Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are difficult to treat due to their high heterogeneity and complexity. SEZ6 (Seizure-related 6 homolog) is a key regulator of dendritic formation and neural signaling and plays an important role in NETs, particularly in small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Research has shown that SEZ6 is overexpressed in SCLC and is closely linked to tumor cell proliferation and invasion. This link makes SEZ6 a potential therapeutic target. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) targeting SEZ6 have shown promising results in preclinical studies, showing their potential as a new precision treatment for NET patients.
ABBV-706: Targeting relapsed/refractory SCLC
ABBV-706 is an ADC targeting SEZ6 developed by AbbVie. It is linked to a topoisomerase 1 inhibitor (TOP1i) via a valine-alanine linker, with a drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) of 6. ABBV-706 specifically targets SEZ6-expressing tumor cells, rapidly internalizes, and delivers the cytotoxic TOP1i payload.
ABBV-706 has demonstrated significant antiproliferative activity across various SCLC cell lines as well as sustained tumor regression in SCLC PDX models. This ADC is currently in Phase 1 clinical trials where it is being evaluated both as a monotherapy and in combination with the PD-1 inhibitor Budigalimab (ABBV-181), and with carboplatin or cisplatin.
ABBV-706 is currently the only SEZ6-targeting ADC in development for SCLC, and is drawing substantial interest within the biopharmaceutical industry.
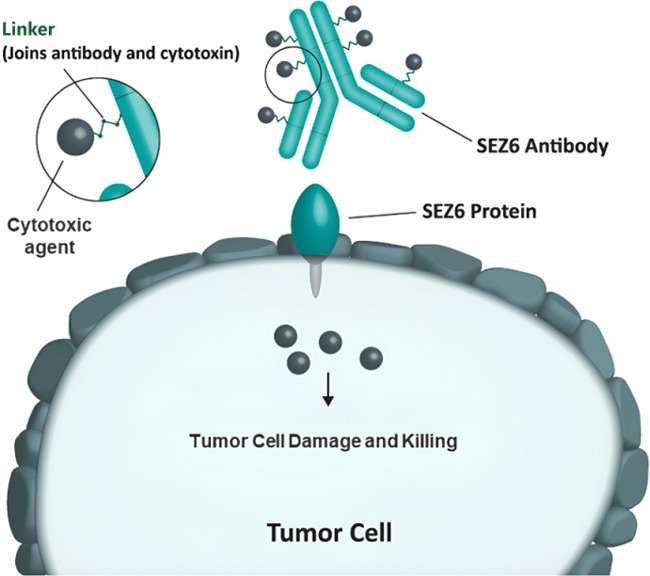
SEZ6-ADC Mechanism of Action. Image Credit: AbbVie Official Website, https://www.abbvie.com
AbbVie presented early data from the first-in-human dose-escalation study of ABBV-706 monotherapy at the ASCO meeting in May 2024. The results showed an overall objective response rate (ORR) of 43.8 % among 48 evaluable patients. The ORR was 60.9 % in the small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cohort and 28.0 % in the neuroendocrine tumor (NET) cohort.
At the data cutoff point, the most common Grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) included neutropenia (42 %), anemia (42 %), and leukopenia (28 %). These findings demonstrate ABBV-706’s potential as a treatment option. In July 2024, China’s Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) approved AbbVie’s clinical trial application for ABBV-706 lyophilized powder for injection.
After its approval by the CDE, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted orphan drug designation (ODD) to ABBV-706 for treating SCLC in October 2024. This ODD highlights ABBV-706’s promise in addressing this rare and aggressive cancer and validates SEZ6 as an effective therapeutic target.
ADC therapy: The future of SCLC treatment
Approximately 15 % of all lung cancers are SCLC, a disease characterized by high malignancy, rapid progression, and a high recurrence rate, making it challenging to treat.
Currently, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are the primary treatment options, but they have limited survival benefits and poor prognosis. Exploring different targeted therapies is essential to improve treatment efficacy and patient survival.
