Multiple studies have shown STAT3 to be a tumor microenvironment modulator and a cancer driver, making it one of the most alluring targets in oncology and immune-oncology. The production of STAT3 inhibitors is accelerating, and the novel strategy PROTAC has effectively broken the “incurable” impasse of STAT3.
Double certification of scientific research and capital, the next outlet of tumor immunotherapy; what is the basis of STAT3?
A class of cytoplasmic transcription factors known as signal transduction and transcriptional activators (STAT, or signal transducer and activator of transcription) attach to DNA and frequently react to various external cytokine and growth factor signals.
After activation, it moves from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, where it binds to certain locations on the target gene’s promoter sequence. This promotes transcription and helps with key physiological processes, including cell division, apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation.
The mammalian STAT family primarily consists of the genes STAT1, STAT2, STAT3, STA4, STAT5a, STAT5b, and STAT6. The oncogenic signaling pathways STAT3 and STAT5 converge, have a strong association with tumor growth and are thought to be the next avenue for cancer therapy.
STAT3 signaling pathway
JAK-STAT signal pathways
A crucial signal sensor for numerous cytokines, growth factors, and interferons is JAK (Janus kinase). Some cytokines connect to the appropriate receptors under certain stress response situations, causing Janus kinase to get phosphorylated and STAT3 to become activated. As a transcriptional regulator, the activated STAT3 dimer will subsequently bind to certain DNA sequences.
Currently, it has been established that the most well-known IL6/JAK/STAT3/pathway affects target gene transcription relevant to breast cancer development and induces chemoresistance in breast cancer.
SRC-STAT signal pathways
The constitutive activation of STAT3 can also result from non-receptor tyrosine kinases like SRC and ABL. SRC has the ability to activate STAT3 and cause the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues, which enhances transport to the nucleus and controls gene transcription.
