Reflecting on fond memories goes a step beyond making you feel warm and fuzzy: nostalgia can reduce pain perception. Nostalgia decreases activity in pain-related brain areas and decreases subjective ratings of thermal pain, according to research recently published in JNeurosci.
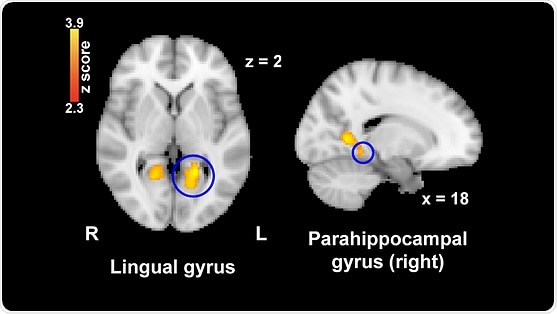
Image Credit: Society for Neuroscience
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences measured the brain activity of adults with fMRI while the participants rated the nostalgia levels of images and rated the pain of thermal stimuli. The nostalgic images featured scenes and items from an average childhood, like a popular candy, cartoon TV show, and schoolyard game. Images in the control condition depicted corresponding scenes and items from modern life. Viewing nostalgic images reduced pain ratings compared to viewing control images, with the strongest effect on low intensity pain.
Viewing nostalgic images also reduced activity in the left lingual gyrus and parahippocampal gyrus, two brain regions implicated in pain perception. Activity in the thalamus, a brain region involved in relaying information between the body and the cortex, was linked to both nostalgia and pain ratings; the thalamus may integrate nostalgia information and transmit it to pain pathways. Nostalgia may be a drug-free way to alleviate low levels of pain, like headaches or mild clinical pain.
Source:
Journal reference:
Zhang, M., et al. (2022) Thalamocortical mechanisms for nostalgia-induced analgesia. JNeurosci. doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2123-21.2022.