Recently, Stressmarq’s HSP70/HSC70, HSP90 and HSP110 antibodies were cited in a research publication in Cancer Cell journal by Pillarsetty et al. The researchers introduce a theranostic platform for precision medicine where properties of the protein networks are employed for cancer therapy. Scientists discover the genetic changes which are responsible for cancer growth to develop targeted therapies in precision medicine.
What is the Epichaperome?
It is widely known that the “chaperome” is a family of proteins which regulate cellular homeostasis. Chaperomes form a stable protein network known as “epichaperome” under cellular stress conditions, it is found only in cancer cells and it is crucial for tumor growth and survival. Chaperones of the Heat Shock proteins HSP90 and HSC70 play a key part in the epichaperome formation.
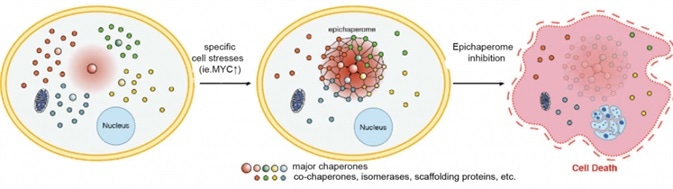
Schematic showing the re-wiring of the chaperome into the epichaperome network, following a specific cell stress. Inhibition of one of the epichaperome components dismantles the network. When the network is key to maintain viability in such cancer cell, epichaperome dismantling results in cell death. Image Credit: http://www.impactjournals.com/oncoscience/index.php?abs=321
PU-PET Assay for Epichaperome Analysis
The synthetic purine-scaffold inhibitor PU-H71, selective for the HSP90, which only works in tumors where an epichaperome has formed, was developed by researchers at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center.
In addition, they developed a radiolabeled [124I] PU-H71 inhibitor in order to examine the distribution and pharmacokinetic properties of PU-H71 in living subjects by utilizing PET (positron emission tomography) imaging. The PU-PET diagnostic assay is employed in order to detect and quantify the epichaperome positivity in solid tumors.
The radioactive probe binds to the HSP90 in the epichaperome and the location of the tumor that carries the epichaperome can be observed in the PET scan. The benefit of this technique is that the user can quantify in real-time how much of the drug gets to the tumor and the time it remains there.
![[124I]PU-H71 dissociates from epichaperomes much more slowly than it does from other HSP90 pools. This difference in the dissociation constant (koff ) provides this probe with epichaperome selectivity. The PU-PET assay is used to measure and visualize the epichaperome, its inhibitor engagement and collect pharmacometric data that can be used to optimize the dose and schedule selection.](https://www.news-medical.net/image-handler/picture/2020/1/paper-image.jpg)
[124I]PU-H71 dissociates from epichaperomes much more slowly than it does from other HSP90 pools. This difference in the dissociation constant (koff ) provides this probe with epichaperome selectivity. The PU-PET assay is used to measure and visualize the epichaperome, its inhibitor engagement and collect pharmacometric data that can be used to optimize the dose and schedule selection. Image Credit: https://www.cell.com/cancer-cell/fulltext/S1535-6108(19)30427-1
Moreover, it can supply real-time tumor pharmacometric data which can be utilized to establish the best schedule and drug dose for an individual. [124I]PU-H71 dissociates from epichaperomes a lot more slowly than it does from other HSP90 pools.
This probe is supplied with epichaperome selectivity by this difference in the dissociation constant (koff). The PU-PET assay is employed to measure and visualize the epichaperome, its inhibitor engagement and collect pharmacometric data which can be employed in order to optimize the schedule and dose selection.
The results which are outlined in this article present a paradigm for precision medicine and can be utilized for the development of other drugs and radioactive agents which also target the epichaperome.
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Christina Korgiopoulou from StressMarq Biosciences Inc.
About StressMarq Biosciences
Established in 2007, StressMarq Biosciences Inc. is a supplier of life science products that operates out of Victoria, Canada with a small, but dedicated group of scientists. Headed by our CEO and President Dr. Ariel Louwrier, StressMarq provides the research community with high-quality reagents backed with rigorous quality control data, expert scientific support, and fast international delivery.
“Discovery through partnership, Excellence through quality”
With over 7,000 products, our growth can be attributed to the continual production of cutting edge research products. Our diverse portfolio of primary antibodies, antibody conjugates, proteins, immunoassay kits and small molecules bridges across the life sciences, including products for cancer research, cardiovascular disease, cell signaling and neuroscience. To aid research worldwide, StressMarq has an extensive network of international distributors that allow us to supply reagents to over 50 countries.
In the years to come, StressMarq will continue to aid life science research by providing “Discovery through partnership, and Excellence through quality”.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.