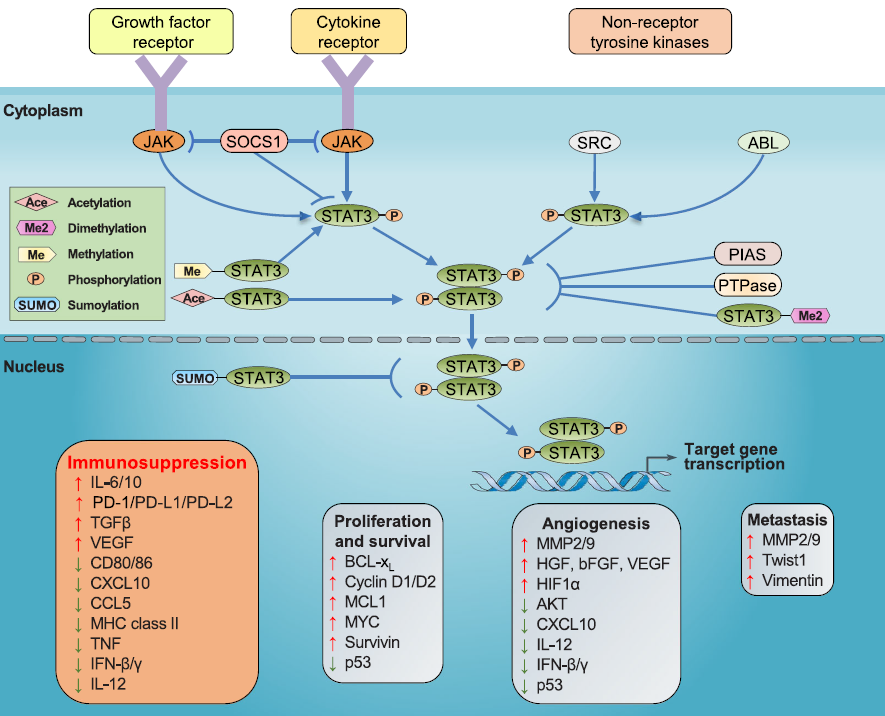
STAT3 signaling pathway. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
STAT3 and cancer
According to research, STAT3 has shown to be overexpressed in a wide range of human malignancies and is crucial for the tumor microenvironment’s (TME) signaling transduction as well as the advancement of the disease in the following ways:
- Promote tumor progression: TME-associated CAFs are activated by STAT3 activation, which increases the production of immunosuppressive substances like IL-6, IL-10, and EGFR. The STAT3 in CAFs promotes stroma remodeling, tumor growth, tumor proliferation, survival, and migration
- Induce TME Immunosuppressive: As STAT3 levels rise in the TME, immunological checkpoint molecules such as PD-L1, PD-L2, and CTLA-4 are released more often. This results in the enrichment of Treg cells and B cells and the polarization of M2 macrophages, which leads to immune evasion
- Reduce anti-tumor immunity: The lysis activity of anti-tumor cells is inhibited by increased STAT3 in CD8+ T cells, NK cells, and neutrophils. By preventing the maturation, activation, and antigen delivery of dendritic cells, STAT3 can also undermine their capacity to fight tumors
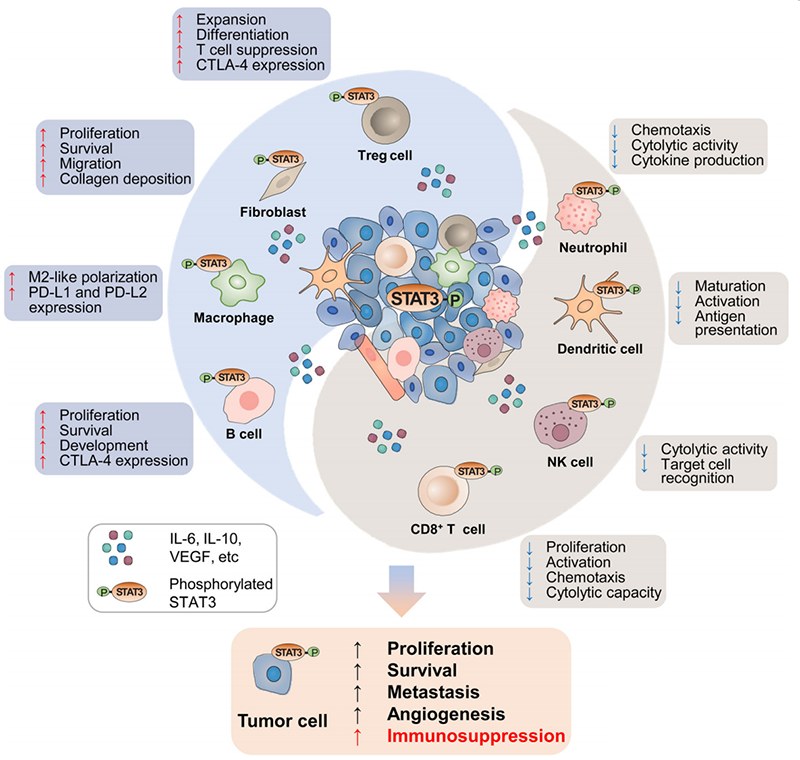
The mechanism of action of STAT3 in TME. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Targeted STAT3 drug development
Multiple studies have shown STAT3 to be a tumor microenvironment modulator and a cancer driver, making it one of the most intriguing targets in oncology and immune-oncology.
STAT3 inhibitors
Currently, STAT3 small molecule inhibitors can directly block STAT3 by preventing STAT3 from being phosphorylated and preventing the synthesis of useful STAT3 dimers. Additionally, certain inhibitors disrupt upstream signal pathways, including EGF, VEGF, JAK, etc., to indirectly decrease STAT3.
Combined therapy
Combined immunotherapy that targets STAT3 is believed to increase anti-tumor activity while simultaneously lowering tumor resistance. Additionally, STAT3 inhibitors and CAR-T cells together can lessen CAR-T cell overexpansion, treat cytokine release syndrome (CRS), and lower the frequency of immune-related adverse effects.
