Fc receptors (FcRs) are a group of glycoproteins that belong to the immunoglobulin superfamily and are classified, like Fc alpha receptors (FcαRs), Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) and Fc epsilon receptors (FcεRs).
Communication of IgG antibodies with the immune system is regulated and mediated by FcγRs, which depend on the information sensed and collected by antibodies to the immune system. IgG is widely studied and is the best characterized among the Igs. It is classified into four distinct subclasses (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4), each exhibiting differences in sequence and structure, attaching properties to FcγRs, and effector functions.
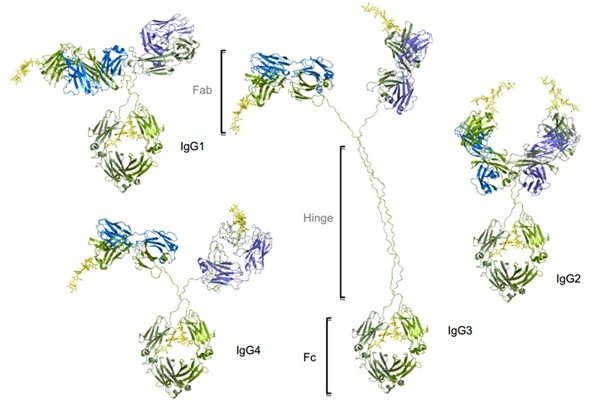
Figure 1. Four subtypes of IgG exist in humans: IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4. Conserved Asn 297 amino acids in the Fc region with N-glycans attached (shown in yellow), Heavy chains are shown in green, and light chains are shown in blue and purple. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
The four subtypes are named depending on their respective abundance in serum and IgG1 is the most abundant. IgG antibodies have two Fab regions that facilitate the binding of both an antigen molecule and the Fc region that interacts with the FcγRs, combined by a greatly flexible hinge region.
IgG1 has the greatest affinity to all FcγRs, which leads to vital effector functions, like ADCP, ADCC, and CDC. Even though human IgG3 mediates competent effector functions, it has a very long hinge region and complex disulfide bonds, resulting in greater polymorphism, which might heighten the risk of immunogenicity.
Thus, the IgG3 isotype is seldom chosen in antibody therapeutics. Comparatively, IgG2 and IgG4 substantially induce weaker or no ADCC and CDC.
Depending on the differences in structure, function and affinity for IgG attachment, FcγRs are divided into three main groups — FcγRI/CD64, FcγRII/CD32 (FcγRIIa, FcγRIIb and FcγRIIc) and FcγRIII/CD16 (FcγRIIIa and FcγRIIIb).
Amongst them, FcγRI, FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa are activating receptors having the signal transduction motif, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM), in the γ subunit of FcγRI and FcγRIIIa or the cytoplasmic tail of FcγRIIa.
On the other hand, FcγRIIb is an inhibitory receptor. Cross-linking of FcγRIIb results in the phosphorylation of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and inhibitory signaling transduction.
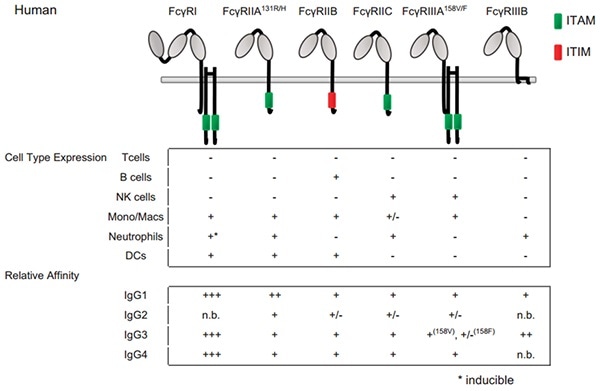
Figure 2. Fc–FcγRs interactions and FcγRs expression across cell subsets in humans. For cell-type expression, + indicates constitutive expression, +* indicates inducible expression, and − indicates no expression. For relative affinities, +++ indicates lower than 1 μM, ++ indicates 1–10 μM, + indicates 10–100 μM, +/− indicates higher than 100 μM and n.b. indicates no binding. †Indicates binding observed with no affinity reported. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems.
FcγRI (Fc gamma receptor I, CD64)
FcγRI is a high-affinity Fc receptor for both the immune complex (IC) and the monomeric IgG. The affinities of FcγRI to IgG1 or IgG4 are the same (1–10 nM KD). However, FcγRI has no binding to IgG2. FcγRI is majorly expressed on dendritic cells (DCs), monocytes/macrophages and activated neutrophils.
