An absence of fucose residues on the antibody immunoglobulin γ (IgG) constant (Fc) region N-glycan moiety has been shown to increase the binding affinity to IgG-Fc-receptor (FcγR) IIIa. Since this receptor is present in immune effector cells such as natural killer cells, it causes an increase in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).
Sino Biological has developed a proprietary “FucoFree” eukaryotic cell culture technology for the custom expression of afucosylated mAbs. The company offers >95% purity, high throughput, high yield, and low endotoxin (<1 EU/mg) antibody expression.
How do antibodies eliminate the antigens?
Targets are destroyed by immune cells recruited by antibodies that selectively bind to their antigen. IgG antibodies mediate inflammation and immunity through their effector functions. The Fc region of the IgG antibody mediates interactions between complement proteins and FcγR on myeloid and Natural Killer (NK) cells.
The target cells are then destroyed by the NK cells using antigens presented on the membrane's surface in a process known as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).1 This is one of the main Fc-dependent effector functions of IgG. NK-cell-mediated ADCC is primarily triggered by IgG-subclasses IgG1 and IgG3 through the FcγRIIIa.
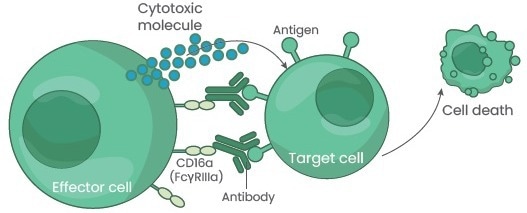
Figure 1. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
For several cancer types, targeted monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy is a viable therapeutic option. Most mAbs that are authorized for use in oncology treatments cause ADCC. Patients with metastatic breast cancer who were given a taxane and trastuzumab responded better as FcgRIIIa antibody binding increased.2
Designing and engineering the Fc region on antibodies, such as by afucosylation, is one technique to enhance the binding.
Numerous physiological and pathological processes, such as infection, cancer, and inflammation, are dependent on the enzyme fucosyltransferase (FUT), which controls the fucosylation of O- and N-glycans.
In general, about 90% of the N-glycans on the Fc part of human IgG are fucosylated. Monoclonal antibodies with little to no fucosylation enhance FcγIIIa binding. Due to its superior efficacy in clinical trials, obinutuzumab, an afucosylated anti-CD20 antibody, has been approved to treat patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.3
How can the fucosylation on Fc be lowered?
The elimination of the fucose residues was initially achieved through a combination of enzymatic and chemical treatment of the mAb, which was a laborious and expensive process. The core fucose residues were added by a gene called α1,6-fucosyltransferase (FUT8).4
T+his gene catalyzes the transfer of fucose from GDP-fucose to N-linked type complex glycopeptides (Figure 2). FUT8 is a crucial enzyme in the fucosylation of the N-glycan core. Due to improvements in gene-editing techniques, it is now possible to make endogenous FUT8 knockout cell lines that produce fucose-free antibodies.
Humanized IgG1 antibodies produced by FucoFree CHO cells demonstrated a 50-fold improvement in binding affinity to human FcgRIIIa compared to those made by wild-type CHO cells.5
FucoFree expression system
Sino Biological has created a proprietary “FucoFree” eukaryotic cell culture system using gene-editing techniques in light of the significance and impact of glycan engineering modification of mAbs for therapeutic use.
In-depth genetic and protein testing on these FucoFree cell lines has confirmed the complete knockout of the FUT8 gene and the absence of fucose residues in the antibody glycan chain.
A FUT8 knockout (FUT-/-) CHO cell line and a FUT-/- HEK293 cell line, each specifically developed to meet the needs of various projects and scale of production, are host cells in the FucoFree system.
Sino Biological will deliver the afucosylated mAbs with its glycan profiling service, starting with the amino acid sequences of the antibodies provided by its customers (Figure 3B).