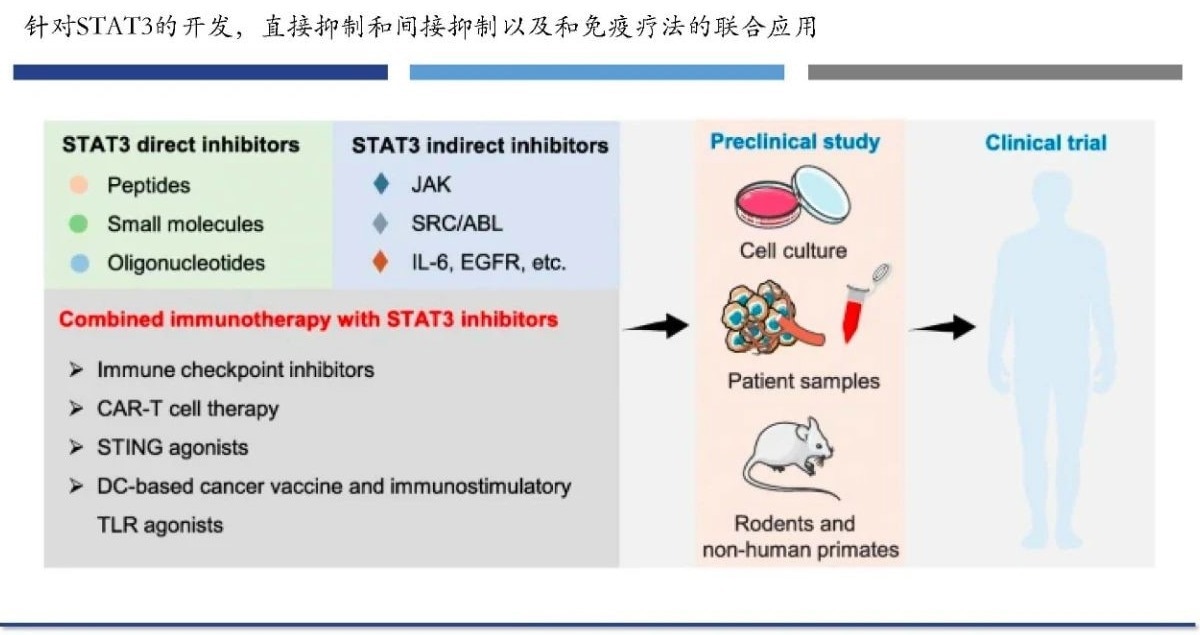
Targets STAT3 inhibitors and combination immunotherapy. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
PROTAC
PROTAC has great drug effectiveness and higher selectivity due to its capacity to inhibit the target protein’s activity and block the target protein’s expression, which makes it a novel way in which to break the non-druggable nature of STAT3.
On June 2nd, 2022, Kymera Therapeutics said that the FDA has given KT-333, a STAT3 protein-degrading agent, orphan drug status for the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).
Conclusion
Multiple studies have shown that STAT3 is overactivated in a variety of human malignancies and functions as a tumor microenvironment regulator and cancer driver, making it one of the most appealing targets in oncology and immuno-oncology.
Several STAT3 inhibitors have undergone clinical trials, and several have had impressive effects in vitro and in vivo. PROTAC has also overcome the impasse in achieving orphan drug classification and can be utilized as a new concept for the creation of potent STAT3 inhibitors.
With expanding research, the creation of STAT3-targeting medications in the future can be anticipated.
The whole range of solutions offered by ACROBiosystems is intended to facilitate the development of STAT3-targeted medicines by offering a comprehensive in vitro validation methodology from binding to functional assay.
