The worm species that were examined in this study were Anisakis, or the herring worm, a nematode (roundworm) parasite that has been studied in many different places and times. The current paper assimilates the results of thousands of different papers to find out how the number of these worms has changed over time.
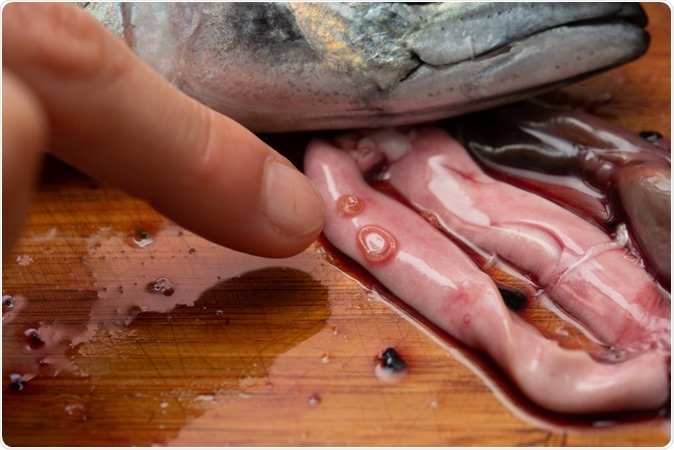

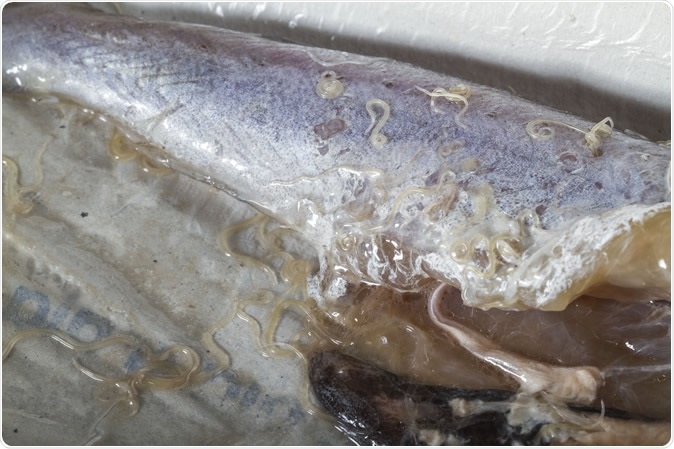
Anisakis infested the viscera of mackerel. Image Credit: Purino / Shutterstock
Herring worms are not confined to herrings, as their name suggests. Instead, they live on numerous varieties of sea fish and squids. When ingested live by humans, along with these fish, they are capable of burrowing through the wall of the gut to produce symptoms typical of food poisoning – nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The worm mostly dies in a few days, and the symptoms then vanish. This condition is called anisakiasis or anisakidosis. It is little known because of its transience, with most people merely putting down their symptoms to a bad case of food poisoning.
Anisakis worms in blue whiting fish. The prevalence of these worms, found in raw or undercooked fish, has increased dramatically since the 1970s. Image Credit: Gonzalo Jara / Shutterstock
Freezing or cooking the fish will kill any parasites that are present.
The herring worms hatched in the ocean first infect small shellfish like the bottom-dweller shrimp or copepods. These infected crustaceans are then preyed on by small fish who then acquire the infection. This chain of transmission continues.
When a human or sea-dwelling mammal eats an infected fish, the parasites transfer to the new host but are unable to survive beyond a few days in the human intestine. However, they can live much longer and reproduce themselves in the gut of a marine mammal. The worms, which may grow to about 2 cm long, are noticeable, and the infected fish can be quickly picked out at any stage of preparation by professional sushi chefs and others who process seafood for export, for instance. The staff eliminates the infected seafood before they are sold in grocery stores, sushi stalls, or seafood markets.
However, some worms do survive this stage. If consumers want to make sure they are not ingesting these parasites, experts advise that each piece be cut in half and inspected for worms before eating it.
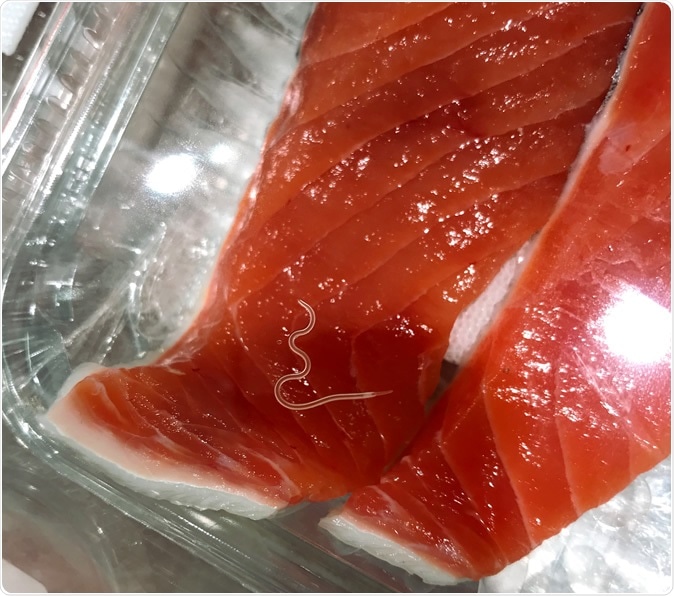

An Anisakis worm is seen in a filet of salmon. These parasitic worms can be up to 2 centimeters in length and are found in the flesh of raw and undercooked fish. Image Credit: Togabi/Wikimedia Commons
The study findings
The researchers performed a literature search online to find all papers in which the herring worm is mentioned, as well as the codworm, Pseudoterranova. They then culled the papers which did not fit their criteria. They finally analyzed those papers which mentioned the estimated numbers of each of these worm species at any given time.
They found that there was no change in the abundance of the cod worm, but the number of Anisakis in 2015 went up to reach 283 times the estimated number in 1978.
Implications
Notwithstanding the relatively minor ill-effects of eating these marine worms in humans, scientists point to the potential for disease in marine mammals – dolphins, seals, and whales. These allow the parasite to multiply after which they are released into the ocean with the feces of the host animal. Another potential concern is the effect of the presence of the parasites for years in the host, which could cause disease.
Wood says, "One of the important implications of this study is that now we know there is this massive, rising health risk to marine mammals. So, the increase in parasitic worms actually could be a good thing, a sign that the ecosystem is doing well. But, ironically, if one marine mammal population increases in response to protection and its Anisakis parasites profit from that increase, it could put other, more vulnearble marine mammal populations at risk of increased infection, and that could make it even more difficult for these endangered populations to recover."
Fisheries expert and researcher Chelsea Wood says, "This study harnesses the power of many studies. It's interesting because it shows how risks to both humans and marine mammals are changing over time. That's important to know from a public health standpoint, and for understanding what's going on with marine mammal populations that aren't thriving."
Journal reference:
Fiorenza, EA, Wendt, CA, Dobkowski, KA, et al. It’s a wormy world: Meta‐analysis reveals several decades of change in the global abundance of the parasitic nematodes Anisakis spp. and Pseudoterranova spp. in marine fishes and invertebrates. Glob Change Biol. 2020; 00: 1– 13. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15048