Cancer immunotherapy has advanced significantly in recent years, dramatically improving patient prognosis and survival.
The majority of cancer immunotherapy research currently focuses on the first T cell activation (TCR) signal and the second signal (CD28), while the third-signal cytokines are understudied and not used clinically. Cytokines represented the first cancer immunotherapy.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the United States approved recombinant IFN-α for the treatment of hairy cell leukemia in 1986.
Cytokines are a group of small proteins (<30 kDa) produced and secreted by immune and non-immune cells — epidermal cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, etc. — that have a variety of biological functions.
Cytokines mediate autocrine and paracrine intercellular communication, regulating immune cell proliferation, differentiation, survival and effector functions. They are classified as interferons (IFNs), interleukins (ILs), colony-stimulating factors (CSTs), tumor necrosis factors (TNFs) and chemokines based on their functions.
Cytokine drugs
Several cytokines have been identified as anti-cancer drug candidates based on preclinical and clinical research due to their critical role in the immune response. Until now, the FDA has only approved two recombinant cytokine products for cancer immunotherapy: Intron A (interferon alfa-2b) and Proleukin (aldesleukin), respectively (Table1).
Table 1. FDA-approved Cytokine Drugs. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Cytokines |
Deliverables |
Brand Name |
Approval Date |
Indications |
| IFN-α |
Interferon alfa-2b |
Intron A |
06/04/1986 |
Hairy Cell Leukemia, Malignant Melanoma, Follicular Lymphoma, AIDS-Related Kaposi's Sarcoma |
| IL-2 |
aldesleukin |
Proleukin |
05/05/1992 |
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma, Metastatic Melanoma |
Intron A is approved for the treatment of malignant melanoma, hairy cell leukemia, follicular lymphoma and AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma,1 whereas Proleukin is approved for the treatment of metastatic melanoma and metastatic renal cell carcinoma.2
Many other cytokines are also being developed, with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), growth-stimulating factors (G-CSF, GM-CSF), IFN-γ and IL-2 being the most intensely studied cytokines in clinical trials (Figure 1).3
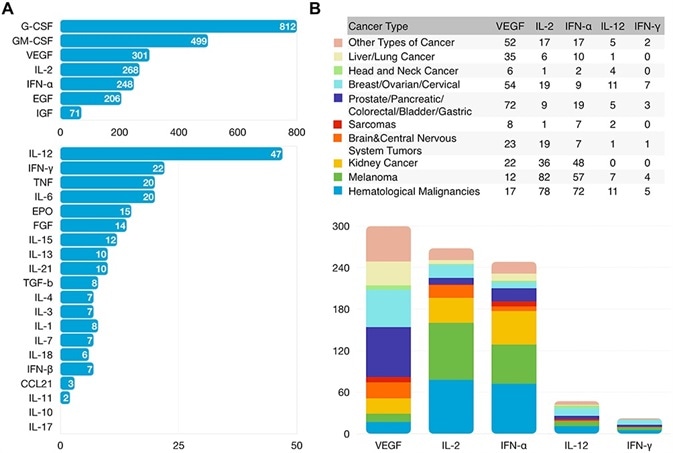
Figure 1. Clinical Research Status of Cytokines. Number of Cancer Clinical Trials Using Cytokine-based Drugs Treating All Cancer Types (A) or Each Cancer Type (B) Registered with ClinicalTrials.gov as of January 2021. Image Credit: doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S308578
These investigations require recombinant cytokine proteins and their highly pure and active receptors for various functional assays like cytotoxicity assay, control experiment of the cytokine drug candidates, and more.
Sino Biological offers a large selection of recombinant cytokines, including all cytokine families and their highly active and pure receptors, as well as multi-label receptors (Figure 2).
