Each year on November 14, World Diabetes Day highlights how diabetes management extends beyond blood glucose control; it’s about optimizing overall metabolic health and related biomarkers.

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
With the global prevalence of diabetes continuing to rise, the value of scientific research and advanced therapeutic development has become increasingly evident.
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition featuring high blood glucose levels. Persistent hyperglycemia can result in severe complications, including cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, kidney damage, retinopathy, neuropathy, and significant reductions in quality of life. This disease also places considerable strain on healthcare systems.
Etiology categorizes the disease as either Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) or Type 2 Diabetes (T2D), which differ significantly in pathogenesis, therapeutic strategies, and drug development considerations.
Pathophysiology of T1D: Autoimmune-mediated insulin deficiency
Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks pancreatic β-cells, resulting in severe or complete insulin deficiency.
Without insulin, a key blood glucose regulating hormone, hyperglycemia develops, disrupting overall metabolic balance. T1D predominantly affects children and adolescents, and so is commonly referred to as “juvenile diabetes.”
Although T1D only makes up around 5-10 % of all diabetes cases, it has an acute onset, progresses quickly, and requires lifelong insulin treatment for blood glucose management.
Currently, approximately 10 million individuals worldwide live with T1D.
In recent years, incidence rates have been growing in certain regions, including North America and Europe, especially among children. The increase is spurred by genetic susceptibility, environmental factors, and early viral infections.
Insulin replacement therapy remains the foundation of T1D treatment. Developments in technology, especially insulin pumps integrated with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, have enabled “closed-loop” glucose management, improving both the precision and convenience of glucose management.
Modern T1D therapeutic approaches aim to restore immune tolerance or selectively suppress autoimmune responses to preserve residual β-cell function.
Researchers are studying several types of treatment, including immune checkpoint modulation (such as the CTLA-4 inhibitor Abatacept), cytokine-targeted therapies (including IL-6R and TNF-α antagonists), lymphocyte-directed interventions (Teplizumab, an anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody, is currently the only approved drug for delaying T1D onset in high-risk individuals), and metabolic–immune combination therapies (such as GLP-1R agonists).
Approved originator biologics for T1D. Source: Pharmacodia
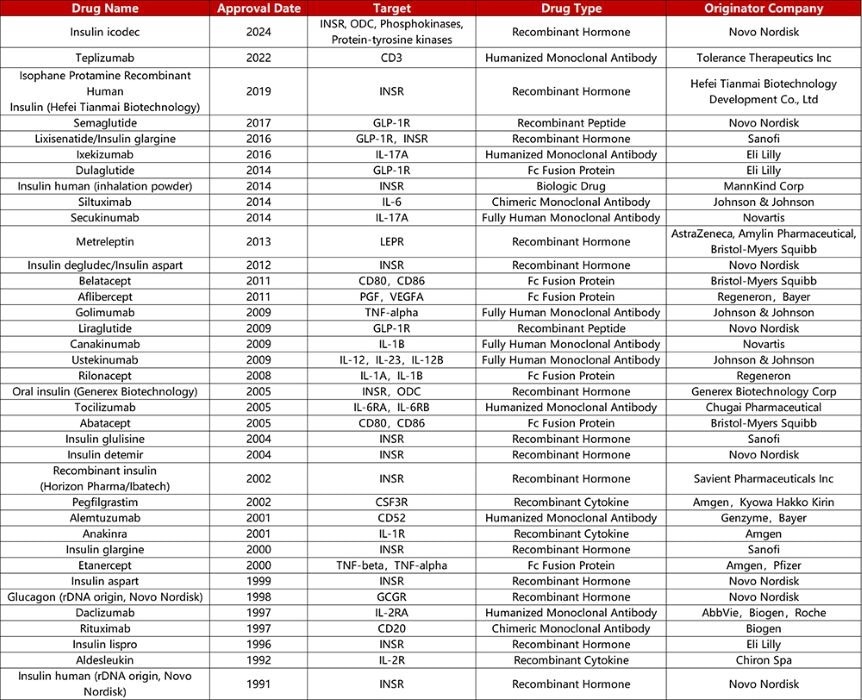
Research trends increasingly focus on combination therapies, such as Teplizumab plus IL-2, along with the incorporation of artificial pancreas technology. However, major obstacles persist, including sustaining long-term efficacy (limited by the “honeymoon period”), patient stratification (relying on autoantibody profiles and HLA typing), and long-term safety concerns such as infection and cancer risk.
Novel targeted therapies, including CD40L inhibitors, are currently undergoing clinical trials. Meanwhile, stem cell transplantation paired with localized immune modulation is demonstrating considerable promise. Together, T1D drug development is moving from pure insulin replacement toward a comprehensive strategy of immune modulation plus β-cell restoration.
Future multi-targeted strategies that combine immune suppression, cell protection, and regeneration may ultimately shift treatment from managing symptoms toward true disease modification.
ACROBiosystems provides a broad range of research tools for autoimmune drug development, including high-activity recombinant proteins, stable cell lines, and inhibitor screening kits. These resources support key stages of the therapeutic pipeline, from target discovery and validation to candidate screening, process development, and quality control.
This integrated platform supports the efficient progression of advanced therapies for autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes, from early research through to clinical application.

