CD40 is a transmembrane protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. It is predominantly expressed on antigen-presenting cells like B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Its ligand, CD40 Ligand (CD40L), is primarily found on activated T cells.
The interaction between CD40 and its ligand is crucial for immune responses such as B cell activation, antibody production, and for the proliferation of inflammatory cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes.
The CD40-CD40L signaling pathway is also implicated in various pathological processes, including autoimmune diseases, inflammatory disorders, and cancers. Recent advancements in understanding this pathway have broadened its potential as a target in therapeutic applications, particularly in neurological disorders and new immunotherapies.
Traditional research and applications of CD40/CD40L
Most current drug development targeting CD40/CD40L focuses on monoclonal antibodies. Studies center predominantly around agonists and antagonists. Agonists are the primary focus in cancer treatment, while antagonists are explored for autoimmune diseases.
Development of CD40 agonists has been slow due to side effects of the drug that limit its dosage. This slow progression has caused issues for several major pharmaceutical companies including Roche, AbbVie, and Novartis. For example, Roche's selicrelumab had to be discontinued because of adverse reactions to the drug.
Many of these companies have shifted their focus toward autoimmune diseases because of these setbacks.
UCB and Biogen have developed Dapirolizumab Pegol, which has shown a significant reduction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) disease activity in the Phase 3 data they presented at the American College of Rheumatology.
Fexalimab, created by Sanofi and ImmuNext's, demonstrated considerable efficacy and tolerability in Phase II trials for multiple sclerosis (MS) and Type 1 diabetes, with Phase III trials ongoing in China. Another autoimmune therapy, Innovent Biologics' IBI355, has commenced Phase I clinical trials for treatment of primary Sjögren's syndrome.
Further innovative therapeutic approaches are being developed to reduce CD40 expression or target different sites, such as small interfering RNA (siRNA), fusion proteins, and peptides. They show potential in minimizing side effects and improving specificity.
Emerging bispecific agonists
In a recent breakthrough, Aman Mebrahtu et al. introduced a novel CD40 agonistic antibody, BiA92_HF. Developed within the Adaptive Drug Affinity Conjugate (ADAC) platform, this agonistic antibody enables cancer-specific peptide delivery. In the IgG2 subclass, BiA92_HF exhibits powerful agonistic activity on monocyte-derived dendritic cells without engaging Fcγ receptors.
By humanizing the anti-pTag scFv, protein quality and yield was improved, and favored fusion to the heavy chain for enhanced production. In vivo studies show that ADAC induces significant antigen-specific CD8+ and CD4+ T cell expansion, with the pTag-peptide linked to BiA92_HF enhancing T cell proliferation.
The platform effectively inhibited tumor growth and improved survival in tumor models, surpassing traditional adjuvants like CpG. ADAC was shown to transform previously ineffective neoantigens into powerful anti-tumor agents, and shows promise for personalized cancer immunotherapy.
ADAC’s ability to induce strong immune responses, enhance anti-tumor immunity, and reduce systemic toxicity highlights its potential in precision oncology.
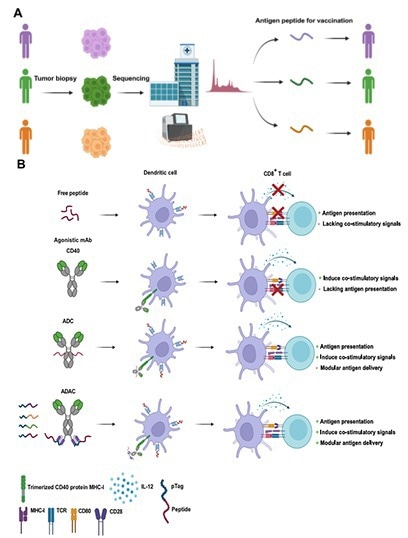
Overview of the principal workflow and advantages of the Adaptable Drug Affinity Conjugate (ADAC) technology. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Potential in neurological disorders
Recent advancements have broadened the understanding of CD40-CD40L beyond traditional roles in autoimmunity and cancer. These research studies demonstrate the potential in targeting the CD40-CD40L pathway in addressing various neurological disorders.
