Traumatic stress can cause aggression by strengthening two brain pathways involved in emotion, according to research recently published in JNeurosci. Targeting those pathways via deep brain stimulation may stymie aggression associated with post-traumatic stress disorder.
The consequences of traumatic stress linger long after the stress ends. People suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder often display heightened aggression, caused by unknown changes in the amygdala. An almond-shaped structure nestled deep inside the brain, the amygdala plays an essential role in emotion, social behaviors, and aggression.
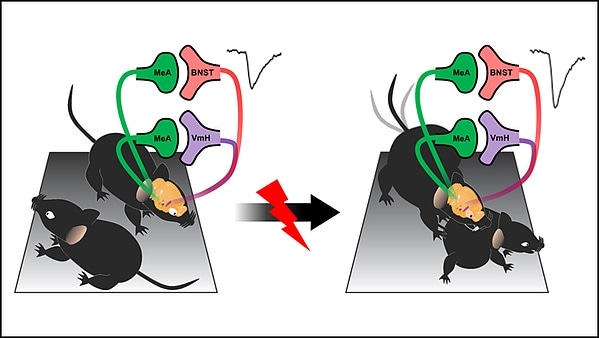
Nordman et al. examined how different amygdala circuits changed in male mice after traumatic stress. Two connections strengthened, resulting in more attacks on other mice: the circuitry connecting the amygdala to the ventromedial hypothalamus and the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. The former modulates the frequency of attacks, while the latter controls the length of attacks. The research team then used low frequencies of light to stop the pathways from strengthening, preventing an increase in aggressive behavior. Deep brain stimulation may elicit the same effect in humans.
Source:
Journal reference:
Nordman, J., et al. (2020) Potentiation of divergent medial amygdale pathways drives experience-dependent aggression escalation. J. Neurosci. doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0370-20.2020.