M protein is the most abundant of all four SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins, with a crucial role in viral assembly. It organizes other SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins, namely spike (S), envelope (E), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins, and directs them to the sites of viral budding. Consequently, it is a target of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines, therapeutics, and anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies.
M protein also interferes with mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS)-mediated signaling and interferon (IFN) production to inhibit the host's innate immune responses. Yet little is known about its structure and the molecular basis of its functions, which is crucial for SARS-CoV-2 assembly, packaging, and pathogenesis.
Experimental studies have revealed homology between SARS-CoV-2 M and the accessory viroporin open reading frame (ORF)3a, indicating a shared ancestral origin. However, how these proteins serve distinct functional roles in the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle remains to be determined.
About the study
In the present study, researchers used lipid nanodiscs to determine the cryo-EM structure of the SARS-CoV-2 M protein. They used Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) cells with a cleavable C-terminal green fluorescent protein (GFP) tag to express full-length M and subsequently extracted it using gel filtration chromatography. For nanodisc formation, the researchers reconstituted the purified M protein into membrane scaffold protein 1E3D1 (MSP1E3D1) with a mixture of 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPE), 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-2-phosphoserine (POPS), 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC) lipids in a 2:1:1 mass ratio.
The final nanodisc formulation contained M, MSP1E3D1, and lipids in a 1:4:400 molar ratio and was used to determine the cryo-EM structure of the M protein. The researchers modeled 189 of 222 amino acids per subunit of M protein in the cryo-EM map de novo, wherein loops connecting transmembrane helices were the least well resolved. It is highly likely that the absence of stabilizing interactions between these and other M regions allowed M to adopt a range of conformations among the particles used to generate a cryo-EM map.
Lastly, the researchers performed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of the SARS-CoV-2 M protein. They used the GROMACS module to calculate the root mean square deviation (RMSD), values of which indicated the similarity between two superimposed atomic coordinates in the M protein. They also measured the root-mean-square-fluctuation (RMSF) per amino acid residue, which quantified amino acids in a protein that contributed the most to a specific molecular motion.
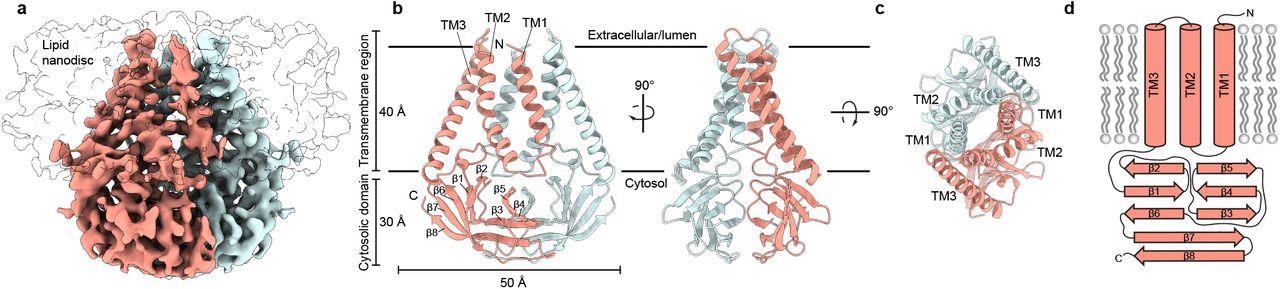
Structure of SARS-CoV-2 M in lipid nanodiscs. (a) 3.5 Å resolution cryo-EM map of SARS-CoV-2 M in MSP1E3D1 nanodiscs viewed from the membrane. One subunit is colored pink, and the second subunit is colored blue. Density corresponding to the lipid nanodisc is shown transparent. (b,c) Model of M viewed (b) from the membrane in two rotations and (c) from the extracellular or lumenal side. (d) Cartoon schematic of an M monomer with secondary structure elements indicated.
Study findings
The cryo-EM structure of SARS-CoV-2 M protein was a homodimeric fold, structurally homologous to the calcium cation (Ca2+)-permeable channel of SARS-CoV-2, ORF3a protein. Each subunit contained three transmembrane helices and a C-terminal beta-sandwich domain, with three patches of positive charge dominating its solvent-exposed surface.
