New research finds saliva testing has a high sensitivity for detecting severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients.
Current diagnostic testing relies on nasopharyngeal tests where they swab for viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 that cause respiratory infections. But collecting viral samples can be an uncomfortable experience, which may deter people from getting tested. There's also an exposure risk for healthcare workers performing the tests.
Andrew C. Nelson from the University of Minnesota and colleagues suggest a viable, alternative method to nasal swabbing is self-collected saliva testing. People collecting their own saliva samples would help with widespread testing efforts. It would also reduce the exposure risk healthcare workers take when performing these diagnostic tests.
The authors write:
"Understanding how anatomic site, the timing of collection in the disease course, handling and transport of the specimen, and analytical platform can influence test results is crucially important to making informed medical decisions regarding COVID-19 management…Overall, our findings support the conclusion that self-collected saliva testing is effective for COVID-19 detection, especially in early stages of disease progression."
The study "Saliva testing is accurate for early-stage and presymptomatic COVID-19" is available as a preprint on the medRxiv* server, while the article undergoes peer review.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Collecting test samples
The team looked for significant differences between patient-collected saliva samples and nasal swabs.
Thirty nasopharyngeal testing samples were collected from several cohorts in an inpatient and outpatient setting.
The first cohort consisted of 354 patients who underwent routine clinical testing for symptomatic or asymptomatic concerns of SARS-CoV-2. The cohort had approximately 80% of symptomatic cases. Thirty negative cases for SARS-CoV-2 were randomly taken for comparison purposes.
Cohort 1 was further divided into two groups based on how samples were evaluated. Cohort 1A consisted of outpatient testing used in hospitals, while Cohort 1B had their nasopharyngeal samples tested with commercial testing platforms.
In a second cohort, the researchers obtained nasal, nasopharyngeal, and saliva samples from hospitalized patients who tested positive for COVID-19. All samples were obtained 48 hours upon hospital admission.
The nasopharyngeal samples were collected by a healthcare professional, while saliva and anterior nasal samples were self-collected but under the researchers' supervision.
To monitor COVID-19 related symptoms, the researchers reviewed medical records to document instances of loss of taste or smell, shortness of breath, cough, sore throat, fatigue, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, appetite loss, chest pain, or signs of a headache.
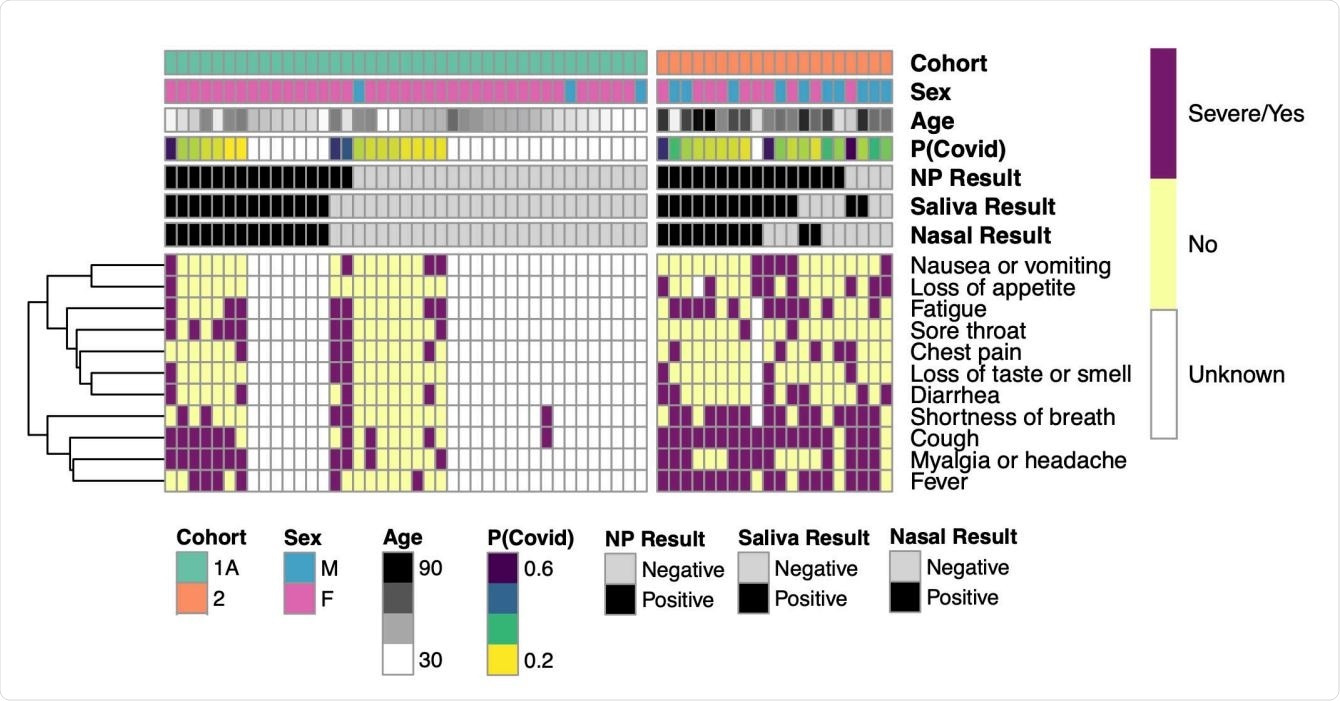
