Endotoxin testing is critical for quality control in drug production, as it has a direct impact on pharmaceutical safety and effectiveness. Traditionally Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) testing is used, but this method has several drawbacks.
LAL reagents are generated from horseshoe crab blood, and large-scale harvesting endangers their populations. Another issue with LAL reagents is their variation between batches, which can affect test accuracy and consistency.
Recent developments in recombinant protein technology have resulted in the creation of the recombinant Factor C (rFC) testing method. This technology provides a more environmentally friendly and efficient alternative to traditional LAL testing.
As rFC endotoxin testing standards evolve they are being embraced by pharmaceutical companies across the world, putting rFC on track to become the mainstream approach for endotoxin detection.
Global pharmacopoeia status
European Pharmacopoeia
Europe has pioneered the development of recombinant Factor C testing standards.
In 2015, the European Pharmacopoeia acknowledged recombinant Factor C as an alternate testing technique. By 2017, this approach was being developed, and in January 2021, Chapter 2.6.32 was formally released. This chapter outlined bacterial endotoxin testing with recombinant Factor C.
Now widely used throughout Europe, recombinant Factor C-based endotoxin testing was approved for medication release in 2020.
United States Pharmacopeia (USP)
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) has recently finalized its research and standardization of recombinant Factor C testing. A 2018 draft added recombinant Factor C as a recognized alternate technique with further standards refinements.
The USP Microbiology Expert Committee officially approved the use of recombinant Factor C for endotoxin testing in July 2024. The final wording of this Bacterial Endotoxin Testing in Chapter 86 was published in November 2024 and came into effect in May 2025.
Japanese Pharmacopoeia
Japan is actively conducting related research to rFC testing. Its expert group has begun discussions about designing a bacterial endotoxin testing method using recombinant Factor C. Comparison tests with horseshoe crab reagents and recombinant Factor C have already been conducted by the group. Further developments are ongoing.
Limitations of the LAL reagent testing method
Susceptibility to product interference
Some products may interfere with the LAL reagent's reactivity to endotoxins.
The kind and shape of glassware used in gel-based procedures can have an impact on test performance, with siliconized glassware and plastics preventing gel formation or interfering with spectrophotometric readings.
Chemical interference, such as fluorescence impacting protein denaturation, and pH levels outside the 6.0-7.5 range, and physical interference, such as endotoxin adsorption and product viscosity, can also cause issues.
Limited applicability
Turbidity and colorimetric procedures cannot be applied to turbid or colored goods when using LAL. Precipitate formation can interfere with testing and result in false positives.
Precipitates may also occur in colorimetric tests after acid is added to terminate the reaction, particularly in compounds that only dissolve at neutral or alkaline pH levels.
Result variability
With LAL testing, each product must be validated for reliability and accuracy because of the variability between LAL reagents. The source of LAL reagents can be unpredictable; therefore, each change in reagent source requires revalidation, making testing more complicated and expensive.
Advantages and future prospects of the rFC method
The rFC does not require animal products for testing, making it superior to traditional LAL reagents, which rely on horseshoe crab blood. The use of crab blood both depletes crab populations and causes quality difficulties, so pharmacopoeias are trying to avoid such testing where possible.
The recombinant rFC approach produces Factor C using recombinant DNA technology, and has improved dependability and control, as well as reducing interference and false positives associated with LAL reagents.
A further advantage of the rFC approach is that it improves sensitivity and specificity. Additionally, it can evaluate complicated samples, ensuring the safety of high-risk items such as biologics and gene therapies.
As technology progresses, rFC will improve pharmaceutical quality control, boost industry growth, and ensure drug safety.
Recombinant C factor endotoxin detection testing kit compliant with pharmacopoeial requirements
The ACROBiosystems Recombinant Factor C Endotoxin Detection Kit (Cat. No. RES-A056) makes use of recombinant DNA technology to identify endotoxins in samples quickly and efficiently.
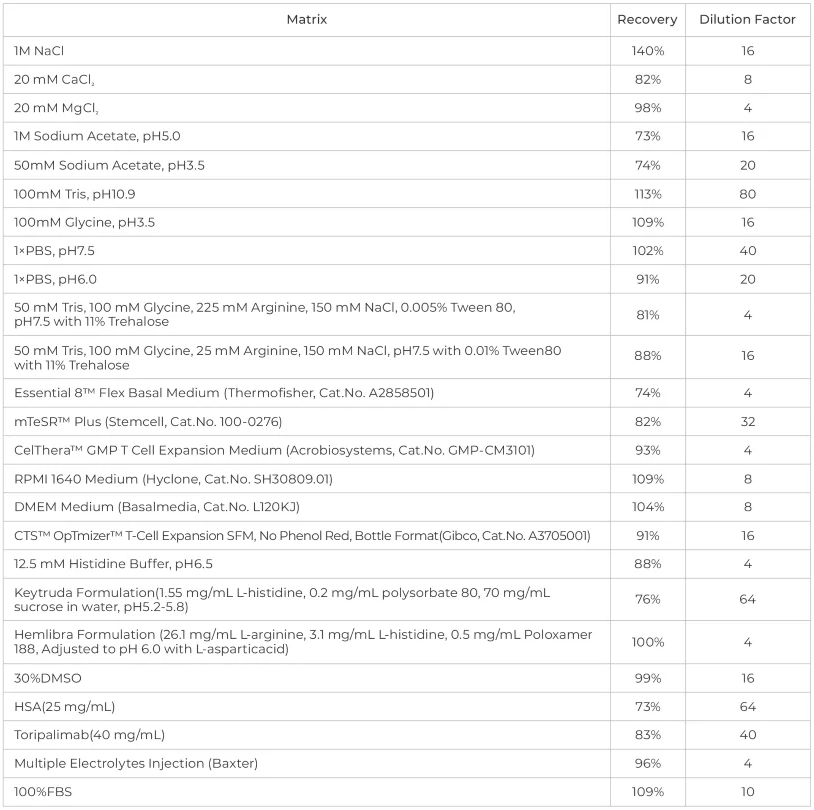
The kit has been verified across multiple sample matrices, displaying high interference resistance and impressive recovery rates.
The endotoxin standard is closely linked with USP (Cat. No. U1235503) standards, ensuring sensitive, specific, and consistent findings across batches. It has been developed to meet the rigorous quality control standards of the pharmaceutical, medical device, and biologics sectors.
Validation data
The kit has excellent buffer compatibility, operating with a variety of buffer systems.
ACROBiosystems performed interference effect experiments on various ionic strengths, pH buffers, and media, and the kit has outstanding buffer compatibility. To determine the minimum dilution ratio of the kit testing recovery for specific buffers or media is advised. Source: ACROBiosystems
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.