Target protein
- Can be used in the study of the STAT3 signaling pathway and the development of STAT3-targeted drugs
- The binding activity with degrader was confirmed by BLI and SPR
- Cover both internal and external targets of the STAT3 classical signaling pathway, including EGF、EGF R、IL-6、IL-6 R alpha、JAK1、STAT3, etc
- Over 90% purity verified by SDS-PAGE and MALS
Product list
Click on the molecule to view the product details
Source: ACROBiosystems
Validation system
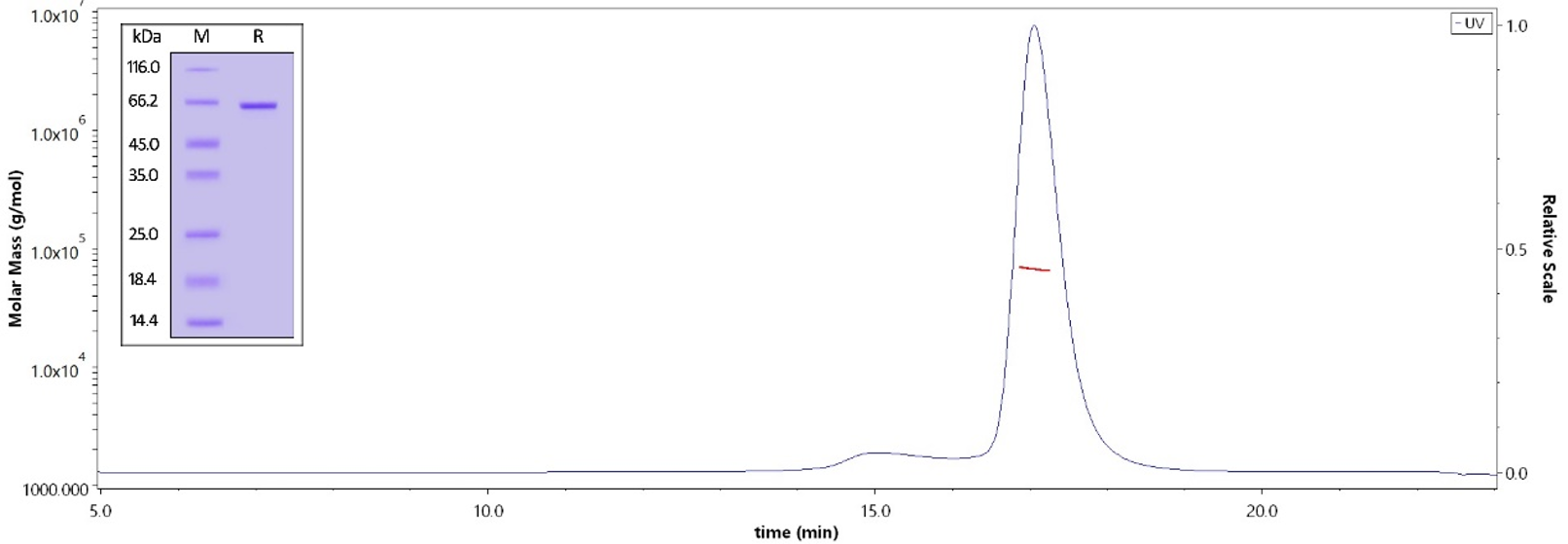
The purity of Human STAT3, His Tag (Cat. No. ST3-H5149) is more than 95% verified by SDS-PAG and greater than 90% verified by SEC-MALS. The molecular weight of this protein is around 60–75 kDa. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
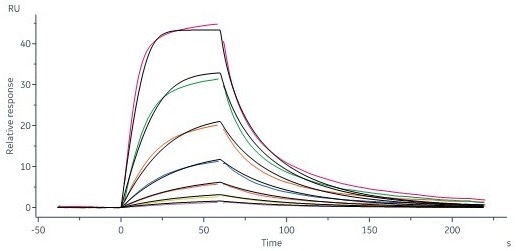
Human STAT3, His Tag (Cat. No. ST3-H5149) immobilized on CM5 Chip can bind STAT3 inhibitor with an affinity constant of 44.6 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore 8K) (QC tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Reporting gene cell line
- For small molecule inhibitors or antibodies that target the STAT3 signaling pathway development and function verification
- Large detection window for different drag screening
- Strong response signal to ensure high sensitivity
- The reporter gene cell lines were designed based on the MOA of drags
- Good generation stability, stable for 10-20 generations
Product list
Source: ACROBiosystems
| Cat. No. |
Product Description |
| CHEK-ATF049 |
EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell |
| CHEK-ATF047 |
STAT3 (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell |
Validation data
Property verification
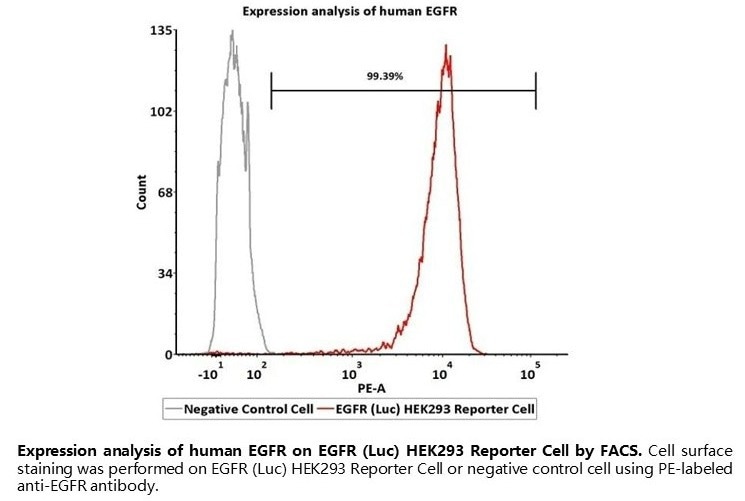
Expression analysis of human EGFR on EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell by FACS. Cell surface staining was performed on EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell or negative control cell using PE-labeled anti-EGFR antibody. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
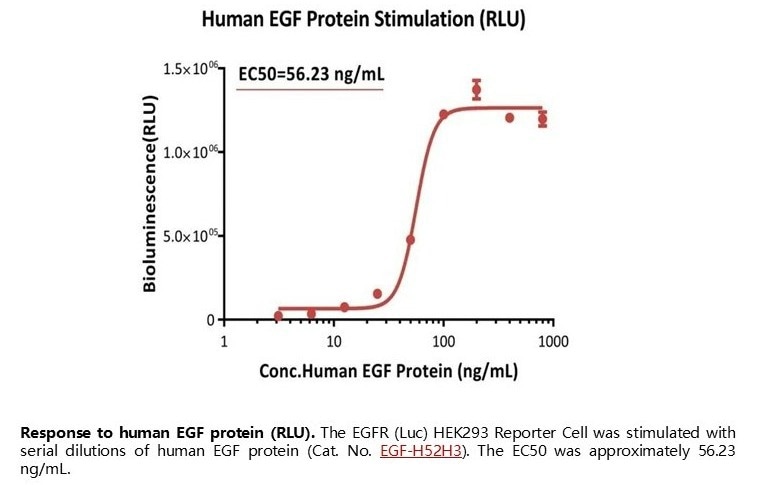
Response to human EGF protein (RLU). The EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell was stimulated with serial dilutions of human EGF protein (Cat. No. EGF-H52H3). The EC50 was approximately 56.23 ng/mL. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
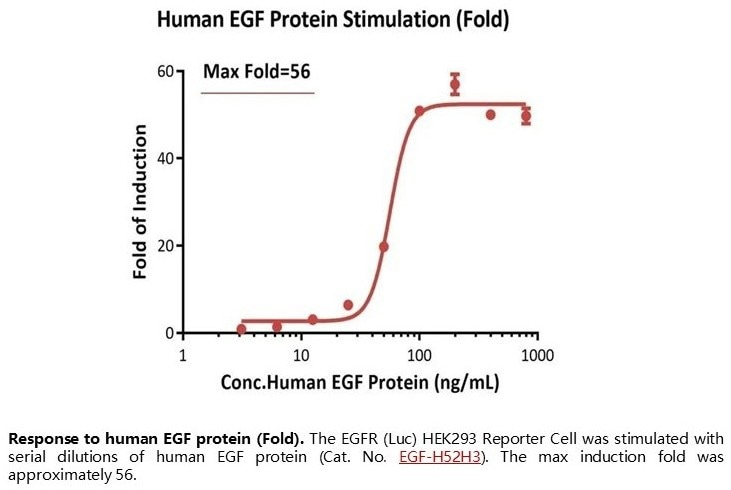
Response to human EGF protein (Fold). The EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell was stimulated with serial dilutions of human EGF protein (Cat. No. EGF-H52H3). The max induction fold was approximately 56. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Generation stability verification
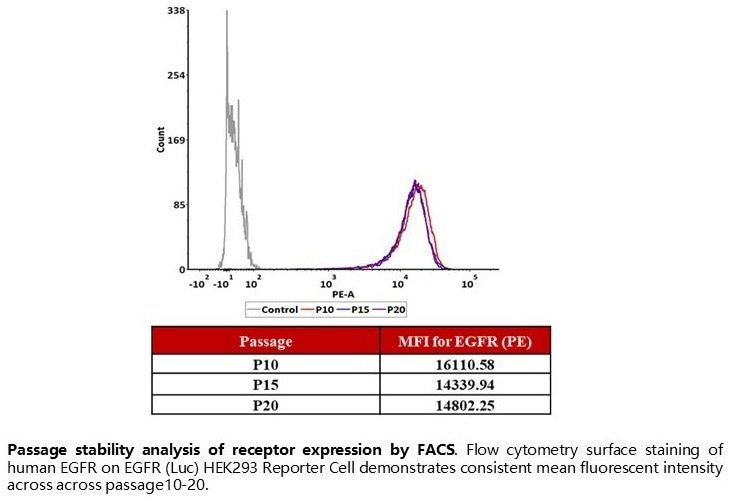
Passage stability analysis of receptor expression by FACS. Flow cytometry surface staining of human EGFR on EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell demonstrates consistent mean fluorescent intensity across passage10–20. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
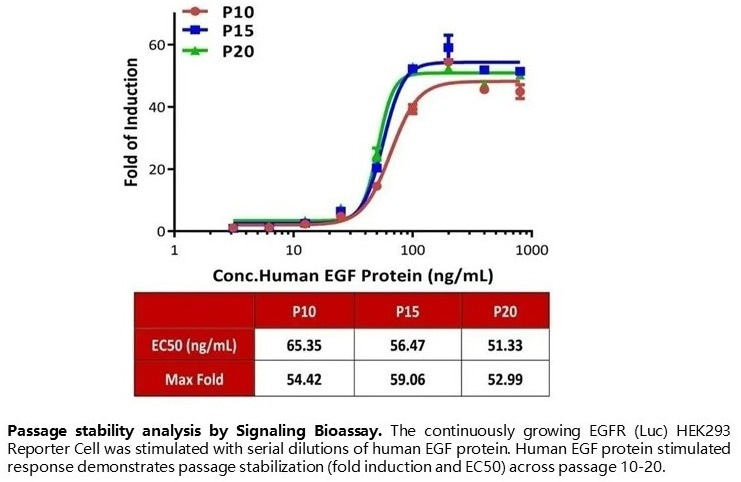
