The biopharmaceutical industry has grown remarkably in recent years, with cell and gene therapy (CGT) emerging as a key area amidst continuous technological advancements.
As biologics dominate next-generation medicine, ensuring that biological medicines are safe becomes vital. This brings additional scrutiny not only to CGT but also to the raw materials used during manufacturing and production.
The FDA emphasizes the utilization of “the highest quality” materials suitable. The International Pharmaceutical Regulatory Plan Cell Therapy Working Group created a document explaining their perspective on utilizing high-quality raw materials in manufacturing and licensed human CGT products.
Ensuring quality in critical raw materials
Cell therapy manufacturers must ensure the quality of their raw materials, whether developed in-house or supplied by a third party.
Necessary steps must be taken before clinical research is instigated for investigational new drug (IND) applications. These include the evaluation of quality control methods and standards for raw materials, such as cytokines and other growth factors.
These standards and methods are developed from various sources. Pharmacopeial methods are standardized approaches that establish a fundamental necessity for production and release. They originate from organizations like the USP and the European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and Healthcare.
Non-pharmacopeial methods, like the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) documents, are supplemental analytical approaches for evaluating specific characteristics of a product and how it is manufactured.
Several commercial products are marketed to comply with these standards and are commonly labeled ‘GMP-grade’ or ‘cGMP-grade.’ Products that adhere to these standards are often self-regulated, meaning that responsibility falls on cell therapy manufacturers to perform due diligence. This can make it difficult to find reliable suppliers.
This article outlines three aspects of GMP-grade quality control systems that are crucial for meeting IND requirements.
Raw material safety
Raw material safety is evaluated through several contaminant control and detection strategies to reduce any residues that may cause harm or affect the final product. This includes sterility testing, which is the evaluation of contaminants like mycoplasma, endotoxins, residual host-cell DNA, and proteins.
There are no simple methods for guaranteeing the sterility of final CGTs (such as sterile infiltration or autoclaving), as the final therapeutic is cells. Manufacturers must therefore be careful during manufacturing to ensure sterility of the final product, and the raw materials used. Manufacturers must assess supplies stringently.
Raw material suppliers for GMP-grade manufacturers must thoroughly regulate cytokines and other growth factors. This includes incorporating automatic fill-finish in B+A cleanrooms, online environmental monitors, and sterility tests which comply with USP regulations. Assessing the sterility of raw materials is the primary method of guaranteeing sterility of the final therapeutic.
Endotoxins are toxins. They are present in bacterial cells and are released following cell disintegration, which sometimes results in diseases like botulism. Maintaining low endotoxin levels in biologics is crucial for ensuring the safety of patients and avoiding endotoxin-related diseases.
Qualitative gel clot and chromogenic LAL-based methods are suitable for controlling these levels. However, if results are conflicting or inconsistent, the gel clot results are considered authoritative.
ACROBiosystems uses a LAL method calibrated against USP Reference Standard endotoxin calibrants to guarantee accuracy with sample results (as presented in Table 1).
To ensure endotoxin testing methods are valid, preparatory testing (as outlined in USP<85>) was performed, with an acceptable endotoxin recovery rate described as being within 50 and 200 %.
Table 1. Endotoxin Sample Curve Evaluation. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Theoretical value |
Detected value |
Recovery rate |
| 50 EU/ml |
55.04 EU/ml |
113.0 % |
| 5 EU/ml |
5.96 EU/ml |
104.7 % |
| 0.5 EU/ml |
0.6 EU/ml |
108.5 % |
| 0.05 EU/ml |
0.06 EU/ml |
108.0 % |
Mycoplasma is a prevalent contaminant in cell and tissue cultures that alters cellular growth and phenotypes. Testing for mycoplasma is crucial for guaranteeing reliability in biologics and its raw materials.
For analyzing mycoplasma, the favored approach is the culturing method, which monitors for growth of standard mycoplasma colonies on solid media. Additional validated methods include the utilization of fluorescent dyes to highlight characteristic filamentous patterns or particulates on cell surfaces.
While nucleic acid amplification methods and enzyme activity-based methods can also be employed, appropriate comparisons and validations between techniques to cell culture must also be addressed.