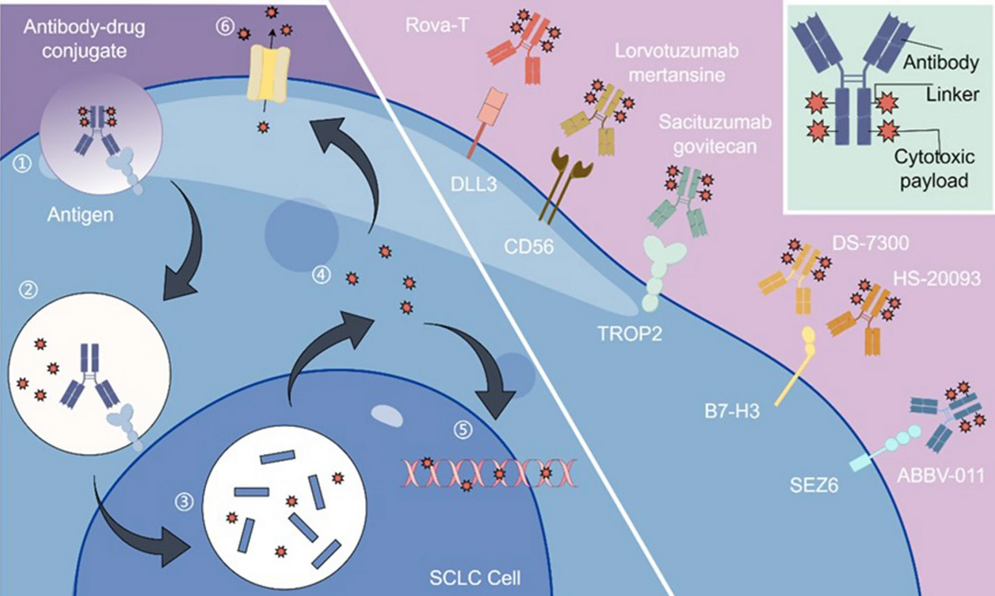
ADC Mechanism of Action and Drug Development Target for SCLC 1. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Compared to traditional chemotherapy and radiotherapy, ADCs offer significant advantages in the treatment of refractory or relapsed SCLC. By precisely targeting specific antigens present in SCLC, ADCs can minimize the damage to normal cells while enhancing cytotoxic effects.
ADCs also address chemotherapy resistance, providing new options for recurrent tumors. In doing so they significantly improve efficacy and patient survival. Additionally, bispecific antibodies, designed to bind to two different antigens or pathological targets, can enhance immune responses, overcome treatment resistance, and improve tumor clearance.
Recently, pharmaceutical companies have begun evaluating combination strategies involving ADCs and bispecific antibodies. These strategies target SCLC-related antigens like DLL3 to achieve better therapeutic outcomes.
High-quality SEZ6 tools support SCLC drug development
ACROBiosystems has launched a series of high-quality biopharmaceutical development tools that focus on SEZ6 recombinant proteins and stable cell lines to meet SCCLC ADC development needs.
SEZ6 recombinant proteins
Expressed in human-derived HEK293 cells and validated by SDS-PAGE, SEC-MALS, ELISA, and SPR, these proteins have high purity, activity, and consistency. They are suitable for immunization, antibody screening, and validation of candidate drug functionality.
SEZ6 stable cell lines
These stable cell lines express the SEZ6 antigen on the surface of host cells and are suitable for long-term use. They support antibody drug activity screening (cell-level binding and blocking) and evaluation of CAR molecule cytotoxicity. They serve as essential tools for drug development optimization of SEZ6-targeted therapies.
Additional targeted drug development tools
ACROBiosystems provides a variety of high-quality tools for SCLC, including DLL3, CD56, TROP2, B7H3, c-MET, HER2, and PD-1/PD-L1, to fully support drug development research.
ACROBiosystems conducts batch-to-batch quality control on all products, verifying properties such as purity and binding activity, and provides free protocols to streamline SEZ6-targeted drug development.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.