The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus, is a major global public health emergency. COVID-19 has a varied clinical spectrum with symptoms ranging from asymptomatic to severe illness characterized by fever and fatal pneumonia in people with comorbidities. To date, COVID-19 has impacted 67 million people worldwide with a global fatality rate of 3.67%. Although COVID-19 can affect anyone, people with underlying conditions such as diabetes are at greater risk of experiencing severe COVID-19 and related mortality than individuals without diabetes.
The prevalence of diabetes in Indonesia
Indonesia is one of the most populous countries in the world, and about 6.2% or 10.7 million of its population are people with diabetes. This makes Indonesia one of the countries with the highest number of diabetes patients in the world. According to 2016 WHO data, diabetes is one of the main causes of death in Indonesia, and diabetes management strategies in the country include dietary management, education, physical activity, and pharmacological treatment.
As a country with a large number of people with diabetes, the COVID-19 pandemic and the related social restriction policy implemented by the Indonesian government to reduce transmissions has affected diabetes management and increased the occurrence of complications related to diabetes.
A cross-sectional study on COVID-19-related difficulties in diabetes management and related morbidity in Indonesia
Researchers from the Fatmawati General Hospital, Indonesia, recently determined the difficulties in diabetes management and how it impacts diabetes morbidity in Indonesia during the COVID-19 pandemic. Their work has been published on the preprint server, medRxiv*.
This cross-sectional study used a national scale web survey and enrolled 1,124 people with diabetes who were 18 years or older. Hypoglycemia, diabetic foot ulcer, or hospital admission in diabetes patients in the study group were defined as diabetes-related complications. The team used a modified cox regression test to determine the correlation between difficulties in diabetes management and diabetes-related complications.
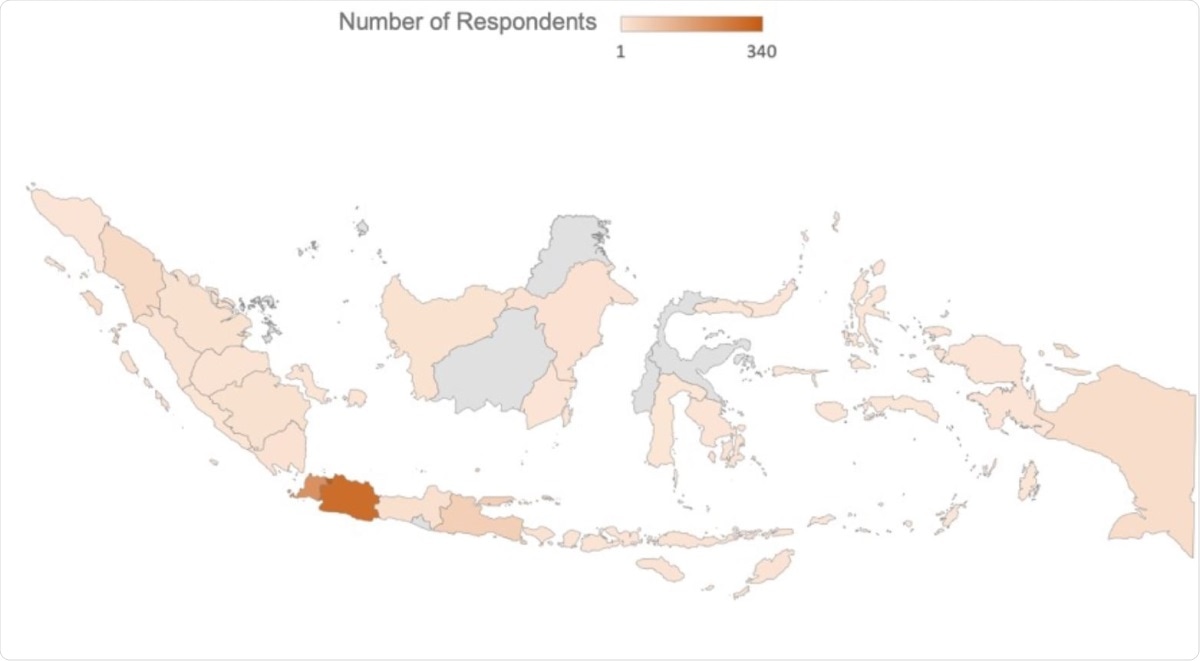
Distribution of Subjects According to Regions in Indonesia. Image Credit: original article figure / medRxiv

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
The majority of diabetes patients experienced disease management difficulties during the pandemic
The results of the study showed that 69.8% of people with diabetes patients in Indonesia experienced difficulties in diabetes management during the pandemic. Attending diabetes consultation (30.1%), access to diabetes medication (12.4%), blood sugar level monitoring (9.5%), diet control (23.8%), and regular exercise (36.5%) were the areas where major difficulties were experienced by the participants during the COVID-19 pandemic.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the majority of PWD experienced difficulties in managing their disease.”
Complications related to diabetes occurred in 24.6% of the study participants, and those who experienced diabetes management difficulties during the pandemic were 1.4 times more prone to have diabetes complications than those who did not have diabetes management difficulties.
Telemedicine and technology-based health education may help diabetes management during the pandemic
The findings show that the COVID-19 pandemic and the related social restrictions have had a significant impact on diabetes management and indirectly increased diabetes-related morbidity in Indonesia.
According to the authors, the findings of this study can be generalized to all people with diabetes in Indonesia and other countries with similar economies, demographics, and geographies as Indonesia. They hope that their research can offer crucial insights to clinicians and people with diabetes patients regarding the need to improve the use of telemedicine in the management of diabetes patients, which may offer a solution to surpass difficulties experienced by diabetes patients during the pandemic.
Utilizing technology to facilitate education on various aspects of diabetes management especially during the pandemic may offer a solution to improve health literacy in the society.”
The team also highlighted the need for better cooperation between health service providers and the government in offering telemedicine services for people with diabetes patients. They suggested that they should collaborate to formulate guidelines or standards for diabetes-related services during the pandemic. They think that improving health literacy using technology-based health promotion may also help reduce the incidence of diabetes-related complications during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Further research is certainly needed to assess the effectiveness and implementation of telemedicine in health services during the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia and how it will be sustainable in the future.”

 This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
This news article was a review of a preliminary scientific report that had not undergone peer-review at the time of publication. Since its initial publication, the scientific report has now been peer reviewed and accepted for publication in a Scientific Journal. Links to the preliminary and peer-reviewed reports are available in the Sources section at the bottom of this article. View Sources
Journal references:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Ida Ayu Kshanti, Marina Epriliawati, Md Ikhsan Mokoagow, Jerry Nasarudin, Nadya Magfira (2020) The Impact of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic on People with Diabetes in Indonesia: A Cross Sectional National Scale Web-Survey. medRxiv preprint server. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.01.20241588, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.01.20241588v1
- Peer reviewed and published scientific report.
Kshanti, Ida Ayu, Marina Epriliawati, Muhammad Ikhsan Mokoagow, Jerry Nasarudin, and Nadya Magfira. 2021. “The Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Diabetes Complication and Diabetes Management in People with Diabetes in Indonesia.” Journal of Primary Care & Community Health 12 (January): 215013272110448. https://doi.org/10.1177/21501327211044888. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/21501327211044888.