other shapes the rings could be changed into and further experiments led to the production of triangles, pentagons and even star shapes that the bacteria and their Z-rings all adapted to.
"Really, we ended up doing these extra shapes for fun, yet there's very fundamental science at the heart of it," says Söderström.
The study shows that the microbes can grow and form cell division rings in very restrictive environments, a finding that could have important implications for future research.
Many antibiotics work based on their ability to target cellular functions involved in cell division and the FtsZ platform.
In the future, scientists investigating new antibiotics would need to look at more than cell shape.
Our study shows that the Z-ring is incredibly robust - geometry isn't an obstacle to ring formation.”
Bill Söderström