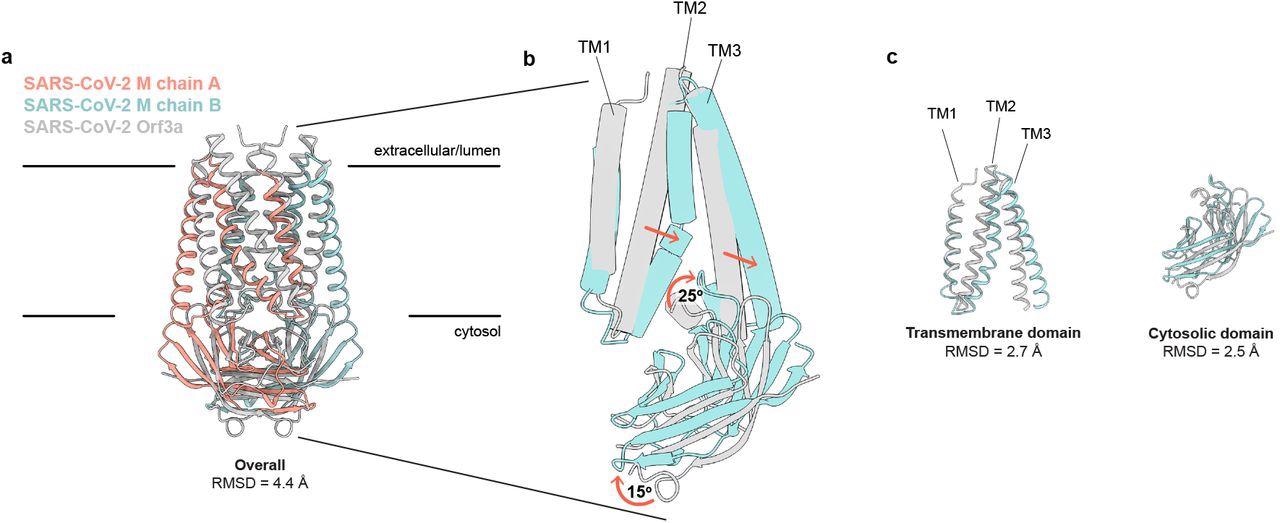
SARS-CoV-2 M and ORF3a proteins are structurally homologous. (a) Overlay of M and ORF3a structures. M is colored with one subunit pink and the second subunit blue and ORF3a is white. (b) Overlay of a single subunit indicating major conformational rearrangements. (c) Overlay of isolated transmembrane and cytosolic domains from each protein.
In addition, M protein was considerably wider and flatter than ORF3a due to its transmembrane helix packing and a rotation about the central axis of the cytosolic domain. Consequently, it showed a tighter dimer interface closer to the host cell membrane's outer leaflet and a tight subunit association. Furthermore, the gap between cytosolic domain subunits of M formed an enclosed pocket lined by polar residues. Conversely, the ORF3a had a loose subunit association that created a large open cavity that served as a conduction path, opening it to both the host cell membrane and cytoplasm.