Studies show that the CD40-CD40L axis is a key regulator in numerous neurological conditions, influencing neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration, and disease progression, making it a valuable therapeutic target.
Zhou et al. explored the role of CD40-CD40L in neurological diseases and therapeutic advancements, highlighting the mechanisms involved.
In traumatic brain injury, elevated CD40 and CD40L levels in macrophages and microglia at the injury site drive neuroinflammation. Soluble CD40L (sCD40L) serves as a biomarker for poor prognosis. It is thought that inhibiting CD40 signaling could reduce brain edema and improve outcomes.
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by CD40-CD40L interactions that promote neuroinflammation through altered amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing and tau phosphorylation. These mechanisms contribute to neurofibrillary tangles and β-amyloid plaques. By targeting this pathway, the progression of Alzheimer’s disease could be markedly decreased.
Parkinson’s disease sees CD40 signaling in microglia and astrocytes, causing the upregulation of pro-inflammatory molecules and leading to selective loss of dopaminergic neurons. By inhibiting interactions between CD40 and CD40L, neurons could be protected from degeneration.
Ischemic strokes involve CD40L expression in atherosclerotic lesions, destabilizing plaques and exacerbating neuroinflammation. Inhibiting CD40 signaling in animal models has reduced infarct volume and improves outcomes, indicating further therapeutic potential.
Epilepsy is associated with elevated plasma sCD40L and leukocyte CD40 expression, correlating with increased seizure susceptibility and severity. Downregulating CD40-CD40L signaling may reduce neuroinflammation and offer therapeutic benefits.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) occurs as a result of CD40L+ T-cells activating microglial CD40 receptors, which release inflammatory molecules, worsening demyelination. Elevated sCD40L levels in cerebrospinal fluid demonstrate the axis’ role in disease progression. Inhibiting CD40-CD40L interactions could serve to reduce neuroinflammation.
CD40 signaling in antigen-presenting cells and T cells has been associated with disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Anti-CD40L antibodies delay paralysis onset and extend survival in mouse models, indicating therapeutic potential.
In Myasthenia gravis (MG), CD40 signaling causes B-cell activation and antibody production. CD40L knockout mice have shown resistance to MG induction, suggesting that targeting CD40-CD40L may reduce autoantibody production.
Brain tumors demonstrate a dual role for the CD40-CD40L axis: enhancing anti-tumor immunity while potentially promoting tumor progression. Elevated CD40 expression in certain gliomas correlates with poor prognosis, underscoring the need for combination therapies to modulate its effects.
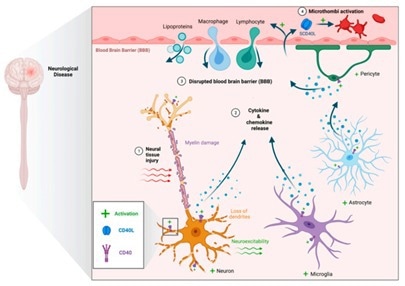
CD40–CD40L in neuroinflammation. Proposed mechanism for cytokine-mediated neuronal. CD40–CD40L in neuroinflammation. Proposed mechanism for cytokine-mediated neu ronal damage, disruption of the blood brain barrier, and microthrombi formation. damage, disruption of the blood brain barrier, and microthrombi formation. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Overall, the CD40-CD40L axis plays a multifaceted role in neurological disorders, providing potential therapeutic targets for modulating neuroinflammation and disease progression. Future research should focus on uncovering its mechanisms and developing targeted interventions.
Summary
Understanding the CD40/CD40L pathway opens new avenues in disease treatment. Research is ongoing and aims to uncover the role of this pathway in immune regulation and explore clinical potential. Global pharmaceutical companies are committed to developing CD40/CD40L-targeted drugs to deliver more effective and safer treatments for patients.
ACROBiosystems has created a series of products to meet the market demands for CD40/CD40L-related drug development. They include high-quality target proteins and CD40L overexpression cell lines.
These products support the entire drug development process, from immunization and antibody screening to characterization, cell function validation, signaling pathway research, and quality control, accelerating the development of treatments for various diseases.
