
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a severe neurological condition. It was first proposed by the German doctor Alois Alzheimer in 1911 and was officially called Kraeplin. Memory loss, mental decline, and impaired motor balance are the most common clinical signs of Alzheimer’s disease.
As an age-related condition, the rise in the older population also drives the demand for Alzheimer’s treatment drugs. According to the World Alzheimer Report, there will be 131 million Alzheimer’s individuals worldwide by 2050.
The pathological alterations in Alzheimer’s disease are complicated and varied. Neuronal loss, synaptic problems (such as synaptic loss and protrusion plasticity deficits), extracellular amyloid-beta (βA) deposition to form amyloid plaques, and improperly phosphorylated Tau protein to produce intracellular neurofibrillary tangles are all frequent in Alzheimer’s disease.
The reasons for various pathological changes cannot be explained at present, and the pathogenesis is still unclear. There are three classic hypotheses on the pathogenesis of AD.
Aβ cascade hypothesis
In the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, the Aβ cascade hypothesis is the most popular theory. One of the key pathogenic features of AD is the accumulation of Aβ to create amyloid plaque. Secretase degradation produces Aβ from amyloid precursor protein (APP). The secretases α-secretase, β-secretase (BACE), and γ-secretase are involved in two routes for APP degradation.
In the amyloid pathway, BCAE cleaves APP to produce sAPPβ protein, which is then cleaved by γ-secretase to produce Aβ polypeptides, such as Aβ1-42, Aβ1-40, and released into the extracellular domain, where they eventually aggregate to form amyloid plaques, leading to the development of AD.
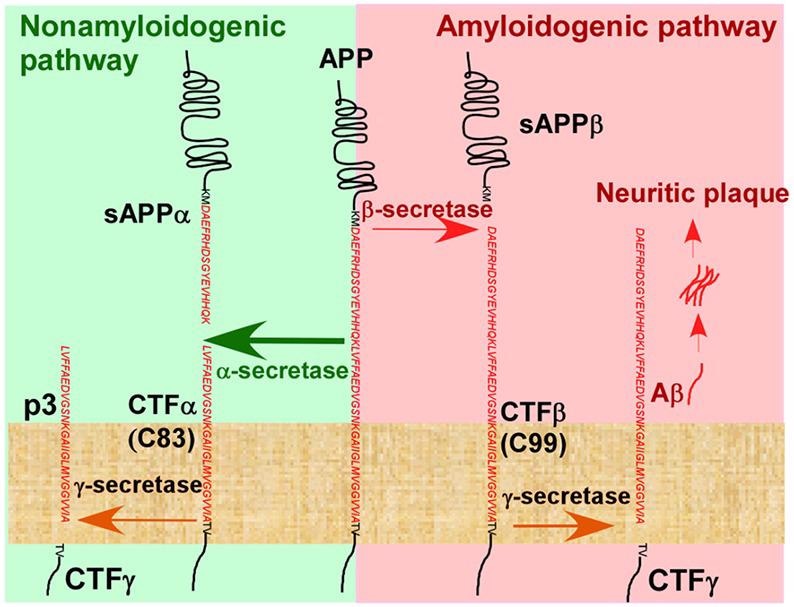
Hydrolysis pathway of APP in vivo. Image from reference
Binding to soluble, toxic aggregates of Aβ selectively to neutralize and eliminate it is thought to help alleviate neurodegenerative processes in AD. Various drugs have been developed based on this hypothesis. Aducanumab is a representative drug targeting APP, a monoclonal antibody of Biogen, and was approved on June 7th, 2021, for marketing by the FDA.
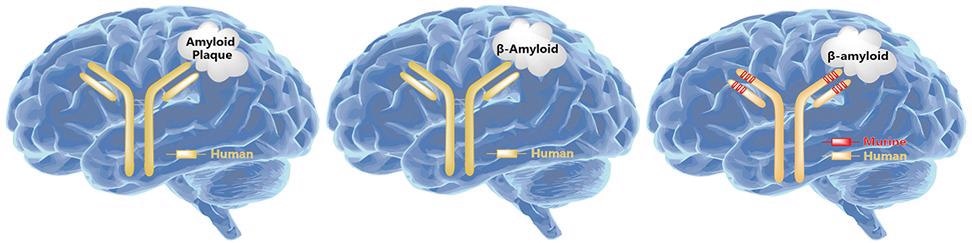
Schematic diagram of monoclonal antibodies targeting APP. Image from reference
Furthermore, Lilly’s Donanemab and Roche’s Gantenerumab are now in clinical phase III, while Eisai and Biogen’s Lecanemab is in the FDA’s rapid application stage, based on the similar mechanism of action and target. Fierce Pharma listed the most anticipated new medication releases for 2022 on February 7th, 2022, with Donanemab and Ganteneruma coming in first and third place.
