Continued replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) under selective pressure from natural and vaccine-induced immunity has led to the emergence of variants of concern (VOCs) with increased transmissibility or virulence.
VOCs elicit one to three RBD mutations, which may overlap. For instance, the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant can acquire the K417NRBD mutation found in the B.1.351 (Beta) variant, generating the Delta AY.2 variant. However, variant monitoring efforts are still under-sampling viral evolution, and an undocumented combination of RBD mutations may have the potential for antibody escape.
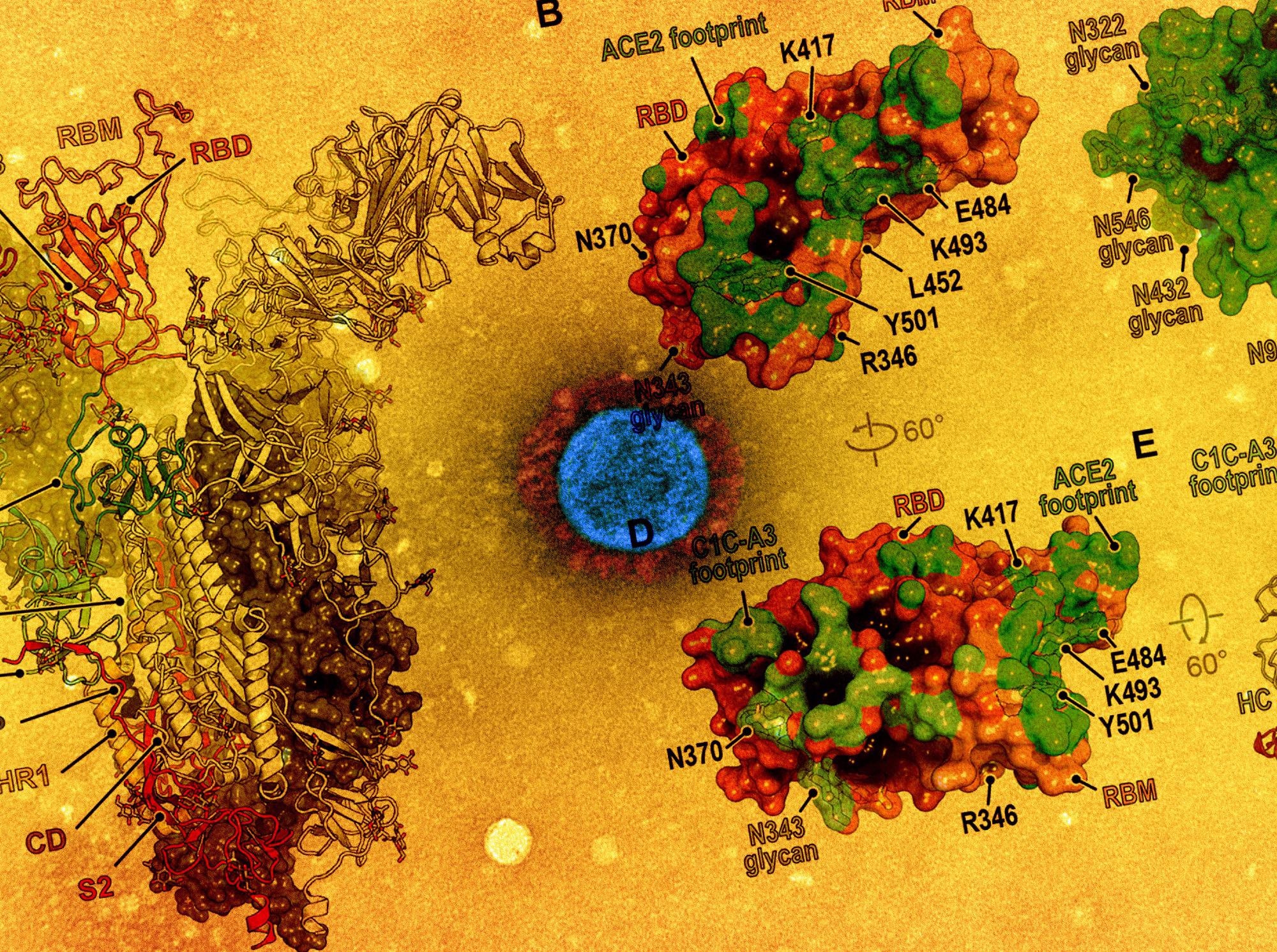 Study: Structural basis for continued antibody evasion by the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain. Image Credit: NIAID and American Association for the Advancement of Science
Study: Structural basis for continued antibody evasion by the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain. Image Credit: NIAID and American Association for the Advancement of Science
The Study
A recent study published in the journal Science investigated the structural pliability of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD and its capacity to evade neutralizing antibodies.