Product list
CD40 Product List. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Product Description |
| CD40 |
CD0-HA256 |
Alexa Fluor™ 647-Labeled Human CD40 Protein, Fc Tag (Site-specific conjugation) |
| CD40 |
CD0-R52H8 |
Rat CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
CD0-M82F3 |
Biotinylated Mouse CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, Fc, Avitag™ (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
CD0-R52H9 |
Rabbit CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
CD0-H525a |
Human CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, Mouse IgG2a Fc Tag, low endotoxin (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
TN5-H82F9 |
Biotinylated Human CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, Fc, Avitag™ (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
CD0-H82E8 |
Biotinylated Human CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, Avitag™, His Tag (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
CD0-C52H6 |
Cynomolgus CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
TN5-M52H8 |
Mouse CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
TN5-M5259 |
Mouse CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, Fc Tag |
| CD40 |
CD0-C5259 |
Rhesus macaque CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, Fc Tag (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
CD0-C52H7 |
Rhesus macaque CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
CD0-H5228 |
Human CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |
| CD41 |
CD0-H5253 |
Human CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein, Fc Tag (MALS verified) |
| CD40 |
CHEK-ATF097 |
Human CD40 (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell |
Click to Learn More about CD40
CD40 Ligand Product List. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Product Description |
| CD40 Ligand |
CDL-H5264 |
Human CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Protein, Fc Tag (N297A), active trimer, premium grade |
| CD40 Ligand |
CD0-R52D9 |
Rabbit CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Protein, His, Flag Tag (active trimer) (MALS verified) |
| CD40 Ligand |
CDL-M52D5 |
Mouse CD40 Ligand / TNFRSF5 Protein, His, Flag Tag, active trimer (MALS verified) |
| CD40 Ligand |
CDL-M82H5 |
Biotinylated Mouse CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Protein, His, Avitag™, active trimer (MALS verified) |
| CD40 Ligand |
CDL-H82Db |
Biotinylated Human CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Protein, Avitag™, His, Flag Tag, active trimer (MALS verified) |
| CD40 Ligand |
CDL-H5269 |
Human CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Protein, Fc Tag, active trimer, premium grade |
| CD40 Ligand |
CDL-H52Db |
Human CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Protein, His, Flag Tag, active trimer, premium grade |
| CD40 Ligand |
CDL-H5256 |
Human / Rhesus macaque CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Protein, Mouse IgG2a Fc Tag, low endotoxin |
| CD40 Ligand |
CDL-H82F1 |
Biotinylated Human CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Protein, Avitag™, Fc Tag |
| CD40 Ligand |
CDL-M526x |
Mouse CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Protein, Fc Tag |
