Sponsored Content by AbcamFeb 25 2019
A review of TUNEL staining kits and an overview of the processes involved in TUNEL staining.
‘TUNEL’ stands for Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling. Otherwise known as the TUNEL assay, TUNEL staining is used to detect DNA breaks formed during the final phase of apoptosis, when DNA fragmentation takes place.
Principles of TUNEL Staining
Terminal deoxynucleotide transferase (TdT) is an enzyme that is expressed in certain immune cells. As it attaches deoxynucleotides to the 3’-hydroxyl terminus of DNA breaks, TdT is pivotal to the TUNEL staining method. TdT acts during the process which generates antibody diversity – V(D)J recombination – and the nucleotides attached by it are tagged in TUNEL staining.
This tagging is either done directly, using a fluorescent label, or indirectly, using a chemical label that can be linked to a fluorescent label or enzyme. The TUNEL staining method offers a contemporary alternative to the traditional method of using agarose gel electrophoresis to analyze the formation of DNA fragments during apoptosis, as seen in Apoptotic DNA Ladder Isolation Kit ab65627.
Different Methods for TUNEL Staining
Light microscopy is the most frequently used method for analyzing TUNEL staining. Fluorescent TUNEL methods can also be used for analysis by flow cytometry.
The most commonly used methods for TUNEL staining use:
- A nucleotide which is directly conjugated to a fluorescent dye (most often FITC) - For example, FITC TUNEL assay kit ab66108
- A biotin-tagged nucleotide which is subsequently bound by streptavidin-HRP. It is then detected using a chromogenic HRP substrate (for instance, DAB) in order to produce a brown color - For example, HRP/DAB TUNEL assay kit ab206386
- A bromo-, digoxygenin-, or FITC-tagged nucleotide. This is subsequently bound by an antibody which is specific to that tag. This antibody is labeled, either using a fluorescent dye or an enzyme such as HRP for chromogenic detection - For example, BrdU-Red TUNEL assay kit ab66110.
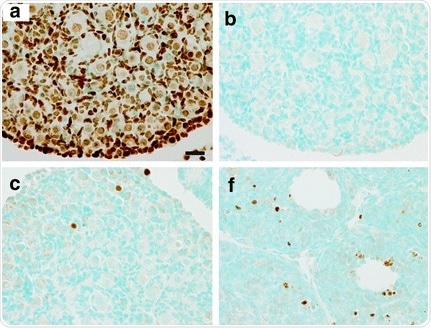
Gao Y et al. used HRP/DAB TUNEL assay kit ab206386 to analyze tissue sections from mouse ovaries. a. Section treated with DNase I as positive control. b. Negative control without TdT enzyme. c and f. representative experimental images. Nuclei stained with the TUNEL assay are brown. Sections were counter-stained with Methyl Green.
Advantages and Disadvantages of TUNEL Staining Methods
Indirect methods which make use of an antibody or a streptavidin-biotin complex are not as fast as TUNEL staining protocols which use a nucleotide directly tagged with a fluorescent dye. This is because TUNEL staining protocols require fewer staining steps.
However, methods relying on biotin-tagged nucleotides may benefit as the streptavidin-biotin complex is amplified. Although additional blocking steps are required, both to reduce background staining and neutralize endogenous biotin, these steps are well known to all researchers running traditional chromogenic immunohistochemistry.
A brighter signal may also be produced by BrdU-based methods, as BrdU is usually incorporated more easily by the TdT enzyme.
The Relative Popularity of TUNEL Staining Methods
A survey of 50 research papers published in 2017 which contained the terms “TUNEL Assay” or “TUNEL Staining”, revealed that:
- 50% of these papers utilized dUTP directly conjugated to FITC
- 15% used FITC-dUTP and an anti-FITC antibody conjugated to HRP
- 15% used biotin-dUTP and streptavidin-HRP
- 12% used digoxygenin-dUTP, as well as an anti-digoxygenin antibody conjugated either to a fluorescent dye or HRP
- 8% used Br-dUTP, as well as an anti-BrdU antibody conjugated to a fluorescent dye
Every paper surveyed utilized the TUNEL assay in imaging as opposed to flow cytometry. DAB substrate was added where HRP was utilized in order to create a brown stain. A kit was used for TUNEL staining in over 90% of these research papers.
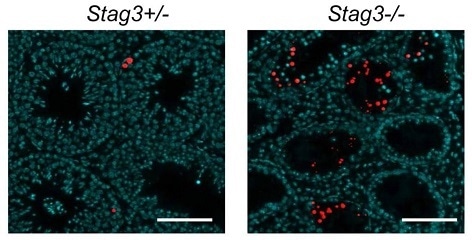
Hopkins J et al used BrdU-Red TUNEL Assay Kit ab66110 to examine apoptosis in testis from 8-week old Stag3+/− and Stag3−/− mice. Apoptotic cells are red. DAPI was used as a counterstain.
To conclude, a practical technique for analyzing DNA fragmentation in apoptosis is provided by TUNEL staining.
References
- Gao Y et al. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology 15:94 (2017)
- Hopkins J et al. Plos Genetics 10(7)e1004413 (2014)
 About Abcam
About Abcam
Abcam is a global life sciences company providing highly validated antibodies and other binders and assays to the research and clinical communities to help advance the understanding of biology and causes of disease.
Abcam’s mission is to serve life scientists to help them achieve their mission faster by listening to their needs, continuously innovating and improving and by giving them the tools, data and experience they want. Abcam’s ambition is to become the most influential life science company for researchers worldwide.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.