In this study, monoclonal antibodies were isolated from the blood of a COVID-19 convalescent individual. Venous blood samples were derived from healthy mRNA-1273 and BNT162b2 vaccine recipients.
Findings
The results showed that many RBD mutations occur in a persistently infected immunocompromised host. Furthermore, structural plasticity at the ACE2-RBD interface facilitates the accumulation of such mutations.
Thus, the phenotypes indicate that further evolved variants were likely to be more elusive to therapeutic antibody neutralization than currently circulating VOCs – and could prove to be resistant to two-component antibody cocktails.
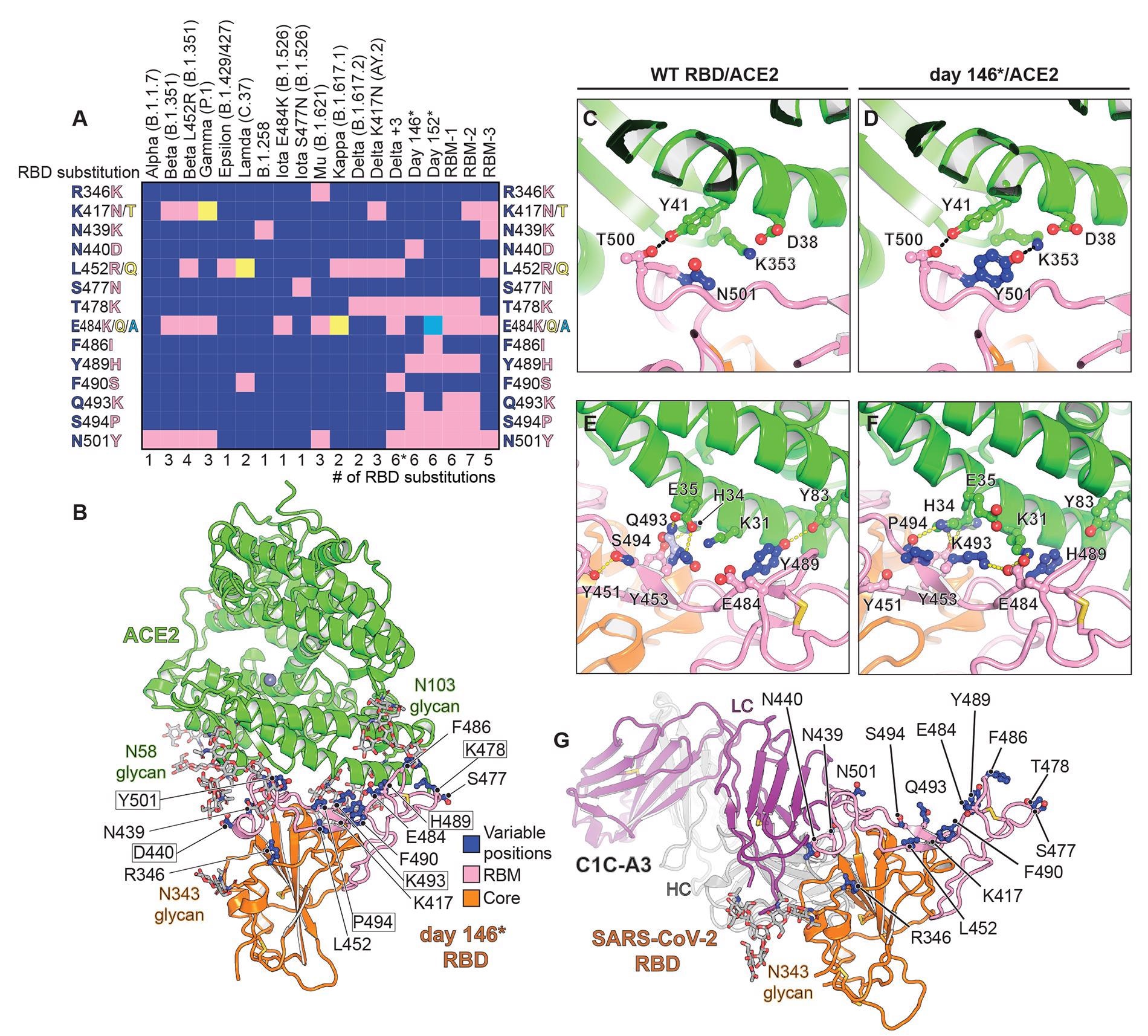 Structure of intra-host evolved RBD bound to human ACE2.(A) Key RBD substitutions discussed in the manuscript and the SARS-CoV-2 variants that contain them. (B) Day 146* RBD/ACE2 ectodomain X-ray crystal structure. RBD residues that are mutated in variants discussed in the text are shown. Boxed residues are mutated in the day 146* RBD as compared to the Wuhan-Hu-1 (wild-type) SARS-CoV-2 RBD. RBM: receptor-binding motif. *In addition to the mutations that are shown, the Delta +3 variant contains an additional RBD mutation that is not shown in the schematic diagram (see table S2). (C) Wild-type RBD ACE2 contacts near N501RBD (PDB ID: 6M0J) (2). (D) Day 146* RBD contacts near Y501RBD. (E) Wild-type SARS-CoV-2 RBD ACE2 interactions near Q493RBD. (F) Day 146* RBD interactions near K493RBD. (G) cryo-EM structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD bound to the C1C-A3 antibody Fab. RBD residues discussed in the text are labeled.