A major function of FcγRI is to trigger myeloid cells to phagocytose IgG1 and IgG-bound target cells through ADCP. Due to the high-affinity binding of FcγRI to monomeric IgG and high serum concentrations of IgG (∼15 mg/mL), it is assumed that the majority of FcγRI is occupied by endogenous IgG.
Recent research revealed that stimulation of myeloid cells with cytokines, like interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), can trigger the clustering of FcγRI and enhance the binding of FcγRI to ICs. Multiple types of research have also demonstrated that FcγRI performs a vital role in modulating immune responses in inflammation, autoimmune diseases and antibody therapy.
FcγRII (Fc gamma receptor II, CD32)
FcγRII receptor is the one that is broadly expressed on hematopoietic cells among FcγRs. FcγRII includes FcγRIIA, FcγRIIB and FcγRIIC isoforms. FcγRIIA is expressed on macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets is also widely expressed on immune cells than FcγRIIC found on NK cells.
FcγRIIA starts phagocytosis, endocytosis, ADCC and inflammatory mediator release. Yet, FcγRIIB is expressed on basophils, B cells, mast cells, macrophages, monocytes and DC. It transduces inhibitory signals that down-regulate immune functions induced by activating receptors when co-ligated with the latter receptors.
FcγRIII (Fc gamma receptor III, CD16)
Two various FcγRIII isoforms are identified. FcγRIIIB is a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored-FcγRIIIB expressed on neutrophils and involved in degranulation and production of reactive oxygen intermediates by these cells. FcγRIIIA is a transmembrane isoform expressed on NK cells and a small subpopulation of T lymphocytes.
It is also expressed on monocytes and macrophages, although in reduced levels. FcγRIIIA is involved in ADCC, phagocytosis, endocytosis and cytokine release.
The mouse IgG system is different from the humans in significant ways (mice expresses IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b and IgG3, with different affinities for mouse FcγRs when compared to humans), with greater affinity Fc–FcγRs engagement by the mouse IgG2a isotype for activating FcγRs than that of human IgG1.
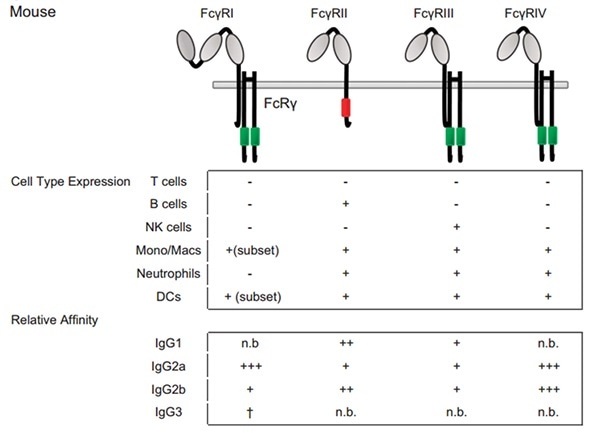
Figure 3. Fc–FcγRs interactions and FcγRs expression across cell subsets in the mouse. For cell-type expression, + indicates constitutive expression, +* indicates inducible expression, and − indicates no expression. For relative affinities, +++ indicates lower than 1 μM, ++ indicates 1–10 μM, + indicates 10–100 μM, +/− indicates higher than 100 μM and n.b. indicates no binding. †Indicates binding observed with no affinity reported. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
FcγRI, FcγRIIB, and FcγRIIIA human equivalents have been elaborated in mice. Mouse FcγRI and FcγRIIIA (called FcγRIII) showcases the same activating properties as their human counterparts. These two mouse receptors bind IgG with a great and a low affinity, respectively. Mouse FcγRIIB (called FcγRII) is also a low-affinity receptor that shows inhibitory functions like the human FcγRIIB that has an ITIM.
All mouse FcγRs can attach human IgG1 and IgG3 subclasses, along with mouse IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b subclasses. Among these subclasses, IgG2a is a strong binder of FcγRI than IgG1 and IgG2b which preferentially binds FcγRIIB and FcγRIII, to which IgG2a also attaches. It is still a topic of controversy whether a specific mouse Fc receptor for mouse IgG3 persists even though this subclass claims to bind mouse FcγRI.