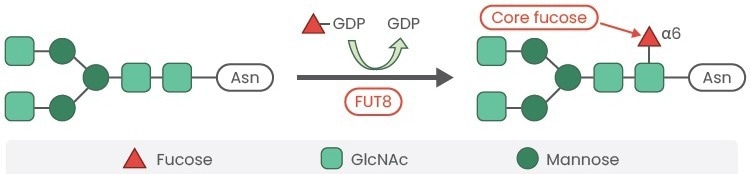
Figure 2. Fucosyltransferase-8 (FUT8) catalyzes the transfer of fucose from GDP-fucose to N-linked type complex glycopeptides. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
High-yield, high-throughput antibody expression services from Sino Biological are provided, with >95% purity and >98% monomer distribution (Figure 3A). Furthermore, the company can evaluate its ADCC reaction and carry out an enhanced ADCC mAb candidate screening.
The production scale can range from milligram to gram level. The HTP services now incorporate afucosylated mAb expression, resulting in a quicker turnaround time and lower prices. Furthermore, a cell line with a high level of afucosylated mAb expression can also be created.
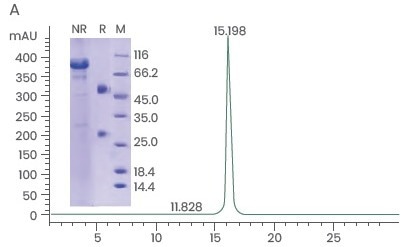
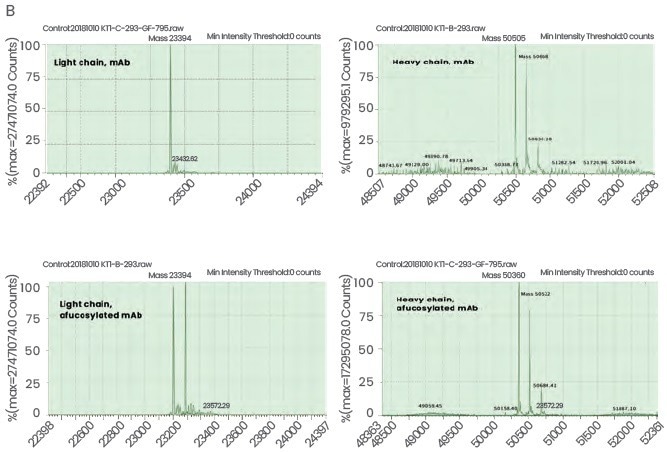
Figure 3. High-quality Antibodies Produced in “FucoFree” Cell Lines. (A) Recombinant antibody demonstrating >95% purity and >98% monomer distribution. (B) LC-MS analysis of a mAb expressed in a conventional (two top panels in B) and the corresponding “FucoFree” (two bottom panels in B) cell line. A difference in the heavy chain molecular weight of 145 Da was observed, corresponding well with the MW of a fucose residue. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Currently, at least 35 glycoengineered antibodies that have had their Fc fucose partially or completely removed have been tested in animal models or clinical trials.
Sino Biological anticipates that its expertise with the expression of afucosylated mAb will benefit the research and development community and pave the way for more afucosylated mAb to enter clinical trials and subsequently be approved for use in humans.
References
- de Taeye SW, et al. (2020) FcγR Binding and ADCC Activity of Human IgG Allotypes. Front. Immunol. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.00740
- Musolino A, et al. (2008) Immunoglobulin G fragment C receptor polymorphisms and clinical efficacy of trastuzumab-based therapy in patients with HER-2/neu-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
- Mossner E, et al. (2010) Increasing the efficacy of CD20 antibody therapy through the engineering of a new type II anti-CD20 antibody with enhanced direct and immune effector cell-mediated B-cell cytotoxicity. Blood
- Costache M, et al. (1997). Evolution of fucosyltransferase genes in vertebrates. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.47.29721.
- Shields RL, et al. (2002) Lack of fucose on human IgG1 N-linked oligosaccharide improves binding to human Fcgamma RIII and antibody-dependent cellular toxicity. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202069200.
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.