Structure of intra-host evolved RBD bound to human ACE2.(A) Key RBD substitutions discussed in the manuscript and the SARS-CoV-2 variants that contain them. (B) Day 146* RBD/ACE2 ectodomain X-ray crystal structure. RBD residues that are mutated in variants discussed in the text are shown. Boxed residues are mutated in the day 146* RBD as compared to the Wuhan-Hu-1 (wild-type) SARS-CoV-2 RBD. RBM: receptor-binding motif. *In addition to the mutations that are shown, the Delta +3 variant contains an additional RBD mutation that is not shown in the schematic diagram (see table S2). (C) Wild-type RBD ACE2 contacts near N501RBD (PDB ID: 6M0J) (2). (D) Day 146* RBD contacts near Y501RBD. (E) Wild-type SARS-CoV-2 RBD ACE2 interactions near Q493RBD. (F) Day 146* RBD interactions near K493RBD. (G) cryo-EM structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD bound to the C1C-A3 antibody Fab. RBD residues discussed in the text are labeled.
It was observed that after two messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) vaccine immunizations and seven days after the second dose, all mRNA vaccine recipients had detectable neutralizing activity against pseudotypes containing an NTD supersite deletion and RBDs with six to seven mutations. However, precise epitopes targeted by this residual neutralizing activity are yet to be identified.
Antibodies targeting the RBD core is speculated to be responsible for the residual vaccine-elicited serum neutralizing activity. The receptor-binding motif (RBM) is a critical site of potent neutralizing antibody binding that is the most antibody accessible and the least masked by glycan and conformational shielding. Hence, continued RBM evolution may modulate antibody responses toward more conserved neutralizing epitopes on the RBD core.
Comparison of immune evasion revealed that variants with an NTD supersite deletion and an E484RBD substitution are the most concerning with respect to resistance to polyclonal antibodies. In fact, E484RBD acts as a significant driver in neutralization escape; furthermore, the pseudotype – Beta, more robustly escapes antibody neutralization than Gamma.