Symptom heat-map for agreement between positive and negative test results by test method and cohort. Heat map columns are participants and rows are symptoms. Symptom presence is indicated as either severe or yes (purple), no (yellow), or unknown (white). Symptoms are clustered by similarity and clustering is indicated by the dendrogram (left). Test results are indicated by color as either positive (black) or negative (light grey). Each participant’s calculated probability of COVID-19 (P(COVID)) is indicated with higher probabilities shown in purple and lower probabilities in yellow. Participant sex, age, and cohort are also indicated.
Variability between diagnostic testing
In Cohort 1A, the nasopharyngeal samples showed a total of 16 positive and 25 negative cases. Results from saliva and nasal samples were also 100% accurate in detecting these cases.
In Cohort 1B, the nasopharyngeal samples showed 14 positive and 5 negative cases. However, the commercial diagnostic tests evaluating nasal and saliva samples showed a lower sensitivity at 57.1% compared to nasopharyngeal clinical testing. There was also variability between nasal and saliva samples showing an 87.5% sensitivity and an 89.5% overall percent agreement.
Cohort 2 had the following positive COVID-19 cases: 16 detected by nasopharyngeal testing, 14 detected by saliva testing, and 11 by nasal samples. Throughout all diagnostic testing, there was a 69%-82% detecting sensitivity and a 65%-75% overall percent agreement.
The clinical sensitivity in Cohort 2 was highest with nasopharyngeal samples at 89%, while saliva testing was 78% sensitive. Of all three diagnostic tests, nasal samples performed the worst at 61%.
Saliva samples did identify two patients with COVID-19 who had received a false negative from nasopharyngeal testing the same day.
Cohort 2 had the most variability for viral load when researchers analyzed cycle threshold data points. They found ranges of viral load across all anatomic sites with values as low as 26.2 during later disease stages.
Saliva testing more sensitive during the early stages of the disease
After conducting a medical chart review, they calculated symptom onset and assigned P(COVID) scores based on a prior prediction model.
They found saliva testing was more sensitive than nasopharyngeal samples in detecting SARS-CoV-2 when symptom onset was still early. The results suggest "that saliva and nasal samples perform well in the population screening setting."
However, the researchers did note P(COVID) scores were more biased towards the symptom of loss of taste or smell, which was subjectively rated by the patient.

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Johnson AJ, et al. Saliva testing is accurate for early-stage and presymptomatic COVID-19. medRxiv, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.03.21252830, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.03.03.21252830v2
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Johnson, Abigail J., Shannon Zhou, Susan L. Hoops, Benjamin Hillmann, Matthew Schomaker, Robyn Kincaid, Jerry Daniel, et al. 2021. “Saliva Testing Is Accurate for Early-Stage and Presymptomatic COVID-19.” Edited by Heba H. Mostafa. Microbiology Spectrum 9 (1). https://doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.00086-21. https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/Spectrum.00086-21.