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Pathophysiology of T2D: Insulin resistance and metabolic dysregulation
As the most common form of diabetes, Type 2 diabetes (T2D) accounts for more than 90 % of global cases. It is defined by the coexistence of insulin resistance and progressive β-cell dysfunction.
In the early stages, insulin secretion remains adequate; however, peripheral tissues, particularly the liver, muscle, and adipose tissue, exhibit reduced insulin sensitivity. This results in reduced glucose uptake and increased hepatic glucose production, both of which contribute to hyperglycemia.
Progression of the disease is marked by a gradual decline of β-cell function, insufficient insulin secretion, and further deterioration of glycemic control. T2D development is strongly linked to genetic predisposition, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, dietary imbalance, and chronic low-grade inflammation.
The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimates that more than 500 million individuals worldwide currently live with Type 2 diabetes, and this number is anticipated to surpass 600 million by 2045.
Chronic hyperglycemia increases the risk of serious complications, including cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy. In contrast to T1D, treatment for T2D focuses on enhancing insulin sensitivity and improving insulin secretion.
In the early stages, lifestyle interventions such as diet or exercise changes can substantially enhance glycemic control. Pharmacologic treatments have progressed from traditional oral hypoglycemic agents, such as metformin and sulfonylureas, to advanced targeted therapies.
Recently, novel agents, including GLP-1R agonists (e.g., semaglutide), dual GIPR/GLP-1R agonists (e.g., tirzepatide), SGLT2 inhibitors (e.g., empagliflozin), and combination approaches (e.g., SGLT2 plus DPP-4 inhibitors), have demonstrated exceptional glycemic control while providing additional metabolic benefits, such as weight loss and cardio-renal protection. These advancements signal a new era of multi-targeted, system-level T2D therapy.
Approved originator biologics for T2D. Source: Pharmacodia
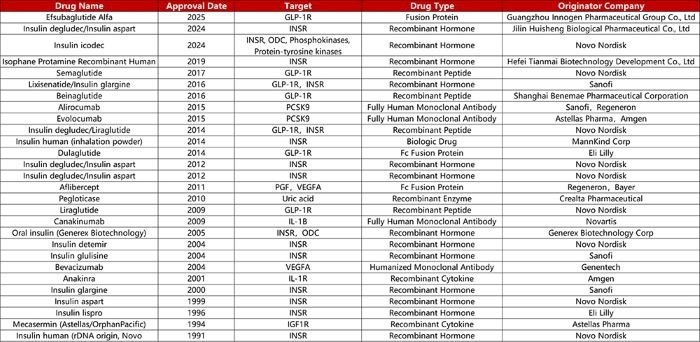
ACROBiosystems provides high-quality recombinant proteins, stable cell lines, and screening kits that support metabolic disease drug development at every stage. Its portfolio is designed to meet the needs of researchers working from target identification and validation through candidate selection, process development, and quality control. These tools can be used to advance new therapies for metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes, from early research into the clinic.

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems pioneers diabetes therapeutics with innovative solutions
ACROBiosystems has launched a series of comprehensive therapeutic development solutions to address the urgent needs of diabetes treatment, covering both autoimmune (T1D) and metabolic (T2D) diseases.
The portfolio includes critical target proteins, high-specificity antibodies, stable expression cell lines, high-sensitivity detection kits, and a suite of analytical tools, complemented by professional, customized technical services, delivering robust support and accelerating drug and therapy development programs.

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Metabolic disease survey: Share insights, get a reward
Metabolic disorders are skyrocketing worldwide, fueling urgent demand for innovative treatments. ACROBiosystems supports therapeutic discovery by providing recombinant proteins, engineered cell models, and antibody screening kits. The Metabolic Disease Drug Development Tools Survey gathers insights to inform the development of next-generation solutions for faster and more effective therapeutic innovation.

Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
From now until December 31, 2025, participants who complete the survey will receive a Delicate llama Mascot as a Thank-you Gift! The gift will be shipped directly to the participant following submission approval.
Click to Participate in the Survey
Hot T1D target recommendations
Source: ACROBiosystems
| |
|
|
|
| Insulin R |
GLP-1R |
GCGR |
GIPR |
| DPP4 |
IL-1 beta |
CD3 |
CD2 |
| CD28 |
CD40 |
CD40 Ligand |
IL-1 RI |
| PD-1 |
TNF-alpha |
CD20 |
IL-12 beta |
| IL-1 alpha |
IL-2 R alpha |
IL-6 |
IL-6 R alpha |
| IL-6 R beta |
MAdCAM-1 |
PD-L1 |
TNF-beta |
| TSLP |
JAK1 |
... |
|
Hot T2D target recommendations
Source: ACROBiosystems
| |
|
|
|
| GLP-1R |
Insulin R |
DPP4 |
GIPR |
| GCGR |
PTP1B |
CNR1 |
LPAR1 |
| GSK-3β |
PCSK9 |
CTR |
AMY3R |
| IL-1 beta |
FGF-21 |
FGF R1 |
FGF R2 |
| FGF R4 |
NF-kB |
TNF-alpha |
IGF1R |
| GPR75 |
Adiponectin |
Activin A |
ANGPTL3 |
| APOE |
GDF-8 |
Activin RIIA |
Activin RIIB |
| Leptin R |
AKT |
THRB |
... |
References and further reading:
- Warshauer, J.T., Bluestone, J.A., and Anderson, M.S. (2020). New Frontiers in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Cell Metabolism, 31(1), pp.46–61. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.11.017. https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(19)30624-2?_returnURL=https%3A%2F%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%2Fretrieve%2Fpii%2FS1550413119306242%3Fshowall%3Dtrue.
- Jiménez-Martí, E., et al. (2022). Novel Therapies for Cardiometabolic Disease: Recent Findings in Studies with Hormone Peptide-Derived G Protein Coupled Receptor Agonists. Nutrients, [online] 14(18), pp.3775–3775. DOI: 10.3390/nu14183775. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/18/3775.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empowers scientists and engineers dedicated to innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.net, which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices, and treatments.