Summary
FcγRs are expressed majorly on leukocytes and they are the most relevant class of receptors for the function of therapeutic antibodies. FcγRs are classified into three types, FcγRI (CD64), FcγRII (CD32) and FcγRIII (CD16).
They are conventionally divided based on their affinity for specific IgG subclasses and the kind of signaling pathway that they induce — activating or inhibitory. Generally, FcγRI is considered a high-affinity receptor that attaches both monomeric IgG and immune complexes, while the affinity of FcγRII and FcγRIII for IgGs is low and intermediate, respectively.
Engineering the Fc region of IgG mAbs or IgG-like bispecific antibodies to modulate IgG/FcγRs interactions is a significant goal of recent research into therapeutic antibodies. The production and manufacture of therapeutic antibodies, including Fc (crystallizable fragment) fusion proteins, depict an important segment of the biopharmaceutical industry and have been significantly beneficial to public health.
The binding of the antibody Fc-hinge region to FcγRs has been found to have a huge effect on antibody function and in vivo effectiveness.
ACROBiosystems provides a comprehensive collection of recombinant Fc receptor proteins, including their common variants, to accelerate antibody drug development.
The use of biotin labeling enables effortless assay development. Various “ready-to-use” biotinylated Fc receptors are provided.
These proteins are generated using in-house developed labeling techniques, which provide high bioactivity and minimal batch-to-batch variation. Additionally, a series of Fc receptors of other species were developed which are appropriate for the screening of non-humanized antibodies or the species’ cross-reaction.
Advantages of Fc receptor protein products
- Expressed by HEK293 Cells: post-translational modification and proper protein folding
- Greater purity: SDS-PAGE verification purity >95%, SEC-MALS verification purity > 90%
- Multiple species: Human, Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Porcine, Feline, Bovine, can be applied to various cross-species experiments
- High stability: Strict quality control to assure high batch-to-batch consistency
- Low endotoxin: <1.0 EU/µg
- Biotinylated Fc Receptor proteins labeled with Avitag™ offered: The labeling efficacy is great, and the labeling site is specific and clear, which is appropriate for ELISA/SPR/BLI detection depending on binding to streptavidin in the drug development and optimization process
- Affinity verified by SPR & BLI: Activity guaranteed, and protocols offered free of charge
Product list (All Fc receptors are expressed from HEK293)
FcRn
Table 1. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Host |
Product description |
Structure |
| FcRn (FCGRT & B2M) |
FCM-H5286 |
HEK293 |
Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |
|
| FCM-H8286 |
HEK293 |
Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His Tag&Strep II Tag, ultra sensitivity (primary amine labeling) (SPR verified) |
|
| FCM-H82W4 |
HEK293 |
Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, Avitag™, His Tag&Strep II Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified)Hot |
|
| FCM-H82W7 |
HEK293 |
Biotinylated Human FcRn / FCGRT&B2M Heterodimer Protein, His, Avitag™(MALS & SPR verified) |
|
Click here to learn about many more FcRns.
FcγR
Table 2. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Host |
Product description |
Structure |
| Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a |
CD8-H52H4 |
HEK293 |
Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |
|
| CDA-H5220 |
HEK293 |
Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (F176) Protein, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |
|
| CDA-H5290 |
HEK293 |
Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, SUMO, His Tag (MALS verified) |
|
| CDA-H52S1 |
HEK293 |
Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (V176) Protein, HSA, His Tag (MALS verified) |
|
| CDA-H82E8 |
HEK293 |
Biotinylated Human Fc gamma RIIIA / CD16a (F176) Protein, Avitag™, His Tag (SPR & BLI & MALS verified) |
|
Click here to learn about many more FcγRs.
FcεR
Table 3. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Molecule |
Cat. No. |
Host |
Product description |
Structure |
| CD23 |
CD3-H5249 |
HEK293 |
Human CD23 / Fc epsilon RII Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |
|
| CD3-H82Q5 |
HEK293 |
Biotinylated Human CD23 / Fc epsilon RII Protein, His, Avitag™ (MALS verified) |
|
Fc epsilon
RI alpha |
FCA-H5228 |
HEK293 |
Human Fc epsilon RI alpha Protein, His Tag (MALS verified) |
|
| FCA-H5259 |
HEK293 |
Human Fc epsilon RI alpha Protein, Fc Tag (MALS & BLI verified) |
|
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine..
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.