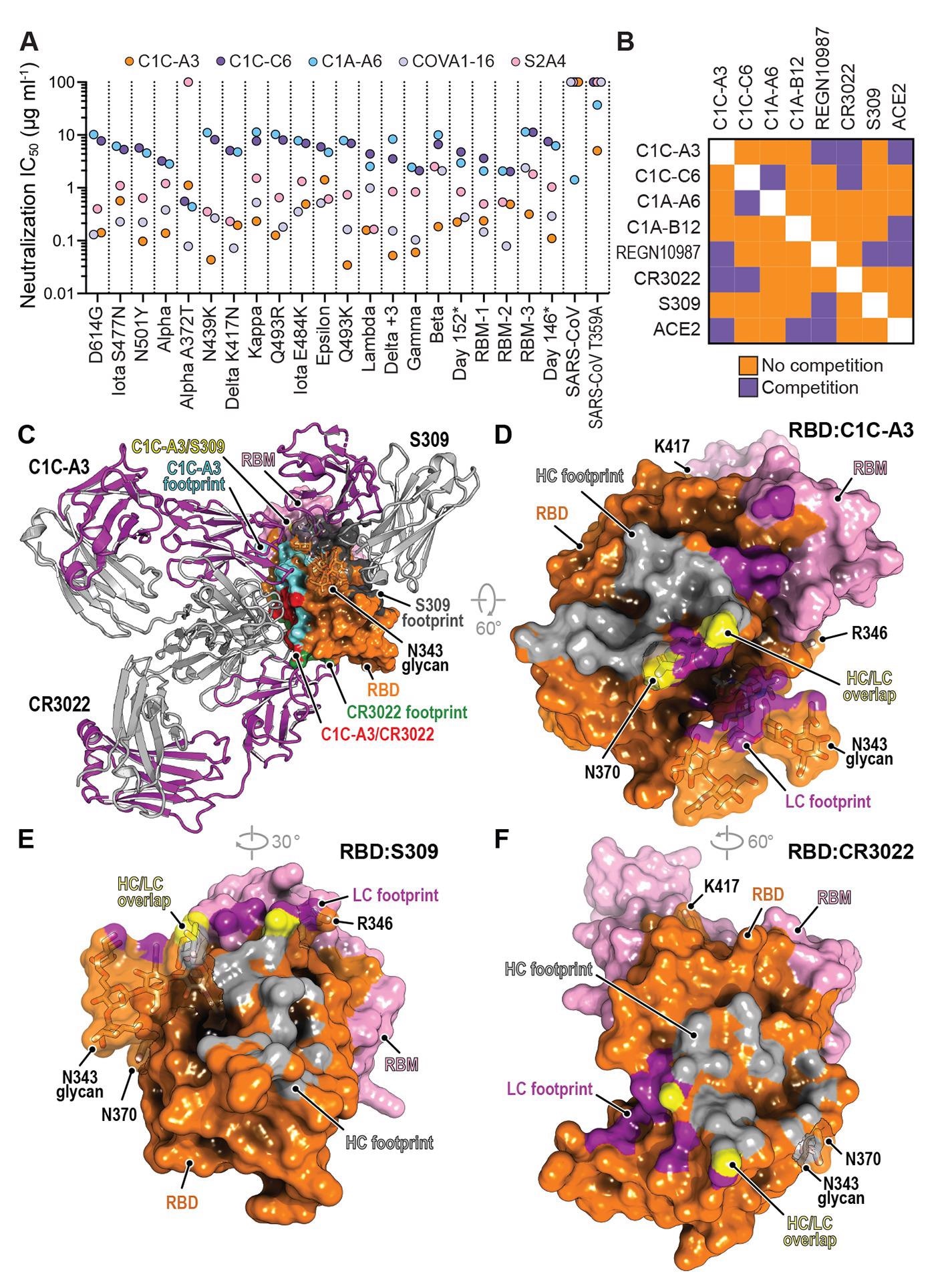 Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by an RBD core targeting antibody.(A) Summary of neutralization IC50 values for pseudotypes and the indicated antibodies. (B) Summary of the results of biolayer interferometry-based competition assays. (C) Superposition of the CR3022 (PDB: 6W41) (55) and S309 (PDB: 6WPS) (44) structures onto the C1C-A3 bound RBD structure. Antibody Fabs are shown as ribbon diagrams and the RBD is shown in surface representation. Antibody footprints are shown on the RBD surface. (D) RBD footprint of C1C-A3. (E) RBD footprint of S309 (PDB: 6WPS) (44). (F) RBD footprint of CR3022 (PDB: 6W41) (55). In panels (D) to (F), key RBD residues discussed in the main text are highlighted.
Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by an RBD core targeting antibody.(A) Summary of neutralization IC50 values for pseudotypes and the indicated antibodies. (B) Summary of the results of biolayer interferometry-based competition assays. (C) Superposition of the CR3022 (PDB: 6W41) (55) and S309 (PDB: 6WPS) (44) structures onto the C1C-A3 bound RBD structure. Antibody Fabs are shown as ribbon diagrams and the RBD is shown in surface representation. Antibody footprints are shown on the RBD surface. (D) RBD footprint of C1C-A3. (E) RBD footprint of S309 (PDB: 6WPS) (44). (F) RBD footprint of CR3022 (PDB: 6W41) (55). In panels (D) to (F), key RBD residues discussed in the main text are highlighted.
Here, D364NRBD was identified as an additional mutation that would introduce a putative N-linked glycosylation site. This independent acquisition on the same surface of the RBD core suggests that this region may be a target of immune selective pressure.
It was stated that the addition of the N370RBD glycan might be associated with reduced virulence, but chances of secondary mutations nevertheless, which may again restore the viral fitness. Such compensatory mutations would promote ACE2 binding and RBD opening.
In summary, viral replication in human hosts under antibody selective pressure will continue to cause further mutations and newer VOCs. Therefore, future strategies to tackle the ongoing pandemic must involve aggressive variant monitoring efforts, designing next-generation antibody-based therapeutics, updating mRNA- or DNA-based vaccines to rapidly adapt to new variants, and examining the consequences of further viral evolution prior to the emergence of the next highly antibody resistant strain.
Journal reference:
- Nabel, K. G., Clark, S. A., Shankar, S., et al. (2021), “Structural basis for continued antibody evasion by the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain”, Science, doi: 10.1126/science.abl6251, https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abl6251?utm_campaign=SciMag