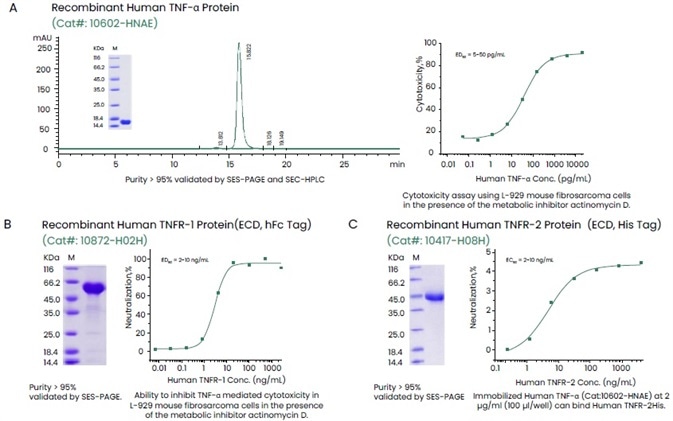
Figure 2. Examples of High-quality Recombinant TNF-α and Its Receptors TNFR-1 (hFc Tag) and TNFR-2 (His Tag). Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Cytokine limitations
Although some cytokines have been approved for cancer treatment as monotherapy, natural cytokines have limitations that need to be addressed further, such as their pleiotropic nature and short serum half-life.
The pleiotropic nature of cytokines represents an ability to affect different cell types, leading to varied or even opposing biological effects.
As cytokines have a short serum half-life, they must be administered in large doses to achieve therapeutic efficacy. These limitations are responsible for the drug’s low antitumor efficacy and adverse side effects.
High IFN-α doses, for instance, cause a severe flu-like syndrome with fatigue, fever, headaches, myalgias and gastrointestinal symptoms as a side effect.4 A common side effect is a decrease in white blood cells, platelets and neutrophils.
Furthermore, neuropsychiatric disorders are a serious possibility. Another example is treatment with IL-2, where high doses can result in increased vascular permeability, which can lead to vascular leak syndrome and even death.5
Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA)-based assays can be used to detect cytokines, determine drug half-lives, and track changes in various cytokines in drug-induced immune responses.
Sino Biological has created a number of ELISA kits that can be used to detect cytokines quantitatively with high sensitivity and specificity (Figure 3).
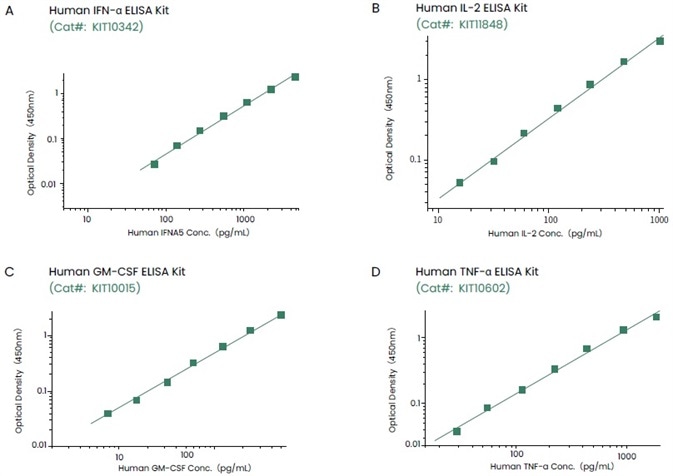
Figure 3. ELISA kits developed by Sino Biological can recognize target cytokines with high sensitivity and specificity. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
New strategies
Multiple strategies for developing new cytokine-based immunotherapies are emerging as cancer immunotherapy and biotechnology advance.
Extending the half-life is the first strategy. Chemical cytokine modification can extend the half-life and improve the pharmacokinetics of the cytokine.
Protein conjugation with polyethylene glycol (PEG), also known as PEGylation, and antibody-cytokine fusion proteins are the most common types.
NKTR-214 (bempegaldesleukin), for instance, is a PEGlyated IL-2 that contains IL-2 as well as multiple covalently linked but releasable PEG chains.6
It activates CD8+ T cells and NK cells by binding to NK cells and IL-2Rβγ (IL-2 receptor) on CD8+ T cells rather than to IL-2Rαβγ on Treg cells. By limiting immediate T cell activation in the peripheral blood, IL-2 PEGylation effectively extends IL-2 half-life (to approximately 20 hours) and reduces systemic toxicity.
Phase I/II clinical trial data revealed that as monotherapy, NKTR-214 had better antitumor effects and greatly reduced tumor size in patients with renal cell carcinoma or metastatic melanoma.7
Enhancing cytokine specificity is the second strategy. Cytokines are modified using mutagenesis techniques to improve their antitumor responses by changing the affinity and specificity for their receptors.
For example, IL-18, a pro-inflammatory factor from the IL-1 family, can attach to the IL-18R receptor on the surface of NK cells and T cells to improve their immune function. Recombinant IL-18 was once used in cancer immunotherapy because of its immune-activating properties.
