Researchers from the University of Granada warn that an accumulation of fatty tissue in the neck (both the double chin and the deeper deposits, located between muscles and around the cervical vertebrae) is a predictor of central and overall adiposity, cardiometabolic risk, and a pro-inflammatory profile in sedentary young adults.
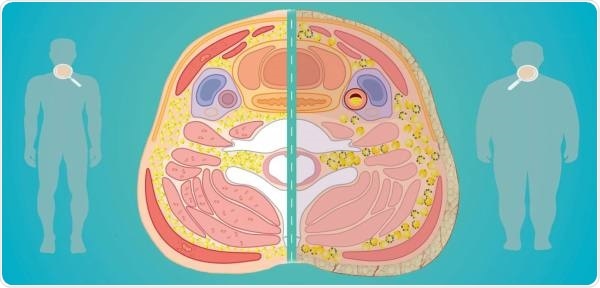
This simplified illustration demonstrates the researchers’ hypothesis about the morphological and cellular characteristics of the fat deposits in the neck, in a person of a normal weight who is relatively healthy vs. a person with obesity and associated comorbidities. This image is reproduced from the doctoral thesis published by Maria Jose Arias-Tellez on the Biomedicine programme of the University of Granada, entitled ‘Neck adipose tissue and neck circumference as predictors of cardiometabolic risk in sedentary adults’. Image Credit: University of Granada
A study conducted by researchers from the University of Granada (UGR) has revealed that an accumulation of fatty tissue in the neck is a predictor of central and overall adiposity, cardiometabolic risk (heart problems), and a pro-inflammatory profile in sedentary young adults.
Traditionally, the accumulation of visceral adipose tissue has been considered one of the factors most strongly related to cardiometabolic risk and chronic (low-grade) inflammation in humans. However, this well-established association has led researchers to neglect, to some degree, the study of other fatty deposits and their clinical/biological relevance.
Curiously, several studies have demonstrated that the accumulation of fat in the neck (both superficial deposits such as the double chin or jowls and the deeper deposits, located between the muscles and around the cervical vertebrae) increases in direct proportion to the weight or adiposity of the individual and that it follows specific accumulation patterns, according to gender."
María José Arias Téllez, Study Main Author and Researcher, University of Granada
In fact, a greater accumulation of fat in certain neck tissue compartments, particularly the deeper ones, is linked to a greater likelihood of cardiometabolic risk.
However, the evidence accumulated to date has been based on experiments performed on patients with benign/malignant tumors or other chronic conditions, and it remains to be seen whether it can be generalized to relatively healthy adults."
María José Arias Téllez, Researcher, UGR
The ACTIBATE project
The study carried out at the UGR is part of the ACTIBATE project (Activating Brown Adipose Tissue through Exercise--see http://profith.ugr.es/actibate). The project is financed by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness and the Health Research Fund of the Carlos III Health Institute (PI13/01393). The research was led by Jonatan Ruiz Ruiz and its results have been published in the International Journal of Obesity.
The study shows that the accumulation of fat in the neck--measured with computed tomography scanning--as well as its distribution in different compartments, is associated with greater overall and central adiposity, greater cardiometabolic risk, and a greater inflammatory status among healthy young adults, regardless of the amount of total and visceral fat. In addition, among the most relevant findings, it was observed that this accumulation of fat in the neck was as powerful a factor (in terms of direction and magnitude) as the accumulation of visceral fat in the prediction of cardiometabolic risk and inflammatory status, especially in men.
"Therefore, these results underline the need for further research in this new direction, to better understand the effect of fat accumulation in the upper part of the trunk (including the neck) and its clinical repercussions, especially in cardiometabolic risk and inflammation," explains Francisco Miguel Acosta Manzano, also among the main authors of the research.
"We still have much work to do. We need to investigate the adipose tissue of the neck in greater depth, to understand its pathogenic role in obesity and associated comorbidities, as well as its biological importance. Furthermore, we only have scant knowledge about the morphological or molecular characteristics of the adipocytes in these deposits, and here basic studies are required.
As we increase our knowledge of this deposit, we can also determine whether specific interventions (for example, physical exercise and/or restricted calorie intake) could help reduce the accumulation of fat in the neck (as well as total fat) and implement them clinically," explain Arias Téllez and Francisco Miguel Acosta Manzano, both PhDs students on the Biomedicine programme of the UGR's International School for Postgraduate Studies and members of the PROFITH-CTS977 Research group.
Source:
Journal reference:
Arias-Tellez, M. J., et al. (2020) Neck adipose tissue accumulation is associated with higher overall and central adiposity, a higher cardiometabolic risk, and a pro-inflammatory profile in young adults. International Journal of Obesity. doi.org/10.1038/s41366-020-00701-5.