The humble house mouse has dramatically shaped parasitic Toxoplasma gondii populations in West Africa and around the world, according to research in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. As different strains affect their hosts differently, the research, led by Lokman Galal and Aurelien Mercier of INSERM and the University of Limoges, provides insights into which populations are infecting humans and animals and suggests mechanisms for their intercontinental spread.
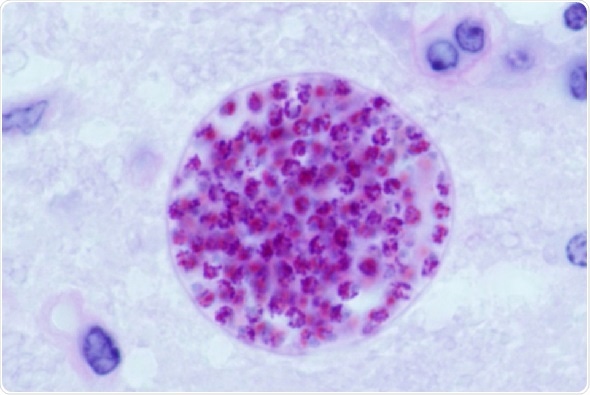
Microscopic cysts containing Toxoplasma gondii develop in the tissues of many vertebrates. Here, in mouse brain tissue, thousands of resting parasites (stained red) are enveloped by a thin parasite syst wall. Credit: Jitender P. Dubey, U.S Department of Agriculture, Public Domain (2013)
T. gondii is found all around the world, using mammals and birds as intermediate hosts with the ultimate aim of infecting cat populations. It is has particularly severe effects in immunocompromised individuals and understanding its spread, lineages and geographical distribution can offer a framework for further studies that will benefit patients.
Galal, Mercier, and their colleagues took samples from just over 2,000 infected chickens and ducks from two port cities — Dakar and Saint-Louis — and in the remote inland region of Kedougou in Senegal. Analyzing the samples, they found four main lineages of the parasite, one of which is described for the first time in their paper.
There were significant differences between the inland and coastal lineages and the researchers believe that human-mediated invasion of the house mouse has caused the decline of indigenous lineages and introduced European ones. Over time, these invasive strains have become more common than the local ones, with regular introductions of European rodents.
Lokman Galal says:
Analyzing Toxoplasma gondii samples from infected animals, we saw distinct differences between the remote inland region and the port cities that have been affected by maritime trade for hundreds of years. The invasive house mouse has a dramatic influence on the populations we see and is an important host for intercontinental migrations of the parasite. This mapping exercise suggests where epidemiological studies can identify the strains that cause the most burden.”
Source:
Journal reference:
Galal, L. et al. (2019) The introduction of new hosts with human trade shapes the extant distribution of Toxoplasma gondii lineages. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0007435.