Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel, highly infectious respiratory virus, and the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. SARS-CoV-2, which first originated in Wuhan, in Hubei province of China, is a member of the Coronavirdae family and has a large, non-segmented RNA genome.
High levels of transmission in regions with low rates of vaccination encourage mutations that boost viral fitness. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) are variants with one or more mutations having adverse epidemiologic, immunologic, or pathogenic properties.
The B.1.1.7 (Alpha) variant has over 20 mutations, including N501Y within the spike (S) protein, and is associated with increased transmissibility compared to the original virus. It also has increased binding affinity to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in host cells that plays a role in viral entry.
The B.1.351 (Beta) variant, originally reported in South Africa, has similar mutations in the spike as well as the K417N and E484K substitutions that could decrease the efficacy of currently available vaccines.
Given the possibility of potential vaccine resistance of the VOCs, it is crucial to understand the impact of the newly emerging variants on host immune response and disease dynamics to guide the development of COVID-19 vaccines and therapeutics.
Analyzing the pathogenic and transcriptomic differences of emerging SARS-CoV-2 VOCs in the Syrian golden hamster model
Syrian golden hamsters are one of the most popular small animal models used in COVID-19 research globally. Recently, researchers from the US conducted a study in which they intranasally inoculated different SARS-CoV-2 variants into hamsters. This study is published on the bioRxiv* preprint server.
The ancestral virus (nCoV-WA1-2020) or the B.1.1.7 variant first identified in the UK and the B.1.351 variant first identified in South Africa caused similar gross and histopathologic pulmonary lesions.
"Syrian golden hamsters were chosen for this study as they are highly susceptible to infection 237 and were found to have high viral replication in the lungs."
While differences in viral genomic copy numbers were observed in the lungs and oral swabs of infected animals, infectious titers were comparable in the lungs. Antibody neutralization capacities varied based on the original virus and cross-variant protective capacity. Transcriptional profiling showed significant induction of antiviral pathways in response to all three viral variants with a more robust inflammatory signature in response to the B.1.1.7 variant. Moreover, no additional spike protein mutations were detected at peak disease.
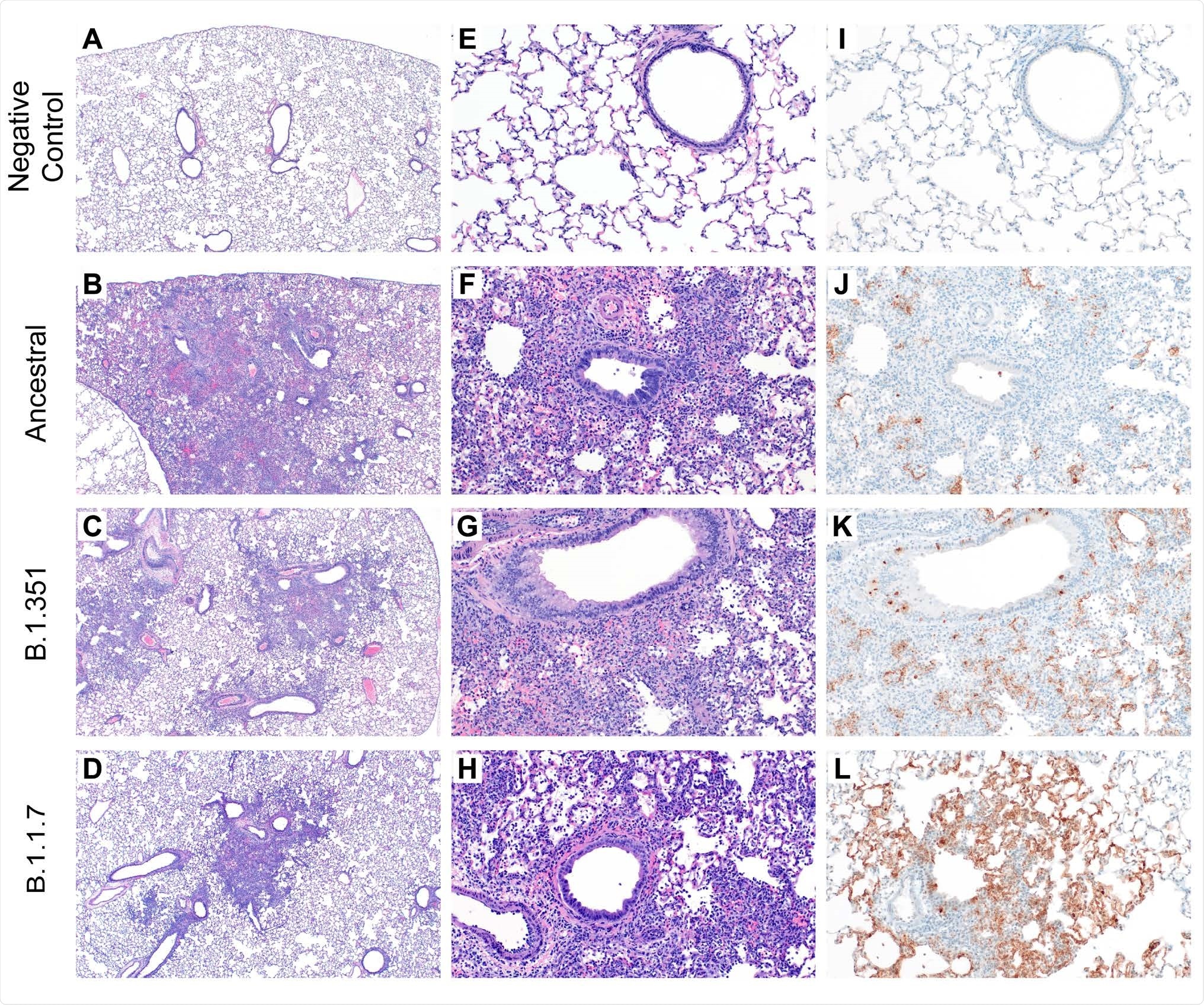
Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry of hamster lungs. (A-H) Representative H&E images of lungs of hamsters infected with 105 TCID50 of ancestral, B.1.1.7, and B.1.351 variants at 4 days post-challenge (DPC). Foci of interstitial pneumonia and bronchiolitis were observed throughout all evaluated lung lobes of infected hamsters. (I-L) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) detected SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid staining in the lungs of all infected hamsters.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
The researchers also detected many differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to tissue morphogenesis and angiogenesis in all three infection challenges. Microvascular injury can further aggravate inflammation-driven lung fibrosis. Also, genes that have a role in tissue repair were downregulated after infection with the B.1.35 and ancestral variants.
"Analysis of the humoral response revealed that the overall IgG response of the infected 249 hamsters did not result in robust differences amongst the variants; however, the neutralization 250 cross-protection depended on the variant the hamster was initially exposed to."
To summarize, this study describes the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 variants and the development of cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies. According to the authors, this is the first study that performed a comparative and longitudinal analysis of the immune response after infection with SARS-CoV-2 VOCs.
They found that infection with the B.1.1.7 VOC results in a better response compared to infection with the B.1.35 VOC. This broader response to B.1.1.7 may be partly mediated by the more robust transcriptional response induced by this variant, including a more significant induction of antiviral and inflammatory pathways. The authors believe that additional studies must investigate the mechanisms through which the mutations detected in the B.1.35 VOC result in reduced neutralization potential.
"Future experiments should assess transcriptional changes beyond 4 DPC to determine the kinetics of the host response at this critical site. "

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Pathogenic and transcriptomic differences of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants in the Syrian golden hamster model, Kyle L O'Donnell, Amanda N Pinski, Chad S Clancy, Tylisha Gourdine, Kyle Shifflett, Paige Fletcher, Ilhem Messaoudi, Andrea Marzi, bioRxiv, 2021.07.11.451964; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.11.451964, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.07.11.451964v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
O’Donnell, Kyle L., Amanda N. Pinski, Chad S. Clancy, Tylisha Gourdine, Kyle Shifflett, Paige Fletcher, Ilhem Messaoudi, and Andrea Marzi. 2021. “Pathogenic and Transcriptomic Differences of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants in the Syrian Golden Hamster Model.” EBioMedicine 73 (November): 103675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103675. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/ebiom/article/PIIS2352-3964(21)00469-2.