Passage stability analysis by Signaling Bioassay. The continuously growing EGFR (Luc) HEK293 Reporter Cell was stimulated with serial dilutions of human EGF protein. Human EGF protein stimulated response demonstrates passage stabilization (fold induction and EC50) across passage 10–20. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Pre-coupled magnetic beads
- It is suitable for high-throughput drug screening
- The magnetic beads are uniform in diameter, have a large specific surface area, excellent repeatability, and high capture efficiency
- To guarantee appropriate coating, use the biotin-streptavidin method with saturated concentration antigens
Product list
Source: ACROBiosystems
| Cat. No. |
Product Description |
| MBE-K012 |
Monoclonal Anti-TNF-alpha antibody, Mouse IgG1 (13B8) |
References
- Wingelhofer, B., et al. (2018). Implications of STAT3 and STAT5 signaling on gene regulation and chromatin remodeling in hematopoietic cancer. Leukemia. doi:10.1038/s41375-018-0117-x
- Zou, S., et al. (2020). Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Molecular Cancer. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01258-7
- He, M., et al. (2022). PROTACs: great opportunities for academia and industry (an update from 2020 to 2021). Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00999-9
- Radi, G., et al. (2021). The First Jak Inhibitor Approved in Europe for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis in Adult Patients. Healthcare (Basel). doi:10.3390/healthcare9111575
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.