| CD40 Ligand |
CDL-M5248 |
Mouse CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Protein, His Tag, active trimer (MALS verified) |
| CD40 Ligand |
CHEK-ATP041 |
HEK293/Human CD40 Ligand / TNFSF5 Stable Cell Line |
Click to Learn More about CD40 Ligand
Assay data
CD40 Ligand trimer structure of CD40L and high purity(>95%) verified by SEC-MALS
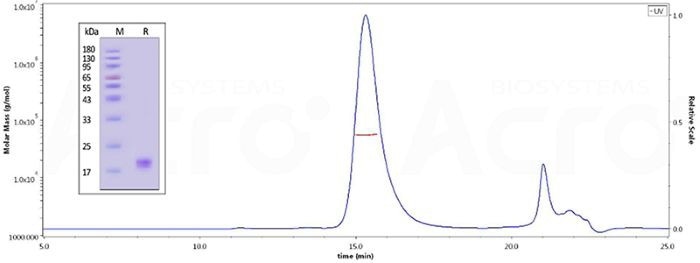
The purity of Mouse CD40 Ligand Protein, His Tag (Cat. No. CDL-M5248) is more than 95% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 50-65 kDa verified by SEC-MALS. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
The binding activity of CD40 and CD40 Ligand was verified by ELISA
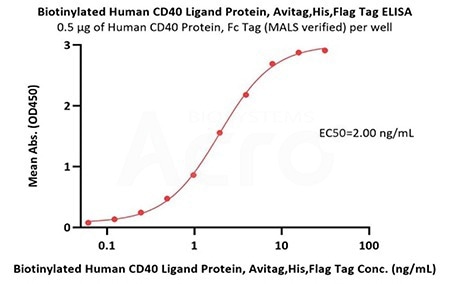
Immobilized Human CD40 Protein, Fc Tag (MALS verified) (Cat. No. CD0-H5253) at 5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Biotinylated Human CD40 Ligand Protein, Avitag, His, Flag Tag (Cat. No. CDL-H82Db) with a linear range of 0.1-2 ng/mL (QC tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
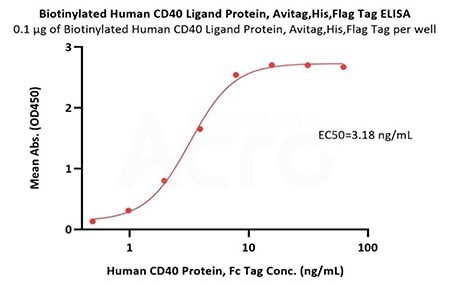
Immobilized Biotinylated Human CD40 Ligand Protein, Avitag, His, Flag Tag (Cat. No. CDL-H82Db) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) on streptavidin (Cat. No. STN-N5116) precoated (0.5 μg/well) plate can bind Human CD40 Protein, Fc Tag (Cat. No. CD0-H5253) with a linear range of 0.5-8 ng/mL (Routinely tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
The binding activity of CD40 and CD40 Ligand was verified by BLI
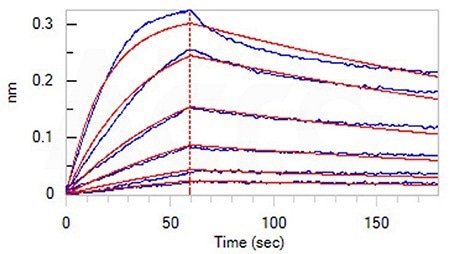
Loaded Human CD40 Protein, Fc Tag (Cat. No. CD0-H5253) on Protein A Biosensor, can bind Human CD40 Ligand, His, Flag Tag, premium grade (Cat. No. CDL-H52Db) with an affinity constant of 1.58 nM as determined in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e) (QC tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
The binding activity of CD40 and CD40 Ligand was verified by FACS
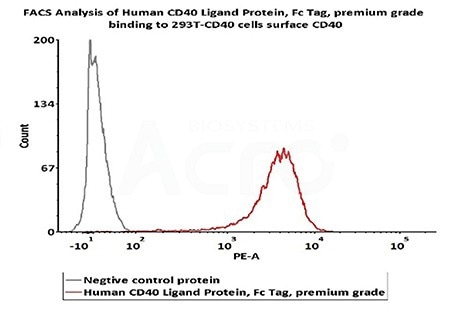
FACS analysis shows that Human CD40 Ligand Protein, Fc Tag, premium grade (Cat. No. CDL-H5269) can bind to 293T-CD40 cells surface CD40. The concentration of Human CD40 Ligand is 0.3 μg/mL (Routinely tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
FACS verified that CD40 Ligand stimulate secretion of IL-6 by human B cells
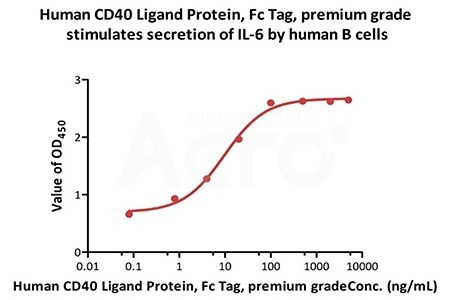
Human CD40 Ligand Protein, Fc Tag, premium grade (Cat. No. CDL-H5269) stimulates secretion of IL-6 by human B cells. The ED50 for this effect is 9.68-11.48 ng/mL in the presence of 5 ng/mL of Recombinant Human IL 4 (Routinely tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
References
- Mebrahtu, A., et al. (2024). A bispecific CD40 agonistic antibody allowing for antibody-peptide conjugate formation to enable cancer-specific peptide delivery, resulting in improved T proliferation and anti-tumor immunity in mice. Nature Communications, (online) 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53839-5.
- Ots, H.D., et al. (2022). CD40–CD40L in Neurological Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, (online) 23(8), pp.4115–4115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084115.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.