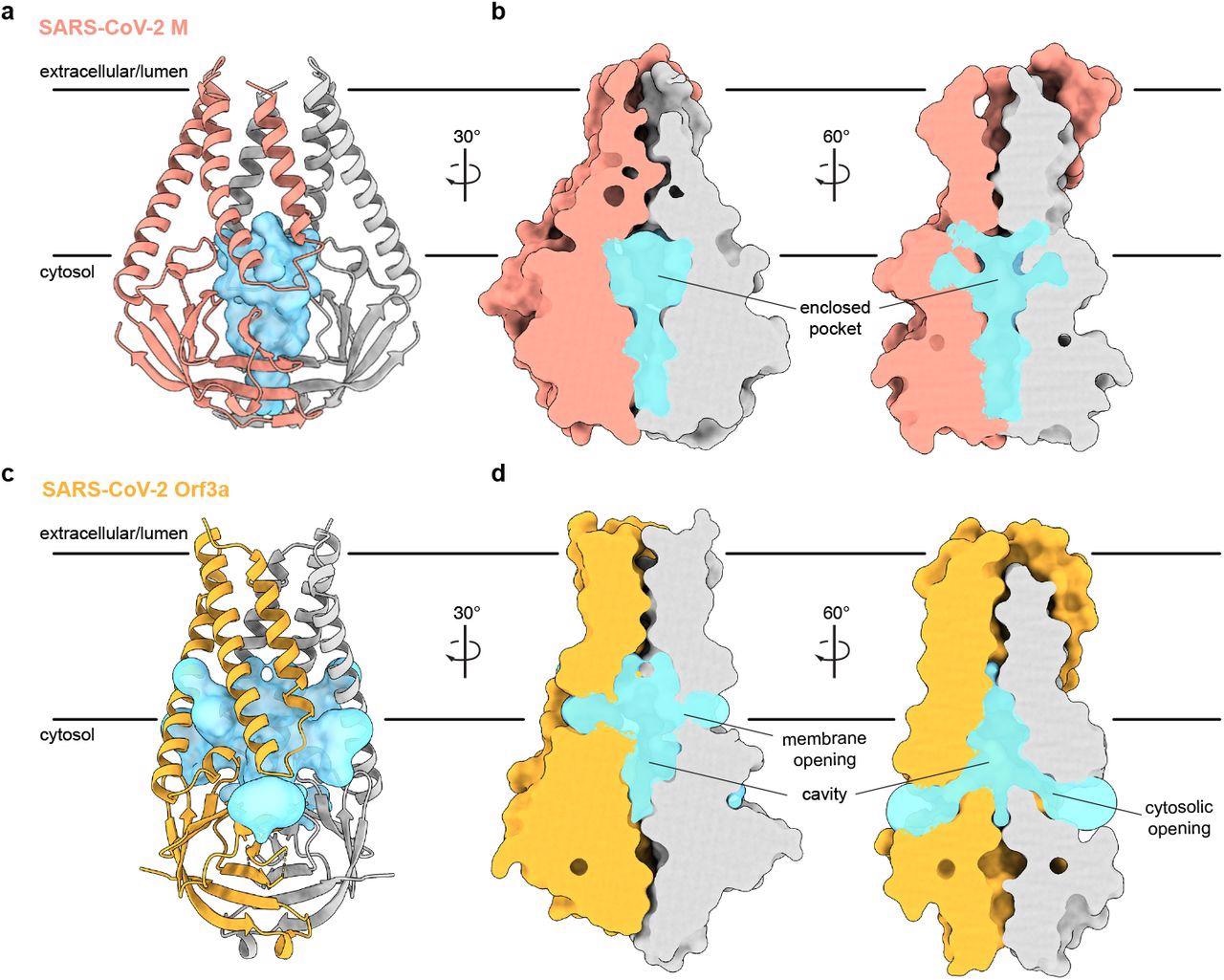
An enclosed polar pocket between cytosolic domains in M. (a) M shown as a cartoon and (b) surface with enclosed pocket volume calculated with CASTp36 shown as a blue surface. The enclosed pocket in M is formed between cytosolic domains and is sealed to the surrounding solution by protein. (c,d) Same as (a,b), but for SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a. The cavity in ORF3a begins closer to the lipid bilayer, extends approximately halfway across the membrane, and is open to surrounding solution and lipids through multiple openings
The MD simulations showed that the M homodimer was stable and not flexible to adopt large-scale conformational changes. Instead, M mediated morphological changes in host cell membranes through interactions with other SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins, negatively charged lipid headgroups, or viral ribonucleic acid (RNA).
For its interaction with the C-terminal domain of SARS-CoV-2 N protein, M used basic patches on the surface of its cytosolic domain. SARS-CoV-2 N and M proteins together facilitated virus-like particles (VLP) formation, where high concentrations of M C-terminal domains recruited and organized many N proteins that physically facilitated viral budding.