Abnormal phosphorylation of tau protein
Another prominent pathogenic characteristic of Alzheimer’s patients is neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). Excessive or abnormal phosphorylation of intracellular Tau protein causes it to lose its biological activity of promoting microtubule assembly, resulting in microtubule depolymerization and axonal dysfunction, which leads to neuron degeneration and nerve cell apoptosis, resulting in Alzheimer’s disease.
The abnormal phosphorylation of Tau protein is caused by the high expression of various phosphorylated kinases, such as glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β), cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5), and tyrosine kinase, which are considered potential drug targets for AD treatment.
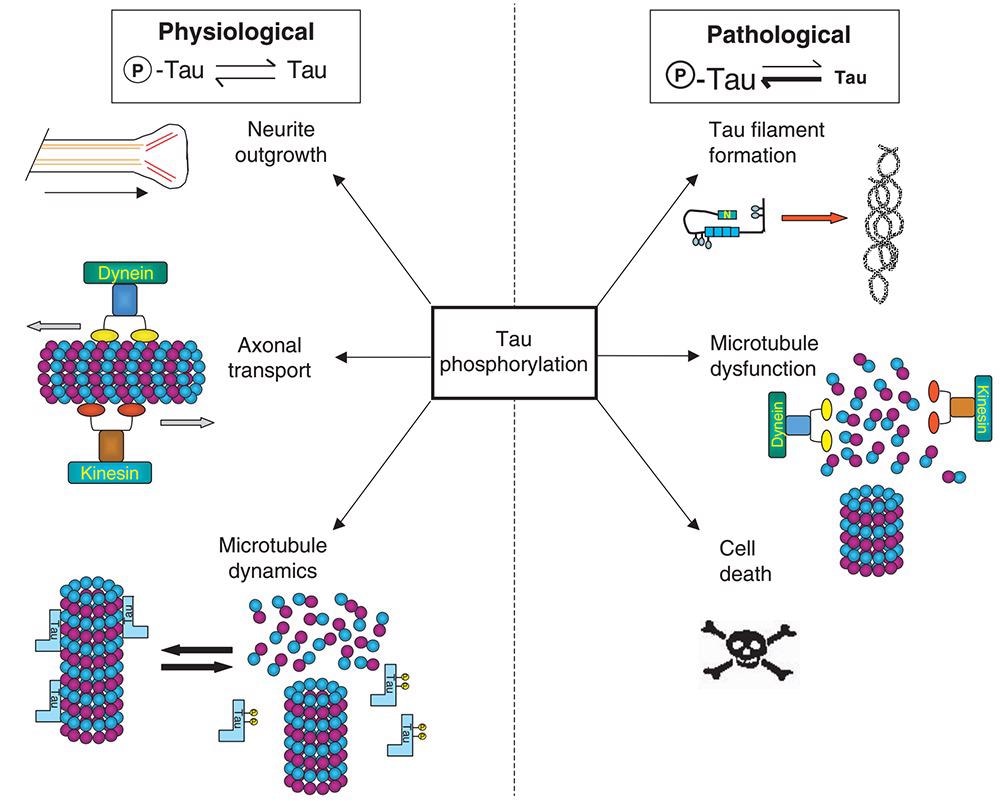
Abnormal phosphorylation of Tau protein. Image from reference
Cholinergic hypothesis
The cholinergic theory was the first to describe the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease.
In Alzheimer’s patients, Doucette et al. discovered a significant loss of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons, which resulted in decreased acetylcholine transferase (ChAT) operation for acetylcholine synthesis and serious depletion of presynaptic cholinergic transmitters, resulting in cognitive function decline.
The cholinergic hypothesis proposes that the fall in cholinergic levels is due to decreasing activity of Cholinesterase, which includes acetylcholinesterase (AChE), butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), and ChAT.
The FDA has authorized many Cholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of AD, including donepezil hydrochloride and memantine hydrochloride/donepezil hydrochloride. They are still used as first-line therapeutic drugs to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease.
Even though these drugs play a significant role in postponing the onset of AD, their limited effects prevent them from effectively treating the disease.
Summary
In addition to the three hypotheses of the Aβ cascade, other reasons for the pathogenesis of AD include aberrant phosphorylation of Tau protein and cholinergic, neuroinflammation, inappropriate excitation of the glutamate system, mitochondrial dysfunction, and others. The pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease is currently being researched by scientists.
Only aducanumab has been introduced to the market in nearly 20 years. More drugs and therapies to improve the condition are urgently needed as the global aging issue becomes more serious.