But it failed to display efficacy in phase II clinical trials8 as IL-18 can induce expression of IL-18BP — an IL-18 decoy receptor and its natural inhibitor — on cancer cells. IL-18BP attaches to IL-18 with greater affinity and inhibits IL-18 from binding to IL-18R, thus preventing the immune-activating function of IL-18.
To address this problem, researchers used directed evolution with yeast surface display to develop a “decoy-resistant” IL-18 variant, DR-18, attaching only to IL-18R but not to IL-18BP.9
DR-18 displayed therapeutic effects comparable to anti-PD-1 in different animal tumor models. It can be combined along with anti-PD-1 to produce a synergistic effect. Eventually, DR-18 will be tested in clinical trials.
Combination drugs is another strategy. To achieve optimal efficacy, therapeutic cytokines are combined with other anti-cancer therapies such as CAR-T cells or monoclonal antibodies. A number of clinical trials involving combination drugs are currently underway.10
For instance, NKTR-214 is evaluated in phase II and III trials along with PD-1 inhibition (NCT03138889 and NCT03635983) or dual CTLA4 and PD-1 inhibition (NCT02983045).
For patients with non-small cell lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma or melanoma, PEGylated IL-10 has also been studied in combination with pembrolizumab or nivolumab.
Conclusion
Recombinant cytokines show great promise for cancer immunotherapy. Despite the fact that only a few drugs have been approved, numerous novel cytokines developed using various strategies have entered clinical trials and fulfilled project milestones.
Sino Biological has developed a series of cytokine-related research reagents, including antibodies, recombinant cytokines and their receptors, genes, ELISA kits, and so on, to support cytokine studies, based on its well-established recombinant protein and antibody technology platform.
Reagents for cytokine therapy research
Recombinant cytokines and their receptors
- High bioactivity
- HPLC-verified purity
- Covering all cytokine families
- Low-endotoxin
- Over 12 species
- Batch-to-batch consistency
Antibodies
- Validated with various methods and cell lysates
- Multiple applications for FCM, WB, IHC, ICC, IP, etc.
- High stability
- Verified specificity
- High sensitivity
- High affinity
ELISA kits
- Ready-to-use
- High sensitivity
- High precision and reproducibility
- High specificity
- Quality antibodies and reagents
- 90% of the kits are McAb-McAb matching
References
- PRODUCT INFORMATION INTRON A (Interferon alfa-2b). www.fda.gov, accessed January 21, 2022. Reference ID: 4160510
- PRODUCT INFORMATION PROLEUKIN (aldesleukin). www.fda.gov, accessed January 21, 2022. Reference ID: 3165255
- Qiu Y, Su M, Liu L, Tang Y, Pan Y, Sun J. Clinical Application of Cytokines in Cancer Immunotherapy. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:2269-2287. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S308578
- Waldmann TA. Cytokines in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018;10(12):a028472. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a028472
- Dutcher JP, Schwartzentruber DJ, Kaufman HL, et al. High dose interleukin-2 (Aldesleukin) - expert consensus on best management practices-2014. J Immunother Cancer. 2014;2(1):26. doi:10.1186/s40425-014-0026-0
- Doberstein SK. Bempegaldesleukin (NKTR-214): a CD-122-biased IL-2 receptor agonist for cancer immunotherapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019;19(12):1223-1228. doi:10.1080/14712598.2019.1685489
- Bentebibel SE, Hurwitz ME, Bernatchez C, et al. A First-in-Human Study and Biomarker Analysis of NKTR-214, a Novel IL2Rβγ-Biased Cytokine, in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2019;9(6):711-721. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1495
- Tarhini AA, Millward M, Mainwaring P, et al. A phase 2, randomized study of SB-485232, rhIL-18, in patients with previously untreated metastatic melanoma. Cancer. 2009; 115(4): 859-868. doi:10.1002/cncr.24100
- Zhou T, Damsky W, Weizman OE, et al. IL-18BP is a secreted immune checkpoint and barrier to IL-18 immunotherapy. Nature. 2020;583(7817):609-614. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2422-6
- Propper DJ, Balkwill FR. Harnessing cytokines and chemokines for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;10.1038/s41571-021-00588-9. doi:10.1038/s41571-021-00588-9
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.