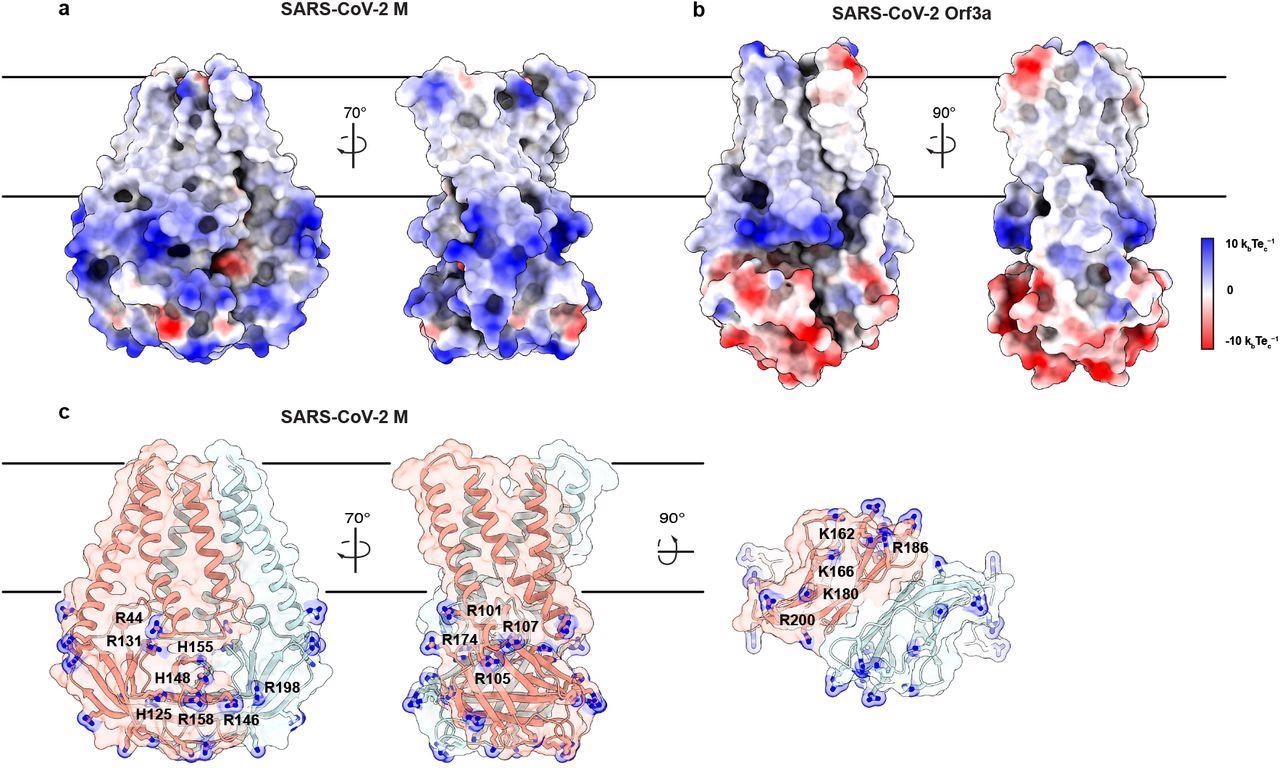
An electropositive cytosolic surface in M. (a,b) Views of the wide and narrow faces of (a) M and (b) ORF3a colored according to electrostatic surface potential from red (electronegative, −10 kbTec-1) to blue (electropositive, +10 kbTec-1). (c) Views of three electropositive surface patches on M cytosolic domains with basic residues labeled and shown as sticks with blue nitrogen atoms.
Conclusion
To summarize, SARS-CoV-2 has undergone many mutations over the past two years; however, its M protein sequence has remained unchanged. Its N-terminus, only 20 amino acids long, has remained the most immunogenic in COVID-19 patients. M also modulates the host's innate immunity to contribute to lung injuries common in severe COVID-19 cases. Indeed, it is a potential therapeutic target for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants in the future.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Structure of SARS-CoV-2 M protein in lipid nanodiscs, Kimberly A. Dolan, Mandira Dutta, David M Kern, Abhay Kotecha, Gregory A Voth, Stephen G Brohawn, bioRxiv pre-print 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.12.495841, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.06.12.495841v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Dolan, Kimberly A, Mandira Dutta, David M Kern, Abhay Kotecha, Gregory A Voth, and Stephen G Brohawn. 2022. “Structure of SARS-CoV-2 M Protein in Lipid Nanodiscs.” Edited by Owen Pornillos and Sara L Sawyer. ELife 11 (October): e81702. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.81702. https://elifesciences.org/articles/81702.