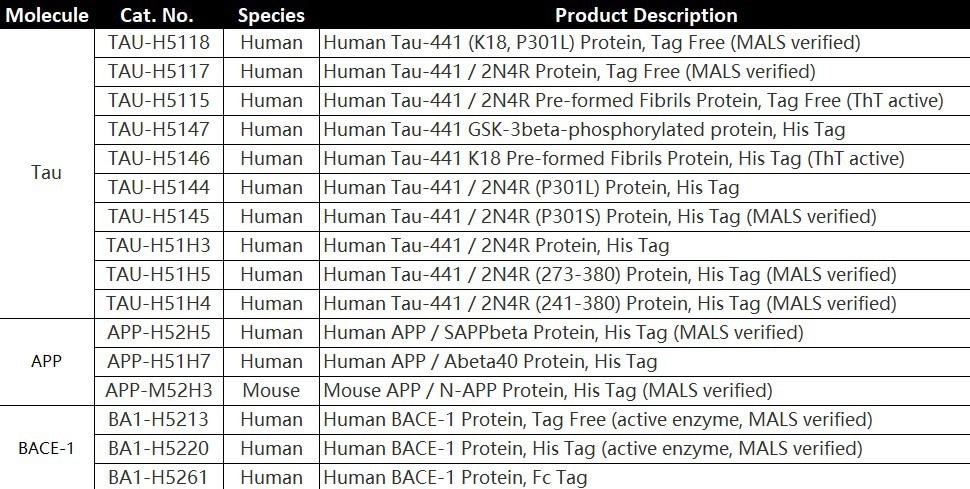
To aid with the development of AD treatment medications, ACROBiosystems has created Tau protein (TAU-441), amyloid precursor protein (APP), and β-secretase-1 (BACE1).
Product list
Source: ACROBiosystems
Verification data
TAU-441 (Met 1 - Leu 441)
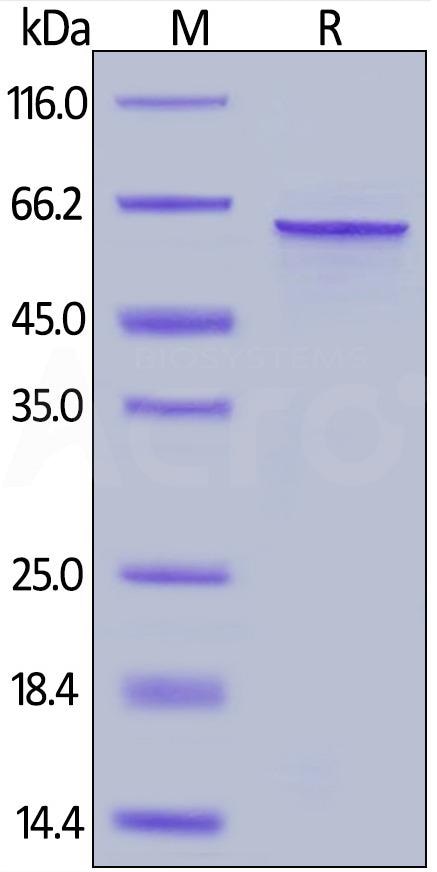

Human Tau-441 / 2N4R Protein, His Tag Human Tau-441, His Tag (Cat. No. TAU-H51H3) on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained overnight with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 90%. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
TAU-441 (Gly 273 - Glu 380)
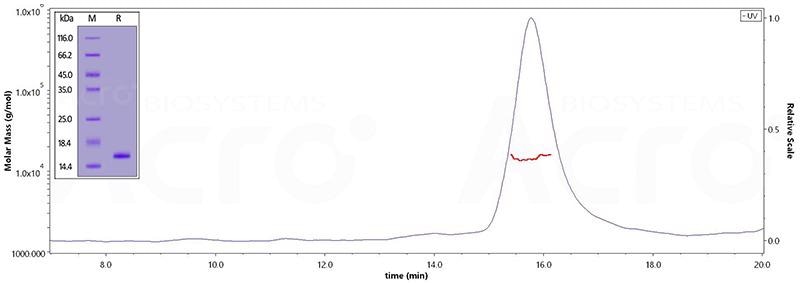
The purity of Human Tau-441 (273-380), His Tag (Cat. No. TAU-H51H5) is greater than 95% verified by SDS-PAGE and more than 90% verified by SEC-MALS. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
TAU-441 (Ser 241 - Glu 380)
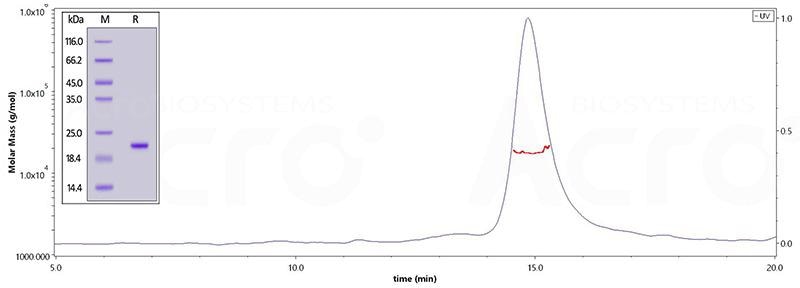
The purity of Human Tau-441 (241-380), His Tag (Cat. No. TAU-H51H4) is greater than 95% verified by SDS-PAGE and more than 90% verified by SEC-MALS. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
