A new study reveals that less than an hour of training the brain could help strengthen the neural connections of the brain. This study could help develop new treatment and management strategies for progressive neurodegenerative disorders such as stroke and Parkinson’s believe the researchers.
The study from researchers at the D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR) revealed that this neurofeedback training could help re-establish the neural connections of the brain. The results of the study were published in the latest issue of the journal Neuroimage.
Theo Marins, a biomedical scientist from IDOR and main researcher of the study said, “We knew that the brain has an amazing ability to adapt itself, but we were not sure that we could observe these changes so quickly. Understanding of how we can impact on brain wiring and functioning is the key to treat neurological disorders.” This study was part of the PhD thesis work of Marins.
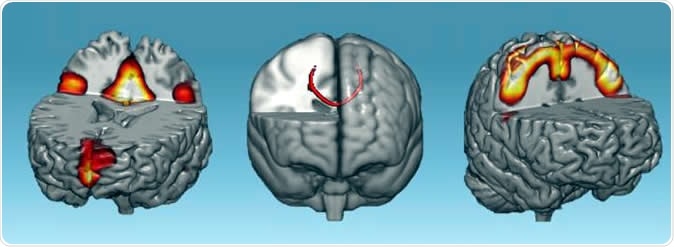
Neural networks that showed increases connectivity after one hour of neurofeedback: default-mode network (left), corpus callosum (middle) and sensorimotor networks (right). Image Credit: D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR)
The researchers explain that neurofeedback is a system by which dysfunctional regions of the brain could be regulated. These regions could be associated with chronic conditions such as pain and depression, they explain. For this method, magnetic resonance equipment is used. The equipment helps the user access their brain activity in real time and control it.
For this study the team recruited 36 healthy participants. They were provided with the neurofeedback training to increase the activity in the regions of the brain dealing with hand movements. While under the training, the participants were asked to imagine their hand movement in complete rest. Among the participants, 19 were given the actual neurofeedback training while the other 17 were given placebo neurofeedback. These 17 acted as control subjects.
The team of researchers within 30 minutes after the brain training, examined the neural networks of the of the brain by scans. They checked the structural and functional connectivity of the brain using scans. Results revealed that there was a marked increase in integrity of the neural network along the corpus callosum that connects the two hemispheres of the brain. This helped strengthening of the signals from the brain and the communications. The whole system, explain the researchers was made more robust due to the training. Where there was a dysfunctional network connection, the training seemed to improve the connections. In the control group these changes were not seen.
Fernanda Tovar Moll, president of IDOR and lead author of the study said, “We showed that the neurofeedback can be considered a powerful tool to induce brain changes at record speed. Now, our goal is to develop new studies to test whether patients with neurological disorders can also benefit from it.”
The researchers worked in collaboration with Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) and Augusto Motta University (Unisuam). More experiments and tests are being conducted to fully explain and understand the benefits offered by neurofeedback training say the researchers.