Sponsored Content by AbcamJan 24 2018
Introduction
Unique sets of cytoskeletal proteins, transcription factors, receptors, and enzymes are expressed by glia and neurons. Abcam’s user-friendly guides help in selecting the best neural subtype markers.
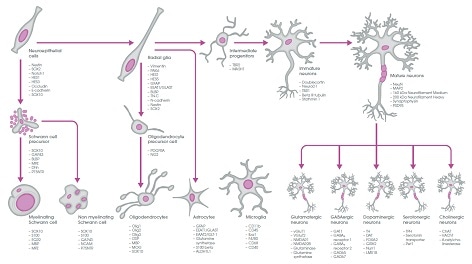
Overview of neural markers
|
Cell type
|
Markers
|
|
Neuroepithelial cells
|
Nestin, SOX2, notch1, HES1, HES3, E-cadherin, occludin.
|
|
Radial glia
|
Vimentin, nestin, PAX6, HES1, HES5, GFAP, GLAST, BLBP, TN-C, N-cadherin, SOX2.
|
|
Intermediate progenitors
|
TBR2, MASH1/Ascl1.
|
|
Immature neurons
|
Doublecortin, beta III tubulin, NeuroD1, TBR1, stathmin 1.
|
|
Oligodendroycte precursor cells
|
PDGF receptor alpha, NG2
|
|
Mature oligodendrocytes
|
Olig 1, olig 2, olig 3, MBP, OSP, MOG, SOX10.
|
|
Schwann cells
|
MPZ, NCAM, GAP43, S100
|
|
Astrocytes
|
GFAP, EAAT1/GLAST, EAAT2/GLT-1, glutamine synthetase, S100-beta, ALDH1L1.
|
|
Microglia
|
CD11b, CD45, Iba1, F4/80, CD68, CD40
|
|
Mature neurons
|
NeuN, MAP2, 160 kDa neurofilament medium, 200kDa neurofilament heavy, synaptophysin, PSD95.
|
|
Glutamatergic neurons
|
vGluT1, vGl,uT2, NMDAR1, NMDAR2B, glutaminase, glutamine synthetase
|
|
GABAergic neurons
|
GABA transporter 1, GABAB receptor 1, GABAB receptor 2, GAD65, GAD67.
|
|
Dopaminergic neurons
|
Tyrosine hydroxylase, dopamine transporter, FOXA2, GIRK2, Nurr1, LMX1B
|
|
Serotonergic neurons
|
Tryptophan hydroxylase, serotonin transporter, Pet1.
|
|
Cholinergic neurons
|
Choline acetyltransferase, vesicular acetylcholine transporter, acetylcholinesterase
|

About Abcam
Abcam is a global life sciences company providing highly validated antibodies and other binders and assays to the research and clinical communities to help advance the understanding of biology and causes of disease.
Abcam’s mission is to serve life scientists to help them achieve their mission faster by listening to their needs, continuously innovating and improving and by giving them the tools, data and experience they want. Abcam’s ambition is to become the most influential life science company for researchers worldwide.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.