SAPP
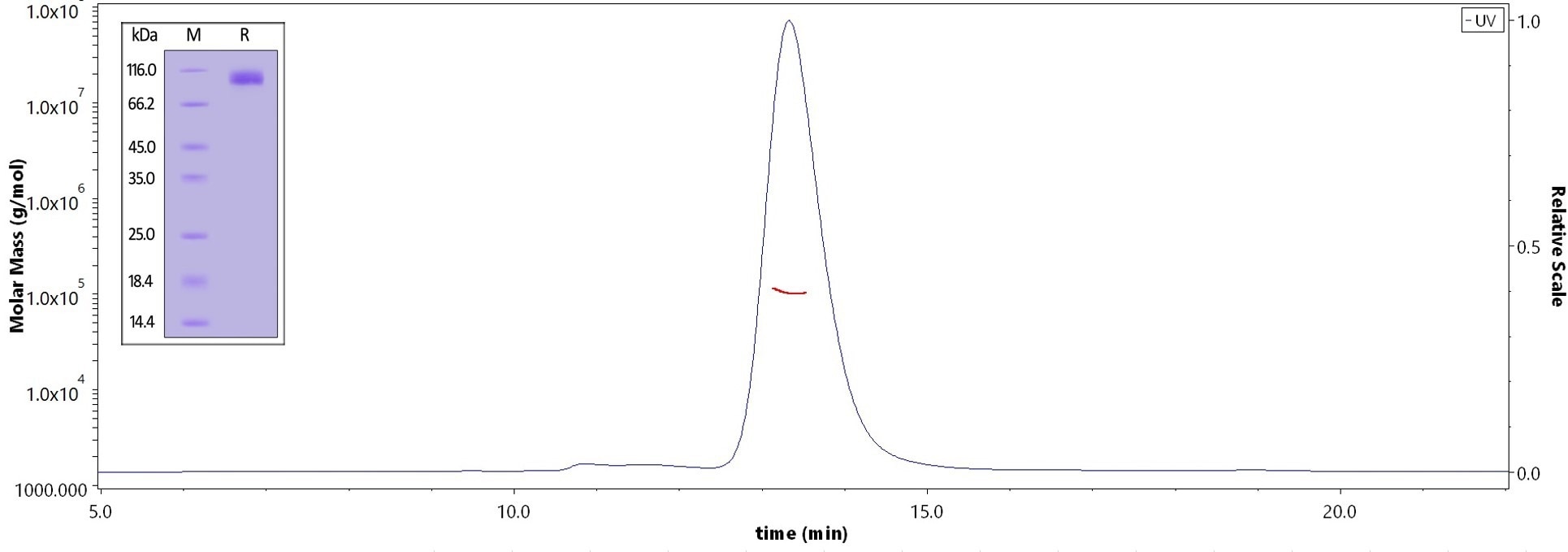
The purity of Human SAPPbeta, His Tag (Cat. No. APP-H52H5) is greater than 95% verified by SDS-PAGE and more than 90% verified by SEC-MALS. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
BACE1
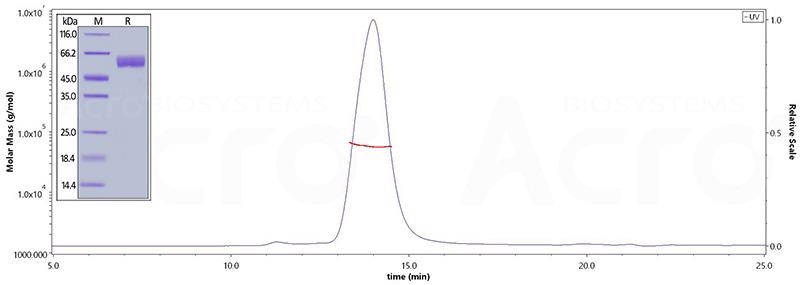
The purity of Human BACE-1, His Tag (Cat. No. BA1-H5220) is greater than 95% verified by SDS-PAGE and more than 95% verified by SEC-MALS. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
References
- Ju Y, Tam KY. Pathological mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2022 Mar;17(3):543-549. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.320970.
- Zhang X, Song W. The role of APP and BACE1 trafficking in APP processing and amyloid-β generation. Alzheimer’s Res Ther. 2013 Oct 8;5(5):46. doi: 10.1186/alzrt211.
- Johnson GV, Stoothoff WH. Tau phosphorylation in neuronal cell function and dysfunction. J Cell Sci. 2004 Nov 15;117(Pt 24):5721-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01558.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.