-
USP< 509, 1132="">residual host cell DNA and proteins
To mitigate safety risks, Host cell DNA and protein must also be controlled to appropriate levels. Foreign DNA and protein can cause immunogenic and oncogenic reactions and could cause further harm.
Analytical method validation for quality
As with any analytical or testing method, validation is required to ensure that the tests are accurate. The USP documents offer assay protocols and criteria for the assessment of tests that are standardized across biologic materials.
For material-specific assessments (for example, bioactivity), analytical methods must be initially validated, often following ICH Q2 (Revision 1): ‘Validation of Analytical Procedures Text and Methodology.’
Table 2. Validation Characteristics for Consideration. Source: ACROBiosystems
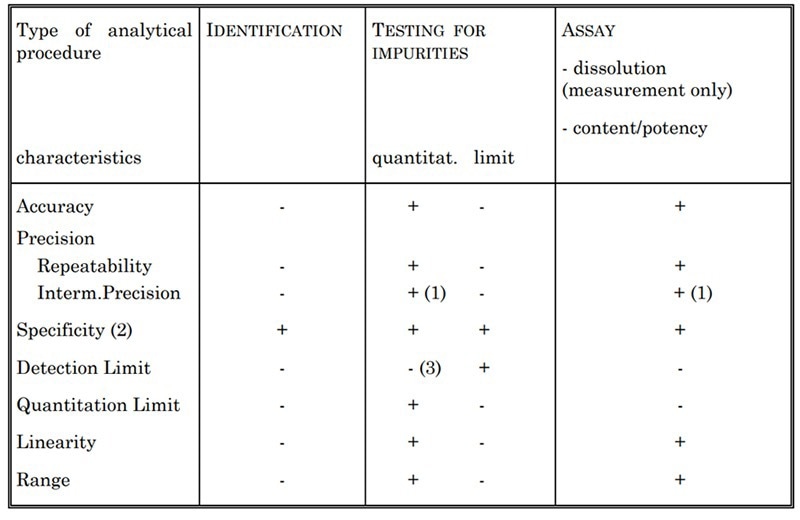
Different characteristics are assessed depending on the type of assay being validated. This includes accuracy, specificity, precision, detection limit, linearity, quantitation limit, and range.
For instance, to establish cytokine concentration, different assay methods are established, such as the Lowry method and the UV-spectrophotometric assay, which are fully validated per USP and ICH Q2 guidelines.
Table 3. Validation of UV-Spectrophotometric Assay. Source: ACROBiosystems
Method Validation
Parameter |
Result |
Criteria |
Conclusion |
| Accuracy |
Recovery Rate: 96 % |
Recovery Rate: 90 %-108 % |
Pass |
| Repeatability |
RSD: 0.05 % |
RSD≤3 % |
Passtd> |
| Intermediate Precision |
RSD: 0.48 % |
RSD≤3 % |
Pass |
| Robustness |
RSD: 0.04 % |
RSD≤3 % |
Pass |
| Linearity |
R2: 0.99925 |
R2>0.999 |
Pass |
| Range |
0.0452-0.452 mg/ml |
0.0452-0.452 mg/ml |
Pass |
To further validate the UV-spectrophotometric assay, the Lowry method was utilized as a secondary confirmatory technique. As a well-established technique, the Lowry method provides a solid basis for comparison.
Direct comparisons of the qualitative results of six spiked samples confirm the reliability and accuracy of a UV method, as highlighted in Table 4.
Table 4. Secondary Confirmation Assay – Lowry Method. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Method Validation |
Lowry |
UV Method |
Conclusion |
| Quantitative Result |
461 ug/ml |
436 ug/ml |
Pass |
| 476 ug/ml |
436 ug/ml |
| 465 ug/ml |
436 ug/ml |
| 472 ug/ml |
436 ug/ml |
| 468 ug/ml |
436 ug/ml |
| 461 ug/ml |
435 ug/ml |
Utilizing the same analytical validation framework, this includes alternative assays like cell activity. For instance, ACROBiosystem’s TNF-α assay includes intermediate precision, accuracy, range, and linearity. However, due to the purpose of the assay, the criteria differ.
Table 5. Example of TNF-α Cell activity validation. Source: ACROBiosystems
| Method Validation Parameter |
Result |
Criteria |
Conclusion |
| Relative Accuracy |
Bias:1.1 %
Slope:1.01 |
Bias within ±12 % range & Slope of regression equation between 0.80 and 1.25 |
Pass |
| Intermediate Precision |
GCV*:11.2 % |
(GCV)* ≤ 20 % |
| Specificity |
Difference % (buffer): 8.8 % |
Difference % (buffer) ≤ ±10 % |
| Linearity |
Correlation Coefficient: 0.97 |
Correlation Coefficient ≥ 0.95 |
| Potency Range |
Potency Range: 64% -156 % |
Range of product efficacy standards (64 % -156 %) |
*GCV is calculated as the anti-log of the standard deviation. GCV = anti-log(SD)
GMP-grade consistency and product stability
Stability testing evaluates the shelf life of a product. It is vital throughout the entire drug development process, clinical, market launch, and post-market monitorization for quality research procedure purposes. Thus, stability testing must be performed based on the distinct characteristics and qualities of the product.
Systematic performance stability studies also ensure minimal lot-to-lot variation, while additionally offering clear instructions for storage after delivery.
A well-recognized strategy for ensuring stability and consistency within a viable timeframe is the accelerated stability testing method, which is based on the Arrhenius equation. This method has demonstrated its accuracy and applicability in several studies in recent years.
The 2002 document ‘EN13640 In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices Stability Testing,’ released by the European Committee for Standardization, and the 2009 document ‘EP25A Evaluation of Stability of In Vitro Diagnostic Reagents,’ published by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, recommend this method for determining the stability of in vitro diagnostic reagents. Varying stability assessment parameters are displayed in Table 6.
Table 6. Stability Assessment Parameters. Source: ACROBiosystems

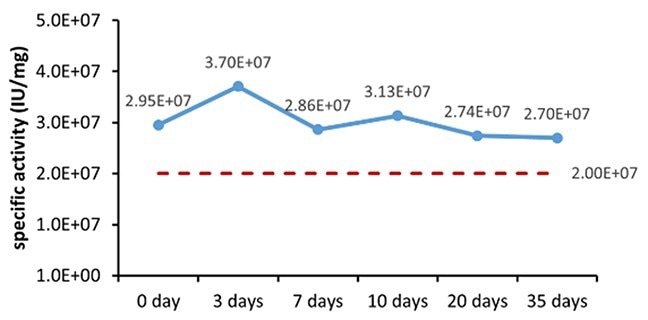
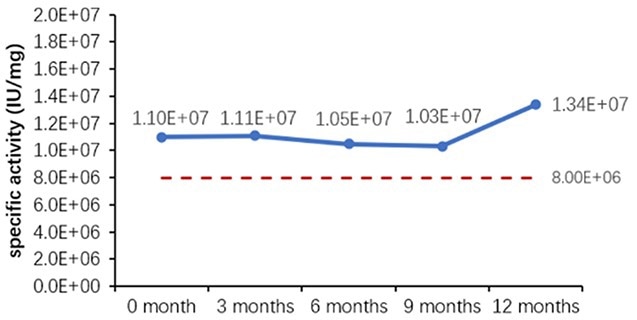
Figure 1. (A) Accelerated and (B) real-time stability evaluations of finished product (powder). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Wrapping up GMP-grade quality control systems
Quality control assessments must meet specific requirements. Analytical methods have limits, and therefore it is advised to utilize simultaneous complementary techniques to thoroughly evaluate raw materials and final products. These methods must also be comprehensively validated.
A stringent, well-established, and high-quality control system is essential for any therapeutical approval process and should refer to pharmacopeia standards like USP.
The global perspective on pharmaceutical quality management has evolved from “drug quality controlled through inspection" to "drug quality is achieved through process control in production" to "drug quality is produced through good design” (Quality by Design, QbD).
Embracing this philosophy suggests establishing a relationship between product quality characteristics and clinical efficacy and safety and efficacy, requiring the development of a comprehensive control system throughout the whole process.
ACROBiosystems continuously advances its systems to deliver reliable support regarding raw materials for CGT.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Our mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, they deliver solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empowers scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.